Subjectivity in opinion refers to the expression of personal beliefs, feelings, or preferences rather than objective facts. For instance, stating "Chocolate ice cream tastes better than vanilla" represents subjectivity because it reflects an individual's personal taste. This type of opinion cannot be proven true or false, as it depends on individual perspectives. Another example is when someone says "The movie was boring," which conveys a personal reaction rather than an objective assessment. Subjective opinions often use adjectives and adverbs that express emotions or judgments. These opinions highlight how personal experience influences interpretation of events or products.
Table of Comparison
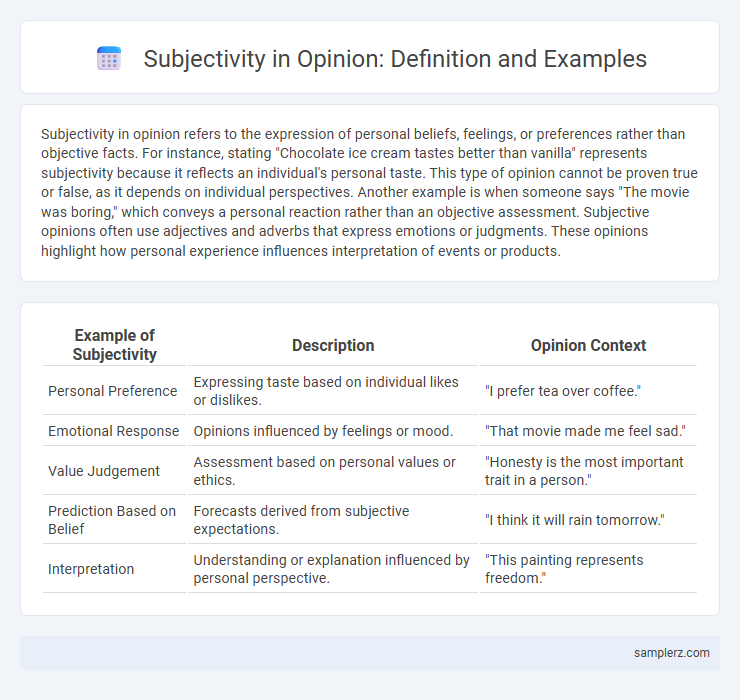
| Example of Subjectivity | Description | Opinion Context |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Preference | Expressing taste based on individual likes or dislikes. | "I prefer tea over coffee." |
| Emotional Response | Opinions influenced by feelings or mood. | "That movie made me feel sad." |
| Value Judgement | Assessment based on personal values or ethics. | "Honesty is the most important trait in a person." |
| Prediction Based on Belief | Forecasts derived from subjective expectations. | "I think it will rain tomorrow." |
| Interpretation | Understanding or explanation influenced by personal perspective. | "This painting represents freedom." |
Defining Subjectivity in Opinions
Subjectivity in opinions reflects personal beliefs, emotions, and individual perspectives rather than objective facts, shaping how information is interpreted and communicated. It highlights the influence of personal experiences and biases on judgment, making opinions unique to each individual. Understanding subjectivity is crucial for analyzing the nuances and variability inherent in human viewpoints.
How Personal Experience Shapes Opinion
Personal experience profoundly shapes opinion by providing unique perspectives and emotional context that objective facts alone cannot offer. Individual encounters and memories influence how information is interpreted and valued, leading to varied and subjective viewpoints. This subjectivity underscores the importance of recognizing personal biases when evaluating opinions.
The Influence of Emotions on Subjective Judgments
Emotions significantly shape subjective judgments by coloring individual perceptions and interpretations of events or information. Psychological studies reveal that feelings such as happiness or anger can bias people's evaluations, leading to varied opinions on identical situations. This emotional influence highlights the deeply intertwined nature of affect and cognition in forming personal viewpoints.
Cultural Background and Subjective Perspectives
Cultural background significantly shapes subjective perspectives, influencing how individuals interpret experiences and express opinions. Diverse cultural norms and values create varying viewpoints, demonstrating that opinions are often rooted in personal and communal contexts rather than objective facts. Recognizing this subjectivity highlights the importance of understanding cultural diversity in discussions and decision-making.
Bias in Opinion: Recognizing Subjective Filters
Bias in opinion manifests through subjective filters that shape individual perspectives, often influenced by personal experiences, cultural background, and emotional states. These filters distort objective reality, leading to selective interpretation and emphasis on information that aligns with preexisting beliefs. Recognizing these biases is crucial for fostering critical thinking and promoting balanced, well-informed discussions.
Examples of Subjectivity in Everyday Choices
Personal preferences significantly influence everyday choices, such as selecting a favorite cuisine or deciding which movie genre to watch, reflecting individual tastes rather than objective criteria. Emotional responses play a key role in shopping decisions, where one might favor brand loyalty or packaging aesthetics over product specifications. Even in social interactions, subjective judgments about people's character or intentions affect how relationships are formed and maintained, underscoring the pervasive nature of subjectivity in daily life.
Media and the Portrayal of Subjective Opinions
Media often blurs the line between objective reporting and subjective opinions by embedding personal biases in news coverage, influencing public perception. Editorial pieces and opinion columns explicitly present subjective viewpoints, shaping audience attitudes through selective framing and language. The portrayal of subjective opinions in media highlights the power of narrative in molding societal beliefs and reinforcing specific ideological perspectives.
Subjective vs. Objective: Key Differences
Subjectivity in opinion reflects personal feelings, beliefs, and preferences, which contrast sharply with objectivity's reliance on factual, verifiable data. Subjective statements often include emotions and interpretations, making them inherently variable across different individuals. Objective claims, by comparison, are measurable and consistent regardless of personal viewpoints, highlighting the fundamental difference between subjective and objective perspectives.
The Role of Subjectivity in Debates and Discussions
Subjectivity plays a crucial role in debates and discussions by shaping how individuals interpret facts through personal experiences, values, and emotions. This influence leads to diverse viewpoints, making discourse richer yet more complex as participants negotiate differing perceptions of truth. Recognizing subjectivity allows for deeper understanding and empathy, fostering productive dialogue rather than mere disagreement.
Ways to Acknowledge and Balance Subjectivity in Opinion
Acknowledging subjectivity in opinion requires recognizing personal biases and the influence of individual experiences on viewpoints. Balancing subjectivity involves actively seeking diverse perspectives and grounding arguments in factual evidence to enhance credibility. This approach fosters open-minded dialogue and reduces the impact of cognitive bias in discussions.
example of subjectivity in opinion Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com