Preferential belief in opinion refers to the tendency of individuals to hold opinions based on personal preferences rather than objective evidence. This phenomenon occurs when people favor ideas or viewpoints that align with their desires, values, or identity. Studies in psychology indicate that preferential belief can influence decision-making processes and reinforce confirmation bias. In market research, preferential belief impacts consumer behavior by shaping brand loyalty and product preferences. Data shows that people often choose products that resonate with their lifestyle or self-image, even if alternative options are superior in quality or price. Understanding preferential belief helps businesses tailor marketing strategies to effectively engage target audiences and predict purchasing patterns.
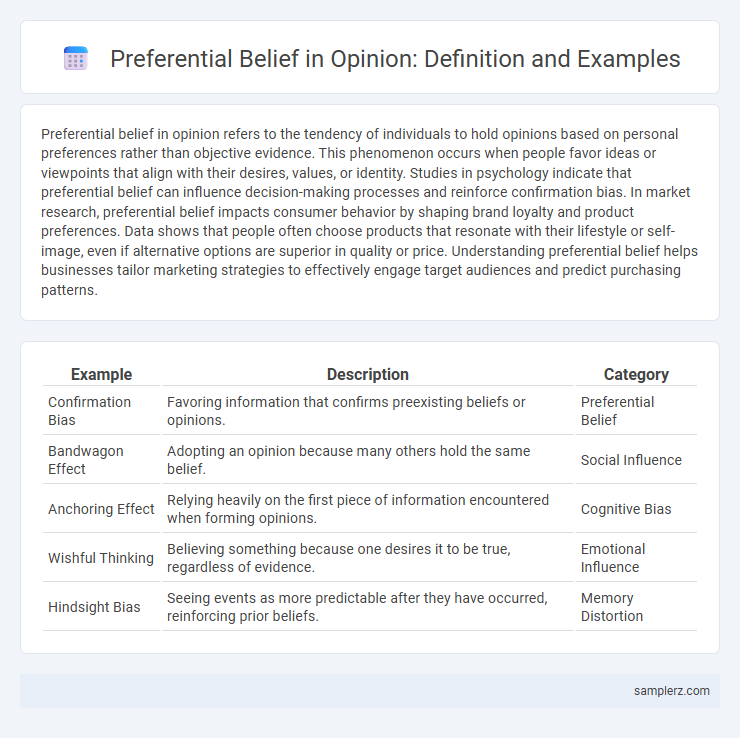
Table of Comparison
| Example | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Confirmation Bias | Favoring information that confirms preexisting beliefs or opinions. | Preferential Belief |
| Bandwagon Effect | Adopting an opinion because many others hold the same belief. | Social Influence |
| Anchoring Effect | Relying heavily on the first piece of information encountered when forming opinions. | Cognitive Bias |
| Wishful Thinking | Believing something because one desires it to be true, regardless of evidence. | Emotional Influence |
| Hindsight Bias | Seeing events as more predictable after they have occurred, reinforcing prior beliefs. | Memory Distortion |
Understanding Preferential Belief in Opinions
Preferential belief in opinions involves individuals favoring information that aligns with their existing values or biases, often leading to selective acceptance of ideas. This cognitive tendency affects how people interpret arguments and reinforces pre-existing viewpoints, impacting decision-making processes. Understanding this concept helps explain why opinions can remain resistant to change even in the presence of conflicting evidence.
Common Scenarios of Preferential Belief
Preferential belief often manifests in common scenarios such as political affiliations, brand loyalty, and cultural preferences, where individuals prioritize subjective values over objective evidence. For instance, voters may support a candidate despite conflicting policy records due to emotional attachment or identity alignment. Similarly, consumers frequently favor products from familiar brands, reflecting a preferential bias that influences purchasing decisions beyond practical features or price.
How Social Identity Shapes Preferential Opinions
Social identity profoundly influences preferential opinions by aligning individuals' beliefs with the values and norms of their social groups. This alignment causes people to favor opinions that resonate with their group identity, reinforcing in-group cohesion and distinguishing them from out-groups. Studies in social psychology reveal that selective exposure to information further consolidates these preferential beliefs, making opinions an extension of social belonging.
The Role of Confirmation Bias in Opinion Formation
Confirmation bias significantly influences opinion formation by leading individuals to favor information that validates their preexisting beliefs while disregarding contradictory evidence. This cognitive tendency reinforces preferential beliefs, making it challenging to change opinions even when presented with factual data. Studies in psychology demonstrate that confirmation bias shapes political, social, and personal opinions through selective exposure and biased interpretation of information.
Preferential Belief in Political Discourse
Preferential belief in political discourse often manifests when individuals selectively interpret information to align with their existing political ideologies, reinforcing confirmation bias. This cognitive tendency impacts public opinion by shaping attitudes towards policies, candidates, and parties based on subjective preference rather than objective analysis. Research in political psychology highlights how preferential belief contributes to polarization by entrenching partisan views and diminishing openness to opposing perspectives.
Media Influence on Preferential Opinion Patterns
Media influence shapes preferential opinion patterns by selectively highlighting specific narratives, thereby reinforcing existing biases and guiding public perception toward particular viewpoints. Algorithms on digital platforms amplify content that aligns with users' past beliefs, intensifying echo chambers and limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. Studies show that repeated exposure to homogeneous media sources strengthens preferential belief, making individuals more resistant to opposing evidence.
The Impact of Groupthink on Preferential Belief
Groupthink significantly influences preferential belief by promoting conformity within groups, often leading members to prioritize consensus over critical analysis. This psychological pressure suppresses dissenting opinions, reinforcing existing biases and skewing decision-making processes. Consequently, preferential beliefs formed under groupthink conditions may lack a balanced evaluation of alternatives, impacting the overall quality and objectivity of group opinions.
Preferential Belief in Scientific Debates
Preferential belief in scientific debates occurs when individuals favor theories that align with their prior values or experiences, despite contrary empirical evidence. This cognitive bias shapes how scientific information is interpreted, often leading to selective acceptance of data that supports preconceived notions. Recognizing preferential belief is crucial for fostering objective discourse and advancing evidence-based scientific consensus.
Personal Experience as a Driver of Preferential Opinion
Personal experience profoundly shapes preferential belief by anchoring opinions in firsthand encounters and emotional resonance. Individuals often prioritize personal narratives over abstract data, leading to strong, subjective convictions that influence decision-making. This experiential foundation enhances the authenticity and intensity of opinions, reflecting deeply held values and memories.
Strategies to Overcome Preferential Belief in Opinions
Strategies to overcome preferential belief in opinions involve actively seeking diverse perspectives and challenging one's cognitive biases to foster open-mindedness. Engaging in critical thinking and evidence-based reasoning helps to reduce the influence of subjective preferences on judgment. Encouraging dialogue and reflection allows individuals to reconsider entrenched beliefs and adopt more balanced viewpoints.
example of preferential belief in opinion Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com