Psychographic segmentation in marketing focuses on categorizing consumers based on their lifestyles, values, attitudes, and interests. For example, a brand selling eco-friendly products targets environmentally conscious individuals who prioritize sustainability and green living. These consumers often participate in recycling programs, prefer organic products, and support social causes, making their lifestyle a key data point for segmentation. Another example involves a luxury automotive company segmenting its market based on personality traits such as status-seeking and risk tolerance. The brand appeals to consumers who value prestige, high performance, and exclusivity in their vehicles. Marketers collect data on customers' hobbies, media consumption, and spending habits to tailor advertising campaigns that resonate with this psychographic profile.
Table of Comparison
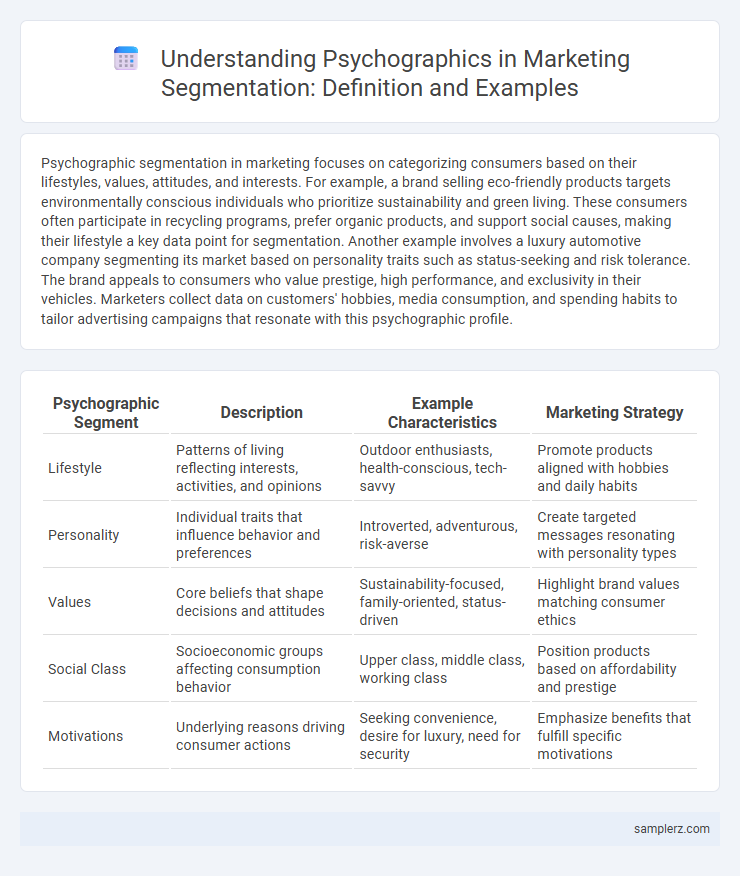
| Psychographic Segment | Description | Example Characteristics | Marketing Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle | Patterns of living reflecting interests, activities, and opinions | Outdoor enthusiasts, health-conscious, tech-savvy | Promote products aligned with hobbies and daily habits |
| Personality | Individual traits that influence behavior and preferences | Introverted, adventurous, risk-averse | Create targeted messages resonating with personality types |
| Values | Core beliefs that shape decisions and attitudes | Sustainability-focused, family-oriented, status-driven | Highlight brand values matching consumer ethics |
| Social Class | Socioeconomic groups affecting consumption behavior | Upper class, middle class, working class | Position products based on affordability and prestige |
| Motivations | Underlying reasons driving consumer actions | Seeking convenience, desire for luxury, need for security | Emphasize benefits that fulfill specific motivations |
Understanding Psychographic Segmentation in Marketing
Psychographic segmentation categorizes consumers based on lifestyle, personality traits, values, interests, and attitudes to tailor marketing strategies effectively. For example, a fitness brand may target health-conscious individuals who prioritize wellness, motivation, and active living. Understanding psychographic factors enables marketers to create more personalized campaigns that resonate emotionally and drive stronger consumer engagement.
Key Components of Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation analyzes consumer lifestyles, values, and personality traits to tailor marketing strategies effectively. Key components include activities, interests, opinions (AIO), social status, and self-concept, which help identify target audience motivations and preferences. Understanding these elements enables brands to craft personalized messages that resonate deeply and increase engagement.
Why Psychographics Matter in Targeting Audiences
Psychographic segmentation divides audiences based on lifestyle, values, interests, and personality traits, enabling marketers to tailor messages that resonate deeply with target consumers. Understanding motivations and attitudes increases campaign relevance, boosts engagement rates, and improves conversion by addressing specific emotional triggers. Brands leveraging psychographics like hobbies, social status, or opinions gain competitive advantage through personalized, impactful marketing strategies.
Lifestyle-Based Segmentation Examples
Lifestyle-based segmentation targets consumers based on their daily habits, interests, and values, such as fitness enthusiasts who prioritize health and wellness products. Brands like Nike capitalize on this by marketing athletic apparel to active lifestyles centered around exercise and sports. Another example includes eco-conscious consumers who prefer sustainable and environmentally friendly products, driving demand for green brands like Patagonia.
Segmenting by Consumer Values and Beliefs
Segmenting consumers by values and beliefs targets groups based on core principles such as environmental sustainability, social justice, or health consciousness. Brands like Patagonia appeal to eco-conscious consumers who prioritize environmental responsibility in their purchasing decisions. Understanding these psychographic factors enables marketers to craft tailored messages that resonate deeply with the audience's identity and motivations.
Personality Traits and Market Segmentation
Personality traits such as introversion, extroversion, and openness play a crucial role in psychographic market segmentation by helping marketers tailor products and messages to align with customer identities. Brands targeting extroverted consumers often emphasize social interaction and adventure, while those focusing on introverted segments highlight solitude and introspection benefits. Understanding personality-driven preferences enables precise segmentation and more effective marketing campaigns, driving higher engagement and conversion rates.
Attitude-Based Segmentation Strategies
Attitude-based segmentation strategies in marketing focus on grouping consumers according to their feelings, beliefs, and perceptions about products or brands. For example, a company selling eco-friendly products may target environmentally conscious consumers who exhibit positive attitudes toward sustainability and ethical consumption. This approach allows marketers to tailor messages that resonate with specific psychological traits, enhancing engagement and brand loyalty.
Social Status and Psychographic Grouping
Psychographic segmentation in marketing categorizes consumers based on social status indicators such as income level, education, and occupation, influencing their purchasing behavior. Brands often target high social status groups with luxury products emphasizing exclusivity and prestige. Understanding psychographic grouping allows marketers to craft personalized messages that resonate with values, lifestyle, and social aspirations within each segment.
Activities, Interests, and Opinions in Audience Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation in marketing often targets consumer activities such as hobbies, sports participation, and lifestyle routines to tailor campaigns effectively. Interests like technology, fashion, and travel preferences help marketers design content that resonates deeply with specific audience niches. Opinions on social issues, brand values, and product preferences further refine segmentation, enabling personalized communication that drives engagement and loyalty.
Real-World Brands Using Psychographic Segmentation
Nike targets fitness enthusiasts who value motivation and self-improvement, using psychographic segmentation to tailor campaigns that emphasize personal achievement and competitive spirit. Apple appeals to creative, innovation-driven consumers by aligning product features with lifestyles centered around design, technology, and uniqueness. Patagonia connects with environmentally conscious shoppers by promoting sustainability and ethical outdoor adventure, reinforcing brand loyalty through shared values and lifestyle choices.
example of psychographic in segmentation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com