A recumbent bike is a type of bicycle that places the rider in a laid-back reclining position. This design enhances comfort by reducing strain on the rider's back and wrists compared to traditional upright bikes. Recumbent bicycles come with a large seat and pedals positioned in front of the rider, optimizing aerodynamic efficiency. Recumbent bikes are popular among long-distance cyclists and those with physical limitations affecting their mobility. They often feature multiple gears and advanced components to improve performance on various terrains. Data shows that recumbent cycling reduces fatigue and increases rider endurance due to its ergonomic design.
Table of Comparison
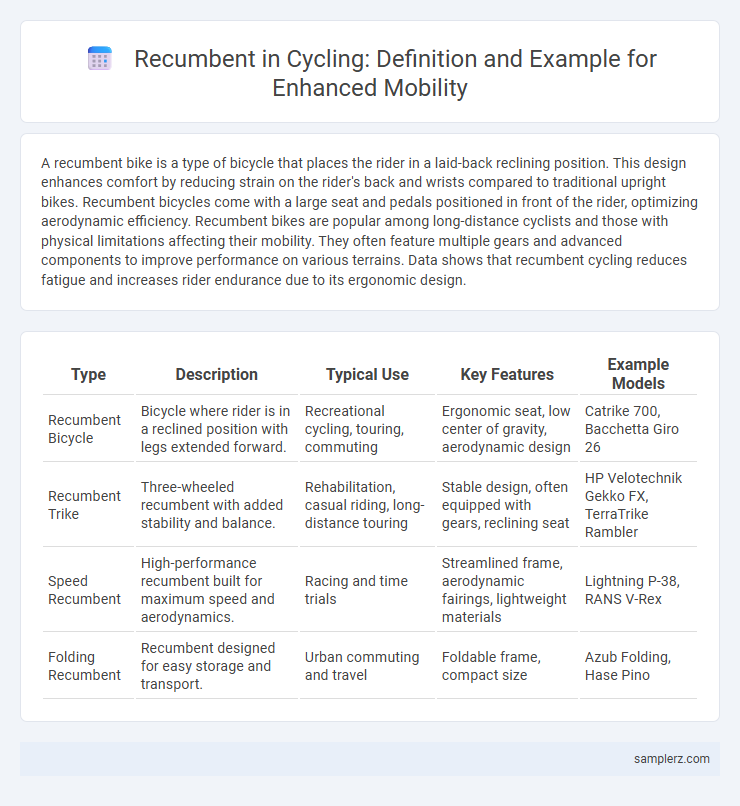
| Type | Description | Typical Use | Key Features | Example Models |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recumbent Bicycle | Bicycle where rider is in a reclined position with legs extended forward. | Recreational cycling, touring, commuting | Ergonomic seat, low center of gravity, aerodynamic design | Catrike 700, Bacchetta Giro 26 |
| Recumbent Trike | Three-wheeled recumbent with added stability and balance. | Rehabilitation, casual riding, long-distance touring | Stable design, often equipped with gears, reclining seat | HP Velotechnik Gekko FX, TerraTrike Rambler |
| Speed Recumbent | High-performance recumbent built for maximum speed and aerodynamics. | Racing and time trials | Streamlined frame, aerodynamic fairings, lightweight materials | Lightning P-38, RANS V-Rex |
| Folding Recumbent | Recumbent designed for easy storage and transport. | Urban commuting and travel | Foldable frame, compact size | Azub Folding, Hase Pino |
Introduction to Recumbent Bicycles in Modern Mobility
Recumbent bicycles offer an ergonomic alternative to traditional upright bikes, enhancing rider comfort through a reclined seating position that reduces strain on the back and wrists. These bikes improve aerodynamics and can increase cycling efficiency, making them ideal for both commuting and long-distance touring. Modern recumbents come equipped with advanced materials like lightweight aluminum and carbon fiber, integrating seamlessly into contemporary urban mobility solutions.
