Hypogamy in marriage occurs when an individual marries someone from a lower social or economic class. For example, a university-educated woman marrying a man with only a high school diploma and lower income exemplifies this social phenomenon. This type of marriage challenges traditional expectations regarding upward social mobility through marriage. Data studies reveal that hypogamous marriages are less common than hypergamous unions, where individuals marry up the social ladder. Research from sociological surveys indicates that factors such as changing gender roles and economic independence contribute to the rise of hypogamy. Social scientists analyze these marriages to understand shifting societal norms and their impact on class dynamics.
Table of Comparison
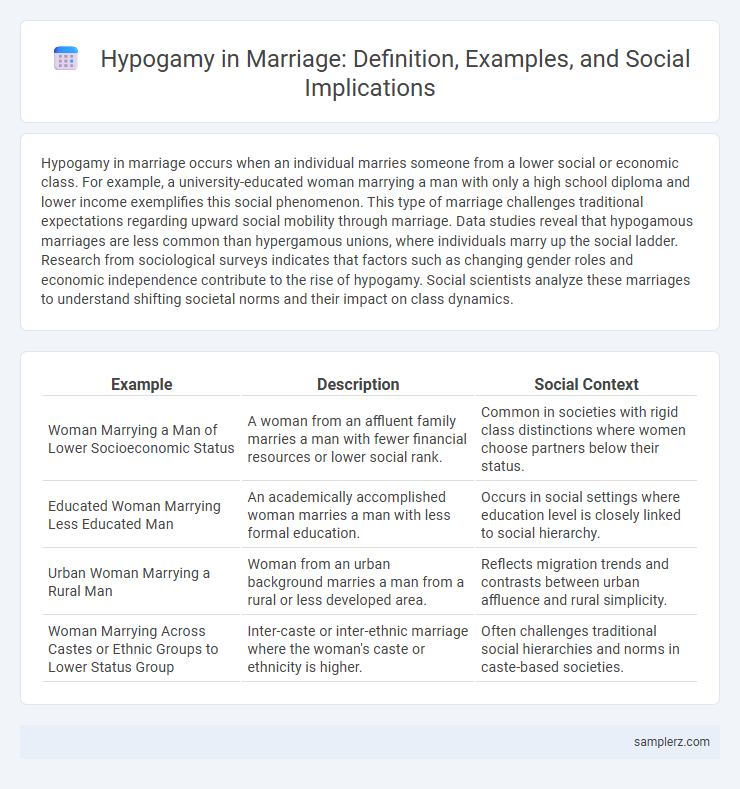
| Example | Description | Social Context |
|---|---|---|
| Woman Marrying a Man of Lower Socioeconomic Status | A woman from an affluent family marries a man with fewer financial resources or lower social rank. | Common in societies with rigid class distinctions where women choose partners below their status. |
| Educated Woman Marrying Less Educated Man | An academically accomplished woman marries a man with less formal education. | Occurs in social settings where education level is closely linked to social hierarchy. |
| Urban Woman Marrying a Rural Man | Woman from an urban background marries a man from a rural or less developed area. | Reflects migration trends and contrasts between urban affluence and rural simplicity. |
| Woman Marrying Across Castes or Ethnic Groups to Lower Status Group | Inter-caste or inter-ethnic marriage where the woman's caste or ethnicity is higher. | Often challenges traditional social hierarchies and norms in caste-based societies. |
Understanding Hypogamy in the Social Context of Marriage
Hypogamy in marriage occurs when one partner marries someone of a lower social or economic status, often seen in relationships where women marry men with less education or income. This pattern challenges traditional social norms that typically favor hypergamy, where individuals marry up to improve their social status. Understanding hypogamy highlights shifting social dynamics and changing gender roles within contemporary marriage trends.
Historical Perspectives on Hypogamy and Social Mobility
Historical perspectives on hypogamy reveal patterns where women married men of lower social status, often due to economic constraints or shifting societal norms. In various cultures, hypogamy enabled upward social mobility by allowing women to leverage marriage for economic or social gains despite partner status disparity. Such unions challenged traditional hierarchical structures, influencing class dynamics and the evolution of social mobility across generations.
Societal Reactions to Hypogamous Marriages
Hypogamous marriages, where a spouse marries someone of lower social or economic status, often provoke mixed societal reactions including stigma and familial disapproval in many cultures. These unions challenge traditional norms and can lead to social exclusion or reduced social capital for the higher-status partner. However, increasing social mobility and changing gender roles are gradually shifting perceptions, fostering greater acceptance of hypogamous relationships in contemporary society.
Notable Examples of Hypogamy in Modern Marriages
Notable examples of hypogamy in modern marriages include high-profile couples where a woman with greater socioeconomic status marries a man with lower status, such as actress Angelina Jolie and Brad Pitt early in their relationship or model Gisele Bundchen and footballer Tom Brady. These unions challenge traditional norms by highlighting shifting gender dynamics and societal acceptance of status differences. Studies show that hypogamous marriages are becoming more common in urban and progressive contexts, reflecting changing attitudes toward gender roles and economic power in relationships.
Gender Dynamics and Hypogamy: Breaking Traditional Norms
Hypogamy in marriage, where a woman marries a man of lower social or economic status, challenges traditional gender dynamics by reversing conventional power structures. This shift disrupts societal norms that typically favor men with higher status, promoting gender equality and empowering women in decision-making roles. Studies show increased acceptance of hypogamous unions correlates with progressive attitudes toward gender roles and marital satisfaction.
Economic Implications of Hypogamous Unions
Hypogamous marriages, where a spouse marries someone of lower socioeconomic status, often result in reduced household income and limited access to economic resources. This economic disparity can influence upward social mobility and affect financial stability, sometimes increasing reliance on social welfare programs. Studies show that households in hypogamous unions may face greater challenges in wealth accumulation and economic resilience compared to homogamous or hypergamous families.
Cultural Attitudes Toward Hypogamous Relationships
In many traditional societies, cultural attitudes toward hypogamous marriages--where the wife is of higher social or economic status than the husband--often reflect deep-rooted gender norms and power dynamics. These relationships frequently face social stigma, as they challenge conventional expectations about male dominance and economic provision. Research in social anthropology highlights that acceptance of hypogamous unions correlates with progressive shifts in gender equality and economic independence of women.
Hypogamy and the Role of Education in Marriage
Hypogamy, the practice of marrying someone of lower social status or education, often reflects complex social dynamics and expectations within marriage. Educational attainment plays a crucial role, as individuals with higher education may choose partners with fewer formal qualifications, challenging traditional norms of social mobility. This behavior highlights the influence of personal values and social factors in shaping marital choices beyond conventional status hierarchies.
Social Stigma and Challenges Facing Hypogamous Couples
Hypogamous marriages, where the wife has a higher socioeconomic status than the husband, often face significant social stigma, particularly in traditional societies that value patriarchal norms. Couples may encounter challenges such as judgment from family members, social exclusion, and pressure to conform to conventional gender roles. These social dynamics contribute to emotional stress and can undermine the stability of hypogamous relationships.
The Future of Hypogamy in Evolving Societies
Hypogamy, where individuals marry into a lower social or economic status, faces shifts due to changing gender roles and increased female educational attainment. Emerging trends indicate a gradual decline in traditional hypogamous marriages as societies embrace gender equality and economic independence. Future patterns of hypogamy will likely reflect broader societal transformations, including greater emphasis on compatibility, shared values, and mutual support rather than class-based hierarchies.
example of hypogamy in marriage Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com