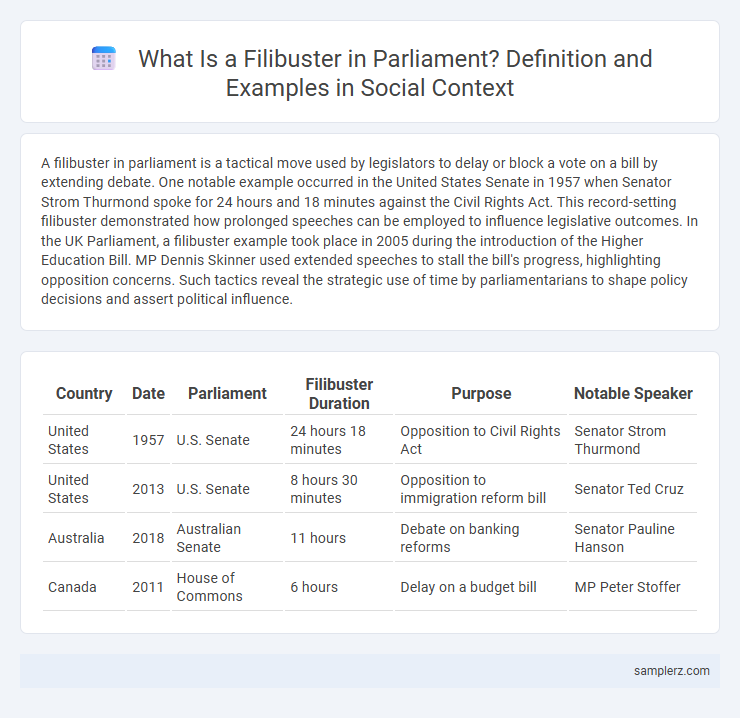
A filibuster in parliament is a tactical move used by legislators to delay or block a vote on a bill by extending debate. One notable example occurred in the United States Senate in 1957 when Senator Strom Thurmond spoke for 24 hours and 18 minutes against the Civil Rights Act. This record-setting filibuster demonstrated how prolonged speeches can be employed to influence legislative outcomes. In the UK Parliament, a filibuster example took place in 2005 during the introduction of the Higher Education Bill. MP Dennis Skinner used extended speeches to stall the bill's progress, highlighting opposition concerns. Such tactics reveal the strategic use of time by parliamentarians to shape policy decisions and assert political influence.
Table of Comparison
| Country | Date | Parliament | Filibuster Duration | Purpose | Notable Speaker |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 1957 | U.S. Senate | 24 hours 18 minutes | Opposition to Civil Rights Act | Senator Strom Thurmond |
| United States | 2013 | U.S. Senate | 8 hours 30 minutes | Opposition to immigration reform bill | Senator Ted Cruz |
| Australia | 2018 | Australian Senate | 11 hours | Debate on banking reforms | Senator Pauline Hanson |
| Canada | 2011 | House of Commons | 6 hours | Delay on a budget bill | MP Peter Stoffer |
Defining Filibuster: Parliamentary Tactic Explained
A filibuster is a parliamentary tactic where a member extends debate to delay or block a vote on legislation, often by speaking for an extended period. This strategy is commonly used in the U.S. Senate, where senators can speak for hours to prevent bills from advancing. Filibusters require a supermajority of 60 votes to invoke cloture and end debate, highlighting its role as a powerful tool in legislative processes.
Historical Overview of Filibusters in Parliament
Filibusters have historically played a crucial role in parliamentary procedures, notably during the 1957 United States Senate debate on civil rights legislation, where Senator Strom Thurmond spoke for 24 hours and 18 minutes to delay the bill. The British Parliament also witnessed filibusters in the 1900s, with members extending speeches to block controversial measures, reflecting strategic use of prolonged debate. These historical instances highlight how filibusters serve as a powerful tool for minority factions in legislative bodies to influence lawmaking processes.
Famous Filibuster Cases in Parliamentary History
Senator Strom Thurmond holds the record for the longest filibuster in U.S. Senate history, speaking for 24 hours and 18 minutes in 1957 against the Civil Rights Act. In the UK, MP Dennis Skinner famously used filibustering tactics to delay legislation and voice opposition during the 1980s and 1990s. Another notable case is Indian politician V.K. Krishna Menon, who conducted extensive filibusters in the Lok Sabha to challenge government policies in the 1950s and 1960s.
Notable Parliamentary Filibusters: Social Issues Spotlight
The 2013 filibuster led by Senator Wendy Davis in the Texas Senate lasted over 11 hours to block restrictive abortion legislation, highlighting the power of parliamentary delay tactics on social issues. In 1957, Senator Strom Thurmond filibustered for 24 hours and 18 minutes against the Civil Rights Act, exemplifying resistance to civil rights advancements through extended debate. These notable filibusters demonstrate how social issues like reproductive rights and racial equality become focal points during marathon legislative speeches.
Filibuster in Modern Parliaments: Recent Examples
Recent examples of filibusters in modern parliaments include the 2013 U.S. Senate where Senator Ted Cruz delivered a 21-hour speech opposing the Affordable Care Act. In the UK Parliament, the 2018 Brexit debates witnessed extended speeches and procedural delays by opposition members to stall legislative progress. Australia's Senate has experienced filibusters in 2019 during debates on environmental policies, with senators using lengthy speeches to block or amend bills.
The Longest Filibusters: Impact and Repercussions
The longest filibusters in parliamentary history, such as Senator Strom Thurmond's 24-hour speech in 1957, have significantly impacted legislative processes by delaying crucial votes and drawing public attention to specific issues. These extended speeches often lead to procedural reforms aimed at balancing debate rights with legislative efficiency, highlighting the tension between minority rights and majority rule. The repercussions include heightened political polarization and strategic use of filibusters as a tool for negotiation or obstruction within democratic institutions.
Filibuster Strategies Used by Opposition Parties
Opposition parties employ filibuster strategies such as extended speeches, repetitive questioning, and procedural motions to delay or block legislation in parliament. Tactics often include reading irrelevant documents or engaging in protracted debates to consume allotted time. These methods aim to force concessions or draw public attention to contentious issues.
Social Consequences of Parliamentary Filibusters
Parliamentary filibusters often lead to legislative gridlock, delaying critical social reforms such as healthcare expansion and education funding. Prolonged debates can erode public trust in democratic institutions, fostering social polarization and apathy among citizens. The blockage of social policies through filibustering exacerbates inequalities by stalling laws designed to address poverty, discrimination, and social welfare.
Filibuster Reform: Debates and Controversies
Filibuster reform has sparked intense debates in parliaments worldwide, particularly in the U.S. Senate, where attempts to limit or eliminate the filibuster often face opposition from minority parties defending their procedural rights. Critics argue that the filibuster enables obstructionism and gridlock, undermining democratic decision-making and legislative efficiency. Proponents claim that reform threats could erode minority influence and Senate traditions, highlighting the polarized balance between maintaining debate and ensuring effective governance.
Public Reactions to Parliamentary Filibusters
Public reactions to parliamentary filibusters often exhibit a mix of frustration and support depending on political alignment and the filibuster's context. Critics argue that filibusters obstruct legislative progress and waste valuable time, while supporters view them as a vital tool for minority voices to influence government decisions and promote thorough debate. Social media platforms and public forums amplify these reactions, highlighting the polarized perceptions surrounding the democratic process.
example of filibuster in parliament Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com