Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) in marketing measures the total revenue a business expects from a single customer throughout their relationship. For instance, an e-commerce company analyzes LTV by tracking purchase frequency, average order value, and customer retention rates. This data helps optimize marketing spend by targeting high-value customers and increasing overall profitability. In another example, a subscription-based streaming service calculates LTV by evaluating subscription length and the cost of acquiring customers through paid ads. Marketing teams use this metric to tailor campaigns, upsell offers, and reduce churn rates. Understanding LTV empowers businesses to allocate resources efficiently and improve long-term customer engagement.
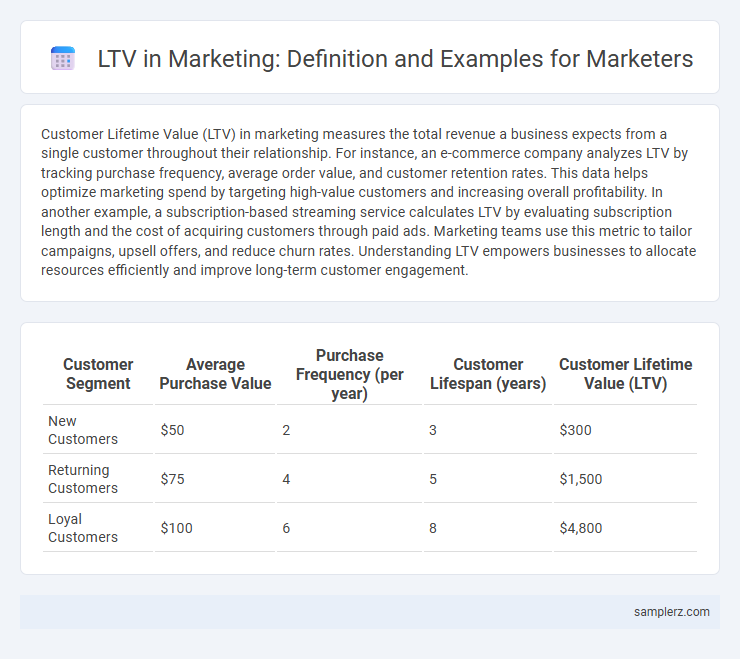
Table of Comparison
| Customer Segment | Average Purchase Value | Purchase Frequency (per year) | Customer Lifespan (years) | Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Customers | $50 | 2 | 3 | $300 |
| Returning Customers | $75 | 4 | 5 | $1,500 |
| Loyal Customers | $100 | 6 | 8 | $4,800 |
Understanding LTV: Definition and Importance in Marketing
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) represents the total revenue a business can expect from a single customer account throughout the entire relationship. Higher LTV indicates more profitable customers, guiding marketing strategies to focus on retention and personalized engagement. Understanding LTV helps optimize acquisition costs and maximize long-term profitability through targeted campaigns.
Calculating Customer LTV: Basic Formula
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) in marketing is calculated using the basic formula: LTV = Average Purchase Value x Purchase Frequency x Customer Lifespan. For example, if a customer spends $50 per purchase, buys 4 times a year, and remains loyal for 5 years, their LTV equals $1,000. Accurately calculating LTV helps businesses optimize marketing budgets by identifying high-value customer segments and tailoring retention strategies.
Real-World Example of LTV in E-commerce
In e-commerce, a customer purchasing an average of $50 per month over two years results in an LTV of $1,200, guiding marketing budgets toward customer retention strategies. By analyzing LTV data, companies like Amazon tailor personalized offers and subscription services that maximize revenue from loyal shoppers. This approach reduces acquisition costs while increasing profitability through targeted upselling and cross-selling campaigns.
SaaS Business: LTV Calculation Case Study
In SaaS marketing, calculating Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) involves analyzing average revenue per user (ARPU), customer churn rate, and gross margin to project long-term profitability. For instance, a SaaS company with an ARPU of $50 per month, a churn rate of 5% monthly, and a gross margin of 80% can estimate LTV by dividing ARPU by churn rate and multiplying by gross margin, yielding $800 per customer. This LTV metric guides customer acquisition costs and retention strategies essential for sustainable growth in subscription-based models.
LTV Example in Subscription-Based Services
In subscription-based services, Lifetime Value (LTV) is calculated by multiplying the average monthly revenue per subscriber by the average subscription duration in months, providing a clear metric of customer profitability. For example, a streaming service with an average monthly subscription fee of $15 and an average customer retention period of 24 months would have an LTV of $360 per subscriber. This LTV metric helps marketers optimize acquisition costs and tailor retention strategies to maximize long-term revenue.
LTV in Retail: Practical Illustration
In retail marketing, Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) quantifies the total revenue a customer generates during their relationship with a brand, guiding targeted retention strategies. For example, a retail clothing store calculates LTV by analyzing average purchase value, purchase frequency, and customer lifespan, optimizing marketing budgets to focus on high-value segments. This practical illustration of LTV enables retailers to tailor promotions and improve customer loyalty, boosting long-term profitability.
LTV for B2B Marketing: Sample Scenario
In B2B marketing, Lifetime Value (LTV) measures the total revenue generated from a client throughout their entire business relationship. For instance, a software-as-a-service (SaaS) company calculates LTV by multiplying the average monthly subscription fee by the average customer lifespan, often spanning several years. Understanding LTV helps marketers allocate budgets efficiently, prioritize high-value accounts, and tailor retention strategies to maximize long-term profitability.
Impact of Customer Segmentation on LTV
Customer segmentation enhances LTV by identifying high-value groups with distinct purchasing behaviors, enabling personalized marketing strategies that boost repeat purchases and average order value. By analyzing demographics, purchase frequency, and engagement metrics, businesses tailor offers that increase retention rates and customer lifetime revenue. Effective segmentation drives optimized resource allocation, resulting in improved marketing ROI and sustainable growth.
Optimizing Marketing Strategies Using LTV Data
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) enables marketers to allocate budgets efficiently by identifying high-value segments and tailoring campaigns for maximum ROI. Using LTV data, businesses can prioritize retention strategies for top customers and design personalized offers that increase average purchase frequency. Optimizing marketing strategies through LTV analysis drives sustainable growth by focusing efforts on long-term profitability rather than short-term acquisition costs.
Increasing Customer LTV: Tactical Examples
Increasing Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) in marketing involves personalized email campaigns that target repeat purchases based on customer behavior analytics. Implementing loyalty programs incentivizes ongoing engagement and higher spending by offering exclusive rewards and discounts tailored to user preferences. Leveraging upselling and cross-selling strategies through AI-driven recommendations boosts average order value while enhancing customer satisfaction and retention rates.
example of LTV in marketing Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com