Stance-taking in opinion pieces involves clearly expressing a viewpoint on a particular issue or topic. Writers use strong, evaluative language to align themselves with specific values, beliefs, or perspectives. This approach helps to persuade readers by emphasizing the writer's commitment and certainty about the subject. Effective stance-taking often incorporates evidence, anecdotes, or rhetorical questions to reinforce the opinion. The writer's position is maintained throughout the text to create consistency and build credibility. By focusing on the entity or issue at hand, the writer shapes the narrative and influences how readers interpret the data and arguments presented.
Table of Comparison
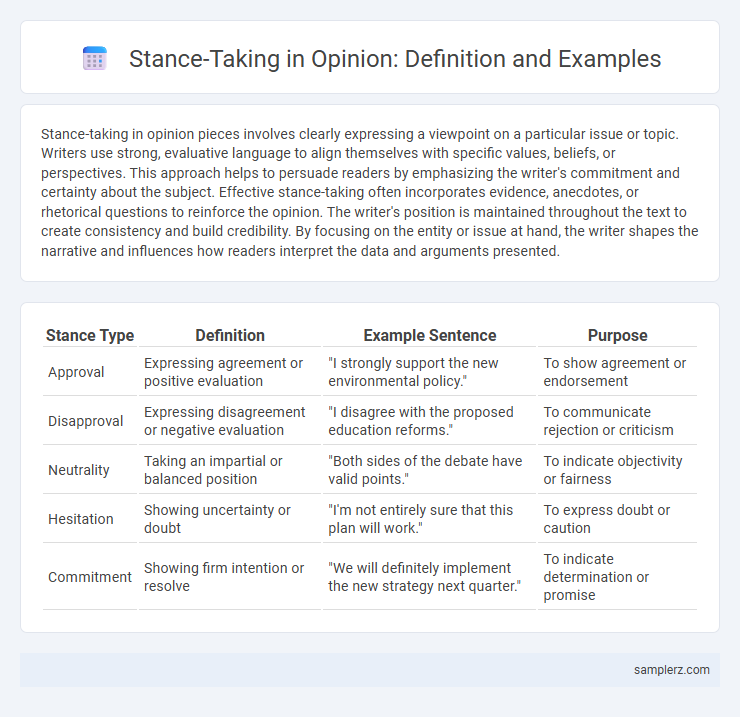
| Stance Type | Definition | Example Sentence | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Approval | Expressing agreement or positive evaluation | "I strongly support the new environmental policy." | To show agreement or endorsement |
| Disapproval | Expressing disagreement or negative evaluation | "I disagree with the proposed education reforms." | To communicate rejection or criticism |
| Neutrality | Taking an impartial or balanced position | "Both sides of the debate have valid points." | To indicate objectivity or fairness |
| Hesitation | Showing uncertainty or doubt | "I'm not entirely sure that this plan will work." | To express doubt or caution |
| Commitment | Showing firm intention or resolve | "We will definitely implement the new strategy next quarter." | To indicate determination or promise |
Defining Stance-Taking in Opinion Writing
Stance-taking in opinion writing involves clearly expressing a writer's viewpoint or attitude on a specific issue to influence readers' understanding and response. This process includes using persuasive language, evidence, and reasoning to establish credibility and effectively communicate the position. Defining stance-taking highlights its role in shaping arguments and guiding readers toward a particular perspective.
Classic Examples of Stance-Taking in Editorials
Classic examples of stance-taking in editorials often feature clear expressions of opinion on pressing social or political issues, utilizing persuasive language and strong assertions to influence public perception. Editorial writers typically employ evaluative adjectives, modal verbs, and first-person plural pronouns to assert authority and align with readers' values. Strategic use of rhetorical questions and evidential support further solidifies the writer's position, enhancing the editorial's impact and credibility.
How Authors Express Stance in Opinion Pieces
Authors express stance in opinion pieces through assertive language, personal pronouns, and evaluative adjectives that highlight their attitudes and beliefs. Use of modal verbs and rhetorical questions further emphasize their commitment or skepticism regarding the topic. Strategic repetition and contrast help reinforce their position, making the argument more persuasive and engaging for readers.
Linguistic Markers of Stance in Opinion Articles
Linguistic markers of stance in opinion articles include modal verbs, evaluative adjectives, and first-person pronouns, which signal the author's attitude and degree of certainty. Phrases such as "I believe," "it seems," and "clearly" function to assert opinion and guide readers' interpretation. These markers play a crucial role in constructing the writer's voice and persuading the audience effectively.
Stance-Taking Strategies Used by Influential Columnists
Influential columnists employ various stance-taking strategies such as presenting strong claims supported by evidence, using rhetorical questions to engage readers, and incorporating personal anecdotes to establish credibility and emotional connection. They often adopt a clear position early in their writing to guide audience interpretation and apply evaluative language to reinforce their viewpoints. These strategies enhance the persuasive impact and foster a sense of authority in opinion pieces.
Role of Evidence in Strengthening Stance
In opinion writing, presenting concrete data and credible sources strengthens the writer's stance by providing verifiable support for claims. Citing statistics, expert testimony, and real-world examples enhances logical appeal and persuades readers through evidence-based arguments. A well-substantiated opinion is more convincing and resilient against counterarguments.
Persuasive Language Techniques for Stance-Taking
Persuasive language techniques such as emotive language, rhetorical questions, and repetition effectively convey a strong stance in opinion writing. Using emotive language appeals to the reader's feelings, enhancing engagement and support for the argument. Rhetorical questions provoke reflection while repetition reinforces key points, making the stance more memorable and convincing.
Common Pitfalls in Stance Expression
Common pitfalls in stance expression include vague language that undermines clarity and weak qualifiers that dilute the author's position. Overgeneralization or unsupported claims often lead to credibility loss and reader skepticism. Effective opinion writing requires precise, assertive language supported by specific evidence to maintain persuasive strength and reader engagement.
Comparative Analysis of Stance in Different Media
Comparative analysis of stance in different media reveals how newspapers often adopt formal and balanced tones, while social media platforms favor more emotive and subjective expressions. For example, mainstream news outlets may present contrasting viewpoints with evidence-based arguments, whereas blogs and forums highlight personal experiences and direct critiques. This variation underscores the impact of platform conventions on how opinions and stances are conveyed and perceived.
Impact of Stance-Taking on Audience Persuasion
Stance-taking in opinion pieces significantly influences audience persuasion by clearly signaling the writer's position, which helps readers align their beliefs accordingly. By employing assertive language and presenting well-founded arguments, authors strengthen their credibility and encourage agreement from the audience. This active positioning shapes audience perception, fostering deeper engagement and prompting shifts in attitudes or behaviors.
example of stance-taking in opinion Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com