A common dark pattern in marketing UX is the use of hidden subscription renewals. Users may initially sign up for a free trial but are unaware that their payment information is automatically charged once the trial ends. This design technique exploits user inattention and leads to unexpected recurring charges. Another example is the implementation of sneaky opt-out checkboxes during checkout. These checkboxes are pre-selected to subscribe users to newsletters or promotional emails, making it easy to overlook them and unintentionally agree to additional marketing communications. Such dark patterns manipulate user consent and inflate mailing list sizes.
Table of Comparison
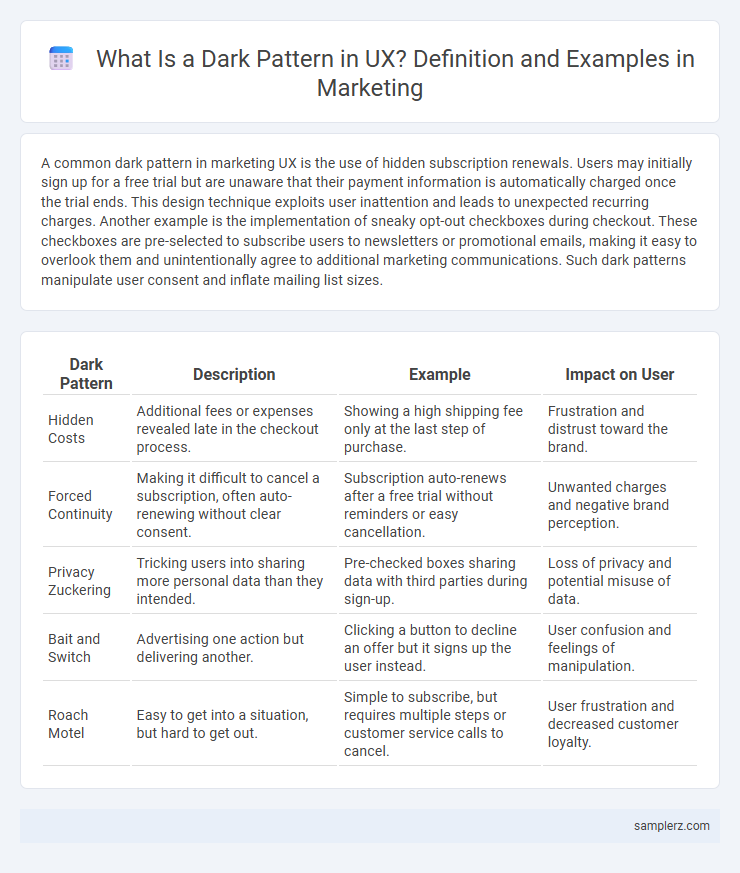
| Dark Pattern | Description | Example | Impact on User |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hidden Costs | Additional fees or expenses revealed late in the checkout process. | Showing a high shipping fee only at the last step of purchase. | Frustration and distrust toward the brand. |
| Forced Continuity | Making it difficult to cancel a subscription, often auto-renewing without clear consent. | Subscription auto-renews after a free trial without reminders or easy cancellation. | Unwanted charges and negative brand perception. |
| Privacy Zuckering | Tricking users into sharing more personal data than they intended. | Pre-checked boxes sharing data with third parties during sign-up. | Loss of privacy and potential misuse of data. |
| Bait and Switch | Advertising one action but delivering another. | Clicking a button to decline an offer but it signs up the user instead. | User confusion and feelings of manipulation. |
| Roach Motel | Easy to get into a situation, but hard to get out. | Simple to subscribe, but requires multiple steps or customer service calls to cancel. | User frustration and decreased customer loyalty. |
Understanding Dark Patterns in UX Design
Dark patterns in UX design manipulate users into actions that benefit the company but may harm the user experience, such as disguised ads or forced continuity subscriptions. An example includes "roach motel" designs, where signing up for a service is easy, but canceling it is intentionally complicated and obscure. These deceptive practices undermine trust and highlight the importance of ethical design principles in marketing strategies.
Common Types of Dark Patterns in Marketing
Common types of dark patterns in marketing UX include hidden costs, where additional fees appear only at checkout, bait-and-switch tactics that advertise one product but deliver another, and disguised ads designed to look like regular content. These manipulative designs exploit user trust, leading to unintended purchases or data sharing. Understanding these patterns helps marketers create transparent, ethical experiences that build long-term customer loyalty.
Examples of Sneaky Subscription Traps
Sneaky subscription traps often manifest as pre-checked boxes or hidden fees that automatically enroll users into recurring payments without clear consent. Pop-ups offering "free trials" that require credit card information and obscure cancellation policies are common dark patterns designed to confuse users. These deceptive tactics exploit user attention to increase subscription rates while making opt-out processes intentionally difficult.
How Forced Continuity Impacts User Trust
Forced continuity tricks users into ongoing subscriptions by requiring credit card details upfront and making cancellation difficult, leading to frustration and diminished trust. This dark pattern exploits user inertia, causing unexpected charges that harm the brand's reputation. Transparent and easy cancellation processes are essential to maintain user confidence and foster long-term loyalty.
Hidden Costs: The Bait and Switch Technique
The bait and switch technique in UX marketing involves advertising a product or service at a low price but revealing hidden costs only during the checkout process, misleading users into unexpected charges. This dark pattern exploits consumer trust by obscuring fees related to shipping, taxes, or additional features until the final purchase stage. Companies employing this tactic often see short-term gains but risk long-term damage to brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Confirmshaming: Guilt-Driven User Choices
Confirmshaming exploits guilt to manipulate users into making specific choices by framing the decline option with emotionally charged language, such as "No, I don't want to save money." This dark pattern in UX design coerces users into consenting to offers or subscriptions through subtle psychological pressure. Studies show that confirmshaming increases conversion rates but significantly damages user trust and brand reputation over time.
Roach Motel: Hard to Leave, Easy to Join
Roach Motel is a dark pattern in UX design where users find it exceptionally easy to sign up or subscribe but face significant obstacles when trying to cancel or leave the service. This manipulative tactic increases user retention artificially by making the exit process confusing, time-consuming, or hidden behind multiple steps. Companies employing the Roach Motel pattern risk damaging brand trust and customer satisfaction despite short-term gains in subscription numbers.
Misdirection in Checkout Processes
Misdirection in checkout processes often involves hidden fees or confusing button placements that steer users toward making more expensive purchases without realizing it. E-commerce sites may display a prominent "Continue" button for adding insurance or warranties, while the option to skip this upsell is less visible or written in smaller font. This dark pattern manipulates user attention, increasing conversion rates at the expense of transparent, user-friendly design.
Fake Urgency and Scarcity Tactics
Fake urgency and scarcity tactics in marketing often involve misleading users with countdown timers or limited stock notifications that are not genuinely time-sensitive or accurate. These dark patterns create a false sense of urgency, pressuring consumers to make impulsive purchases without adequate consideration. Employing such strategies can damage brand trust and result in higher bounce rates due to user frustration and skepticism.
Ethical Marketing: Avoiding Dark Pattern Pitfalls
Dark patterns in UX, such as hidden subscription renewals or disguised opt-out options, undermine user trust and violate principles of ethical marketing. Transparent design choices and clear communication help brands build lasting customer relationships while respecting user autonomy. Avoiding manipulative tactics not only fosters brand loyalty but also aligns marketing practices with legal and ethical standards.
example of dark pattern in UX Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com