The butterfly stroke in swimming is characterized by its symmetrical arm movement and powerful dolphin kick. Swimmers bring both arms forward over the water simultaneously while executing a strong, undulating body motion. This stroke requires precise timing to maximize propulsion and minimize drag, making it one of the most physically demanding competitive swimming techniques. In competitive events, the butterfly stroke is commonly seen in distances such as 100 meters and 200 meters. Elite swimmers like Michael Phelps have popularized this stroke, setting numerous world records due to their exceptional technique and strength. The butterfly stroke emphasizes upper body strength, core stability, and cardiovascular endurance to maintain speed and efficiency.
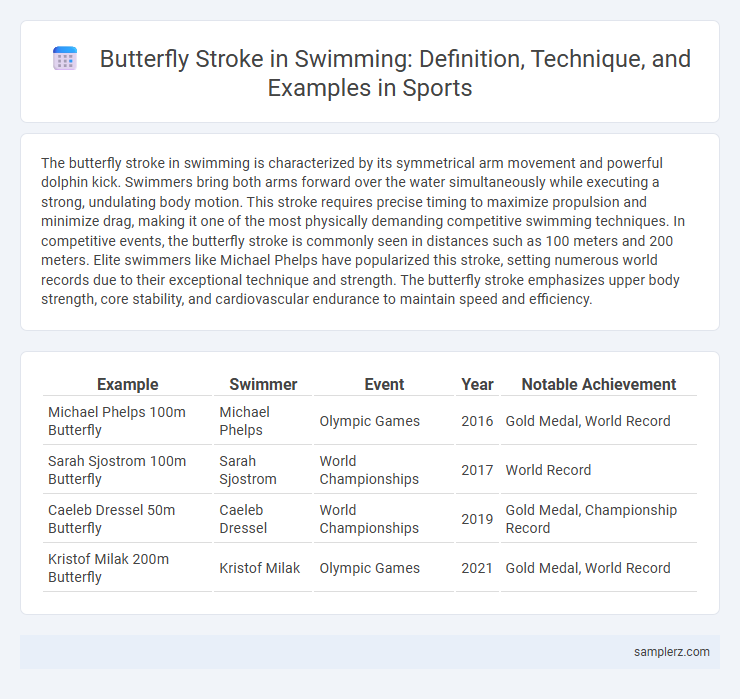
Table of Comparison
| Example | Swimmer | Event | Year | Notable Achievement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Michael Phelps 100m Butterfly | Michael Phelps | Olympic Games | 2016 | Gold Medal, World Record |
| Sarah Sjostrom 100m Butterfly | Sarah Sjostrom | World Championships | 2017 | World Record |
| Caeleb Dressel 50m Butterfly | Caeleb Dressel | World Championships | 2019 | Gold Medal, Championship Record |
| Kristof Milak 200m Butterfly | Kristof Milak | Olympic Games | 2021 | Gold Medal, World Record |
History and Origins of the Butterfly Stroke
The butterfly stroke originated in the early 1930s as a variation of the breaststroke, developed by American swimmers who experimented with bringing both arms over the water simultaneously to increase speed. It became an official competitive stroke in 1952, distinguished by its unique simultaneous arm movement and dolphin-like kick. Early pioneers like Henry Myers and Jack Sieg contributed to refining the technique, which revolutionized competitive swimming by combining power and fluidity.
Key Techniques in Butterfly Stroke
The butterfly stroke relies heavily on precise arm movement, where both arms simultaneously perform a powerful pull under the water, followed by a recovery phase over the surface. A strong dolphin kick, generated by the undulating motion of the hips and legs, propels the swimmer forward while maintaining balance. Proper breathing technique involves lifting the head forward quickly during the arm recovery without disrupting body alignment or stroke rhythm.
Step-by-Step Butterfly Stroke Swimming Guide
Master the butterfly stroke by first positioning your body horizontally with a slight undulating motion. Propel forward using simultaneous arm pulls sweeping outward and inward beneath the water, combined with a powerful dolphin kick generated by synchronous leg movements. Coordinate breathing by lifting your head forward during each arm recovery phase to maintain rhythm and maximize propulsion.
Common Mistakes in Butterfly Stroke and How to Fix Them
Common mistakes in butterfly stroke include improper body undulation, poor timing between arm pulls and dolphin kicks, and excessive breathing that disrupts rhythm. To fix these issues, swimmers should focus on mastering the wave-like motion starting from the chest through the hips, synchronizing arm movement with two coordinated dolphin kicks, and practicing quick, minimal breaths to maintain streamlined form. Consistent drills targeting timing, core strength, and breathing technique significantly improve butterfly stroke efficiency.
Famous Swimmers Who Excel in Butterfly Stroke
Michael Phelps is widely recognized for his dominance in the butterfly stroke, holding multiple Olympic gold medals and world records in the 100m and 200m butterfly events. Another prominent swimmer, Sarah Sjostrom, has set world records and won numerous international titles, showcasing exceptional technique and speed in butterfly races. Caeleb Dressel also excels in butterfly, known for his explosive power and multiple championships at World Championships and Olympic Games.
Training Drills for Improving Butterfly Stroke
Effective butterfly stroke training drills include dolphin kicks, which enhance core strength and rhythm, and single-arm butterfly drills that improve arm technique and coordination. Incorporating underwater pullouts helps swimmers focus on streamline body position and powerful propulsion. Consistent practice of these drills accelerates muscle memory development and stroke efficiency in competitive swimming.
Benefits of Mastering Butterfly Stroke
Mastering the butterfly stroke enhances overall cardiovascular fitness and builds upper body strength due to its powerful, simultaneous arm movements and dolphin-like kicks. This stroke improves lung capacity and breathing control by requiring rhythmic breath timing during intense muscle exertion. Skilled execution of the butterfly stroke also boosts swimming speed and efficiency, making it valuable for competitive swimmers aiming to excel in medley events.
Butterfly Stroke in Olympic Competitions
The butterfly stroke, recognized for its simultaneous arm movement and dolphin kick, plays a crucial role in Olympic swimming events such as the 100m and 200m butterfly races. Elite swimmers like Michael Phelps have set multiple Olympic records in this discipline, showcasing the stroke's demand for strength, timing, and endurance. Dominating the pool, the butterfly stroke is celebrated for its complexity and is a staple event in the Olympic swimming program.
Comparing Butterfly Stroke to Other Swimming Styles
The butterfly stroke, characterized by its simultaneous arm movements and dolphin-like kick, generates more propulsion than freestyle and backstroke, making it one of the fastest swimming techniques. Unlike the freestyle's alternating arm action, butterfly demands higher energy expenditure and precise timing to maintain efficiency and speed. This stroke's powerful, wave-like motion contrasts with the breaststroke's slower, more glide-oriented technique, emphasizing strength and coordination over endurance.
Tips for Beginners Learning the Butterfly Stroke
Mastering the butterfly stroke requires synchronized arm movements and a strong dolphin kick to propel the body efficiently through the water. Beginners should focus on developing a smooth undulating body motion by engaging core muscles and timing their breathing with each stroke cycle. Consistent practice of coordinating the simultaneous arm pull and timed breath helps improve rhythm and reduces fatigue in butterfly swimming.
example of butterfly stroke in swimming Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com