Jet lag occurs when travelers cross multiple time zones rapidly, disrupting the body's internal clock. For example, flying from New York (Eastern Time Zone) to London (Greenwich Mean Time) results in a five-hour time difference. This shift can cause fatigue, sleep disturbances, and impaired concentration as the body adjusts. Crossing from Tokyo (Japan Standard Time) to Paris (Central European Time) presents an eight-hour time change. The significant difference challenges the circadian rhythm, leading to symptoms such as daytime sleepiness and nighttime insomnia. Managing jet lag often involves exposure to natural light and gradual adjustment of sleeping patterns before travel.
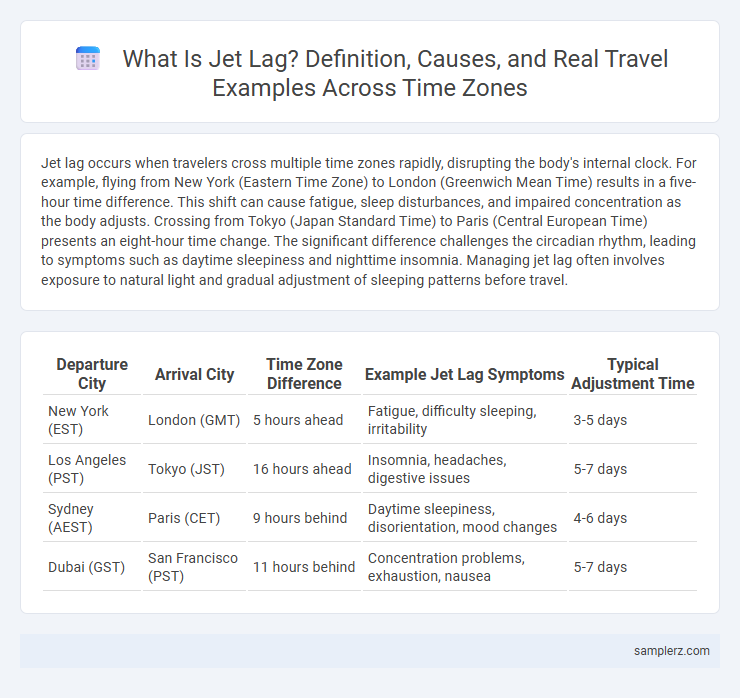
Table of Comparison
| Departure City | Arrival City | Time Zone Difference | Example Jet Lag Symptoms | Typical Adjustment Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New York (EST) | London (GMT) | 5 hours ahead | Fatigue, difficulty sleeping, irritability | 3-5 days |
| Los Angeles (PST) | Tokyo (JST) | 16 hours ahead | Insomnia, headaches, digestive issues | 5-7 days |
| Sydney (AEST) | Paris (CET) | 9 hours behind | Daytime sleepiness, disorientation, mood changes | 4-6 days |
| Dubai (GST) | San Francisco (PST) | 11 hours behind | Concentration problems, exhaustion, nausea | 5-7 days |
Understanding Jet Lag: A Timezone Travel Challenge
Jet lag occurs when travelers cross multiple time zones rapidly, disrupting the body's internal clock or circadian rhythm. Symptoms often include fatigue, insomnia, and difficulty concentrating, resulting from the misalignment between local time and the body's natural sleep-wake cycle. Adjusting exposure to natural light and gradually shifting sleep schedules can help mitigate the effects of jet lag during international travel.
Common Scenarios: Experiencing Jet Lag Across Timezones
Travelers crossing multiple timezones often experience jet lag, resulting in disrupted sleep-wake cycles and fatigue. For example, flying from New York to Tokyo involves crossing 13 time zones, causing significant desynchronization between the body's internal clock and local time. Symptoms typically include insomnia, daytime sleepiness, and impaired concentration, which can last several days as the body adjusts.
Eastward vs. Westward Travel: Jet Lag Differences
Eastward travel often causes more severe jet lag because the body's internal clock finds it harder to advance, leading to difficulty falling asleep earlier than usual. In contrast, westward travel typically results in milder jet lag as it involves delaying the internal clock, which aligns more easily with natural circadian rhythms. Research shows that travelers crossing multiple time zones eastward experience longer adjustment periods and greater fatigue compared to those traveling westward.
Case Study: Jet Lag After Crossing the Atlantic
Crossing multiple time zones during transatlantic flights often leads to jet lag, characterized by disrupted circadian rhythms and prolonged fatigue. A case study involving travelers flying from New York to London shows symptoms peaking 24 to 48 hours post-arrival, including insomnia, impaired cognitive function, and digestive issues. Strategic light exposure and melatonin supplementation have proven effective in realigning sleep patterns and reducing recovery time.
Real-Life Example: Business Trip from New York to London
A business traveler flying from New York to London often experiences jet lag due to the five-hour time difference, causing fatigue and disrupted sleep patterns. Meetings scheduled immediately after arrival may be affected by reduced cognitive function and slower reaction times. Managing exposure to natural light and strategic napping helps alleviate symptoms and improves productivity during the trip.
Family Vacation: Managing Jet Lag with Kids
Family vacations often involve crossing multiple time zones, causing jet lag in kids that disrupts their sleep and mood. Adjusting bedtime gradually before travel and exposing children to natural daylight upon arrival can help reset their internal clocks more quickly. Managing hydration and maintaining familiar routines during the trip also supports smoother transitions across time zones.
How Long Does Jet Lag Last? A Transpacific Example
Jet lag typically lasts anywhere from a few days up to one week, depending on the number of time zones crossed and individual differences in circadian rhythm adjustment. For example, when traveling from Los Angeles to Tokyo, crossing approximately 17 hours ahead, travelers often experience severe jet lag symptoms for about 5 to 7 days. The body usually resets its internal clock by about one time zone per day, making eastward flights like transpacific routes particularly challenging for sleep and alertness patterns.
Symptoms of Jet Lag: Traveler Stories
Travelers crossing multiple time zones often experience symptoms of jet lag such as fatigue, insomnia, and irritability. Many report difficulty concentrating and digestive issues, which disrupt daily activities and work performance. Personal accounts highlight the impact on mood and physical well-being, emphasizing the need for effective adjustment strategies post-flight.
Jet Lag in Frequent Flyers: Personal Accounts
Frequent flyers often experience severe jet lag due to rapid travel across multiple time zones, leading to disrupted circadian rhythms and chronic fatigue. Personal accounts reveal symptoms such as difficulty sleeping, impaired concentration, and mood swings that persist for days after transcontinental flights. Strategies like controlled exposure to natural light, melatonin supplementation, and adjusting sleep schedules before travel are commonly used to mitigate jet lag effects.
Overcoming Jet Lag: Lessons from World Travelers
World travelers often experience jet lag due to rapid crossing of multiple time zones, leading to disrupted circadian rhythms and fatigue. Strategies such as gradually adjusting sleep schedules before departure, exposure to natural light upon arrival, and staying hydrated help realign the body's internal clock. Regular exercise and avoiding caffeine or alcohol during flights also contribute to minimizing jet lag symptoms effectively.
example of jet lag in timezone Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com