Sgraffito is a decorative technique used in fresco painting, where artists scratch through a surface layer of plaster to reveal a contrasting color beneath. This method creates intricate patterns or images that enhance the texture and depth of the fresco. Famous examples of sgraffito in fresco can be found in Italian Renaissance art, such as the works in the Palazzo Massimo alle Terme in Rome. The technique involves applying multiple layers of plaster tinted in different colors and then carefully scraping away portions of the top layer. This process reveals the color of the underlying layer, producing a striking visual effect that plays with light and shadow. Artists like Andrea Mantegna and Piero della Francesca employed sgraffito in their frescoes to add detail and dimension to their compositions.
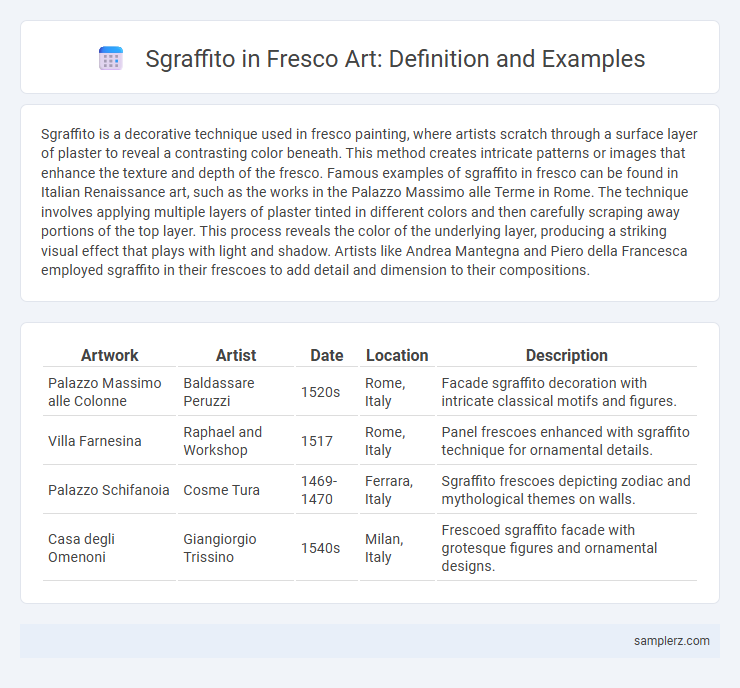
Table of Comparison
| Artwork | Artist | Date | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palazzo Massimo alle Colonne | Baldassare Peruzzi | 1520s | Rome, Italy | Facade sgraffito decoration with intricate classical motifs and figures. |
| Villa Farnesina | Raphael and Workshop | 1517 | Rome, Italy | Panel frescoes enhanced with sgraffito technique for ornamental details. |
| Palazzo Schifanoia | Cosme Tura | 1469-1470 | Ferrara, Italy | Sgraffito frescoes depicting zodiac and mythological themes on walls. |
| Casa degli Omenoni | Giangiorgio Trissino | 1540s | Milan, Italy | Frescoed sgraffito facade with grotesque figures and ornamental designs. |
Introduction to Sgrafitto in Fresco Art
Sgraffito in fresco art involves scratching through a surface layer to reveal a lower layer of contrasting color, creating intricate designs and textures. This technique was widely used during the Renaissance to add depth and detail to wall murals, combining both painting and sculptural effects. Masterpieces such as those in the Palazzo Massimo alle Terme in Rome highlight the durability and visual impact of sgraffito in fresco compositions.
Historical Origins of Sgrafitto Fresco Techniques
Sgrafitto fresco techniques originated during the Italian Renaissance, where artists scratched through a top layer of plaster to reveal contrasting colors beneath, creating intricate designs and textures. This method evolved from ancient Roman wall paintings that employed similar incising techniques for decorative purposes. Early examples of sgrafitto fresco can be seen in the works of artists like Polidoro da Caravaggio, who popularized this approach in 16th-century Rome.