Key Features of Recumbent Bikes for Cyclists
Recumbent bikes feature a reclined seating position that reduces strain on the rider's back and neck, enhancing comfort during long rides. Their aerodynamic design improves speed and efficiency by minimizing wind resistance, making them ideal for endurance cycling. With larger seats and extended leg positioning, recumbent bikes provide superior support and distribute weight evenly, reducing pressure points common in traditional upright bicycles.
History and Evolution of Recumbent Cycling
Recumbent cycling traces its origins to the 19th century with early designs like the 1890s Steeple Bicycle, which introduced a reclined seating position to enhance rider comfort and aerodynamics. The 1930s saw the development of the American "Vetta Veloce," a streamlined recumbent bicycle that improved speed and efficiency, influencing modern recumbent designs. Innovations in materials such as aluminum and carbon fiber during the late 20th century accelerated the evolution of recumbent bikes, making them lighter, faster, and more accessible for diverse cycling disciplines.
Health and Ergonomic Benefits of Recumbent Bicycles
Recumbent bicycles promote improved spinal alignment and reduced pressure on wrists and shoulders, significantly enhancing ergonomic comfort during cycling. Their design supports a reclined seating position that decreases lower back strain and encourages better circulation, reducing fatigue and the risk of nerve compression. Health benefits include decreased joint impact and increased aerobic efficiency, making recumbent bikes ideal for individuals with mobility issues or those seeking low-impact exercise alternatives.
Popular Types of Recumbent Bikes in the Market
Popular types of recumbent bikes in the cycling market include long wheelbase, short wheelbase, and compact designs, each offering unique benefits for rider comfort and efficiency. Long wheelbase recumbents provide enhanced stability and smooth handling suitable for touring and long-distance rides. Short wheelbase models offer increased maneuverability ideal for urban commuting, while compact recumbents emphasize portability without sacrificing ergonomic support.
Recumbent Cycling vs. Upright Cycling: A Comparative Overview
Recumbent cycling offers enhanced aerodynamics and reduced strain on the back and joints compared to upright cycling, making it ideal for long-distance rides and rehabilitation. The reclined seating position distributes weight more evenly, which minimizes pressure on the rider's spine and wrists, unlike the forward-leaning posture in upright bikes. Performance studies show recumbent cyclists can achieve higher speeds with less perceived effort, while upright cycling provides better maneuverability and is more common for urban commuting.
Success Stories: Recumbent Bikes in Competitive Racing
Recumbent bikes have achieved remarkable success in competitive racing, setting multiple world speed records due to their aerodynamic design and enhanced rider comfort. Notable events like the International Human Powered Vehicle Association (IHPVA) championships showcase the dominance of recumbent cyclists, with athletes consistently outperforming traditional upright bike competitors. Innovations in lightweight materials and ergonomic engineering continue to propel recumbents as leading choices for endurance and speed-focused races.
Accessibility: Recumbent Bicycles for People with Disabilities
Recumbent bicycles offer enhanced accessibility for people with disabilities by providing ergonomic seating that reduces strain on the back and joints, making cycling more comfortable for individuals with limited mobility. Their low-to-the-ground design improves stability and balance, which benefits riders with coordination challenges or muscle weakness. Innovative adaptive features, such as customized hand controls and adjustable seating, further enable inclusive cycling experiences for a diverse range of physical abilities.
Choosing the Right Recumbent Bike: Essential Considerations
Selecting the right recumbent bike involves evaluating frame design, seat comfort, and terrain compatibility to ensure optimal riding experience. Consider factors such as adjustable seating positions for ergonomic support, wheelbase length for maneuverability, and gear systems suited for varied inclines. Prioritizing these elements aids in enhancing cycling efficiency, reducing strain, and matching the bike to specific mobility needs and cycling goals.
Future Trends of Recumbent Technologies in Cycling Mobility
Advancements in lightweight materials and aerodynamic design are driving the future trends of recumbent technologies in cycling mobility, enhancing speed and rider comfort. Integration of electric assist systems and smart connectivity features is transforming recumbent bikes into efficient and user-friendly urban transportation options. Emerging innovations in battery technology and regenerative braking are expected to extend the range and sustainability of recumbent cycling solutions.
example of recumbent in cycling Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com