A bogey in golf occurs when a player completes a hole one stroke over par. For example, if a hole is designated as a par 4 and a golfer takes five strokes to finish, the score is recorded as a bogey. This scoring term helps golfers track performance relative to the expected number of strokes for each hole. Bogeys can impact overall game strategy and scoring in tournaments. Golfers often aim to minimize bogeys to maintain a competitive scorecard. Understanding and managing bogeys contributes to improving consistency and lowering total scores during play.
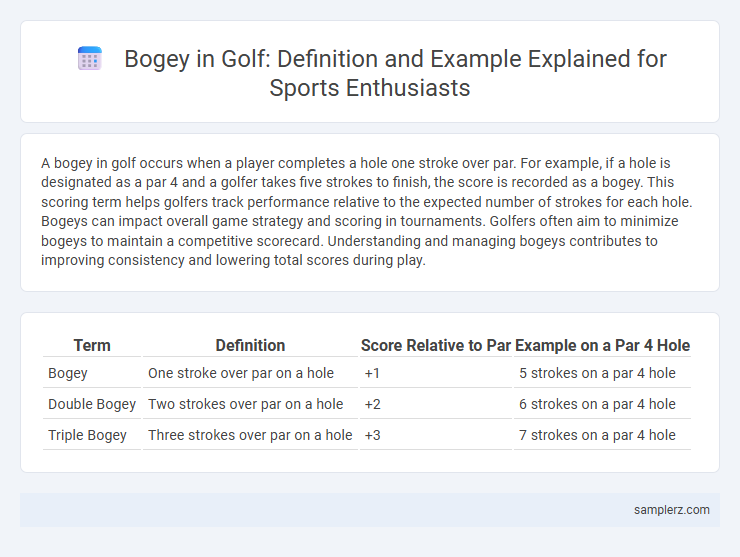
Table of Comparison
| Term | Definition | Score Relative to Par | Example on a Par 4 Hole |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bogey | One stroke over par on a hole | +1 | 5 strokes on a par 4 hole |
| Double Bogey | Two strokes over par on a hole | +2 | 6 strokes on a par 4 hole |
| Triple Bogey | Three strokes over par on a hole | +3 | 7 strokes on a par 4 hole |
Understanding the Definition of a Bogey in Golf
A bogey in golf is a score of one stroke over par on a particular hole, meaning if the hole's par is 4, completing it in 5 strokes results in a bogey. This scoring term helps golfers track performance relative to the expected number of strokes set for each hole by the course. Understanding a bogey is essential for assessing skill level and strategy during play, as it reflects slight deviation from optimal scoring.
Classic Bogey Scenarios on the Golf Course
A classic bogey scenario in golf often occurs when a player misjudges the distance to the green, resulting in an approach shot landing short or long of the pin and leading to a challenging chip or pitch. Another common example is missing a par putt by one or two strokes after a solid drive and approach, ultimately causing a score of one over par for the hole. Navigating hazards like bunkers or water on par-4 or par-5 holes frequently contributes to bogey outcomes due to penalty strokes or difficult recovery shots.
Famous Bogey Moments in Tournament History
Tiger Woods' infamous bogey on the 12th hole during the 2006 PGA Championship at Medinah Country Club marked a turning point, costing him a chance to secure the title. Another memorable bogey occurred when Phil Mickelson's triple bogey on the 17th hole at the 2010 Masters dramatically altered the leaderboard. These high-profile bogeys exemplify how even top professionals face critical challenges under pressure on golf's biggest stages.
How a Bogey Impacts a Golfer’s Scorecard
A bogey in golf adds one stroke over par for a given hole, increasing the total score and potentially impacting tournament standings. Recording multiple bogeys can lead to a higher overall score, diminishing a golfer's chances of winning or qualifying for playoffs. Maintaining a score close to par is crucial, as bogeys signify minor setbacks that accumulate over an 18-hole round.
Typical Causes of a Bogey in Golf
A bogey in golf typically occurs due to misjudging distances, resulting in inaccurate club selection or swinging errors that lead to missed fairways and greens. Poor course management, such as failing to account for hazards like bunkers or water, increases the likelihood of extra strokes. Fatigue and inconsistent swing mechanics also contribute significantly to scoring a bogey during a round.
Strategies to Avoid Making a Bogey
To avoid making a bogey in golf, players should focus on accurate club selection and controlled swing execution, prioritizing consistency over power. Effective course management includes aiming for the fairway and strategically avoiding hazards, which helps maintain manageable shot distances. Practicing short game techniques such as chipping and putting enhances scoring opportunities and minimizes the risk of adding extra strokes.
Bogey Examples Across Different Types of Holes
Bogey examples across different types of holes illustrate common scoring outcomes in golf. On par-3 holes, a bogey often results from missing the green in regulation and needing a chip and two putts to finish. On par-4 and par-5 holes, bogeys typically occur after landing in hazards or rough, forcing difficult recovery shots that slow progress and increase stroke count.
Psychological Effects of Scoring a Bogey
Scoring a bogey in golf often triggers frustration and self-doubt, disrupting a player's focus and rhythm. This psychological setback can lead to increased tension and riskier decisions on subsequent holes, impairing overall performance. Managing these emotional responses is crucial for maintaining mental resilience and sustaining competitive play.
Comparing Bogey to Par, Birdie, and Double Bogey
A bogey in golf means completing a hole one stroke over par, such as scoring a 5 on a par-4 hole. Compared to par, which denotes the expected number of strokes, a bogey represents a slightly higher score, while a birdie is one stroke under par, indicating a better performance. A double bogey, two strokes over par, reflects a less favorable result than a bogey, highlighting the range of scoring outcomes relative to par.
Lessons Learned from Bogey Situations
Experiencing a bogey in golf highlights the importance of course management, emphasizing the need to avoid risky shots that can lead to higher scores. Players learn to focus on consistent ball striking, improving accuracy over distance to minimize errors. Analyzing bogey situations fosters strategic thinking and mental resilience, which are crucial for long-term improvement in golf performance.
example of bogey in golf Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com