Notable Renaissance Sgrafitto Fresco Examples
Notable Renaissance sgrafitto fresco examples include the Palazzo Massimo alle Colonne in Rome, where intricate layered plaster reveals classical motifs through contrasting textures. The Villa Farnesina's Loggia of Cupid and Psyche showcases sgrafitto techniques that highlight delicate mythological scenes with precision and depth. These frescoes exemplify the Renaissance mastery of combining sculptural effects with painted decoration to enhance architectural surfaces.
Techniques Used in Sgrafitto Fresco Decoration
Sgrafitto fresco decoration involves layering contrasting colors of wet plaster, where artists skillfully scratch through the top layer to reveal the different hues beneath, creating intricate patterns and detailed imagery. This technique requires precision tools like styluses or knives to achieve fine lines and textures while the plaster is still damp. Mastery of timing and control over plaster drying rates ensures crisp, lasting designs in the sgraffito fresco artwork.
Iconic Sgrafitto Fresco Works in Italian Architecture
Iconic sgrafitto fresco works in Italian architecture are exemplified by the Palazzo Schifanoia in Ferrara, where intricate layers of colored plaster reveal mythological scenes and allegories through precise scratching techniques. The Renaissance Palazzo Massimo alle Terme in Rome also showcases finely detailed sgrafitto frescoes emphasizing classical motifs and ornamental patterns. These masterpieces demonstrate the fusion of artistic skill and architectural embellishment that defines sgrafitto's unique visual impact in historic Italian buildings.
Sgrafitto Fresco Motifs and Symbolism
Sgrafitto fresco motifs often feature geometric patterns, floral designs, and figurative elements that convey cultural narratives and spiritual symbolism. These motifs symbolize themes such as fertility, protection, and the cycle of life, prominently used in Renaissance and Baroque art across Mediterranean regions. The layered technique of sgraffito enhances the fresco's depth, allowing symbolic imagery to emerge through contrasting textures and colors.
Sgrafitto Frescoes in Religious Spaces
Sgrafitto frescoes in religious spaces serve as powerful visual narratives that combine intricate line work with layered plaster techniques to depict biblical scenes and saints. This art form enhances spiritual ambiance through contrasting textures and monochromatic palettes, often found in European churches from the Renaissance period. These frescoes not only illustrate religious devotion but also demonstrate artisans' mastery in integrating architectural surfaces with narrative art.
Modern Interpretations of Sgrafitto Fresco
Modern interpretations of sgrafitto fresco combine traditional excavation techniques with contemporary abstract motifs to create layered, textured surfaces that evoke both history and innovation. Artists often use vivid pigments and dynamic line work to highlight contrasts between plaster layers, enhancing visual depth and narrative complexity. This fusion revitalizes sgrafitto fresco as a versatile medium in large-scale public art and experimental installations.
Conservation and Restoration of Sgrafitto Frescoes
Sgraffito frescoes, characterized by their intricate layers and delicate surface, require specialized conservation techniques to preserve their historic and artistic value. Restoration efforts focus on stabilizing the plaster layers, carefully removing salt efflorescence, and retaining original pigments through controlled cleaning methods to prevent further deterioration. Advances in non-invasive imaging technology, such as infrared reflectography and 3D scanning, enhance the precision of restoration planning and ensure the longevity of sgraffito artworks in varying environmental conditions.
Inspiring Contemporary Artists Using Sgrafitto in Fresco
Sgraffito in fresco, exemplified by Renaissance masterpieces such as those by Andrea Mantegna, harnesses layered plaster techniques to create intricate textures and depth. Contemporary artists draw inspiration from these traditional methods, integrating sgraffito to add tactile dimension and historical resonance to modern murals. This fusion of ancient craftsmanship with present-day themes revitalizes fresco art, pushing boundaries in public and gallery spaces.
example of sgrafitto in fresco Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com