Slow gardening in the yard emphasizes mindful planting and nurturing over rushing to complete tasks. This approach involves selecting native plants and perennials that thrive in the local climate, reducing the need for intensive maintenance. Gardeners focus on creating a sustainable ecosystem, encouraging beneficial insects and birds to support plant health naturally. In practice, slow gardening might include hand-weeding flower beds instead of using chemicals, allowing soil to naturally improve through composting. The method promotes observing seasonal changes and adjusting care routines accordingly, such as watering deeply but less frequently to encourage strong root development. This intentional pace fosters a deeper connection to the environment and enhances yard biodiversity.
Table of Comparison
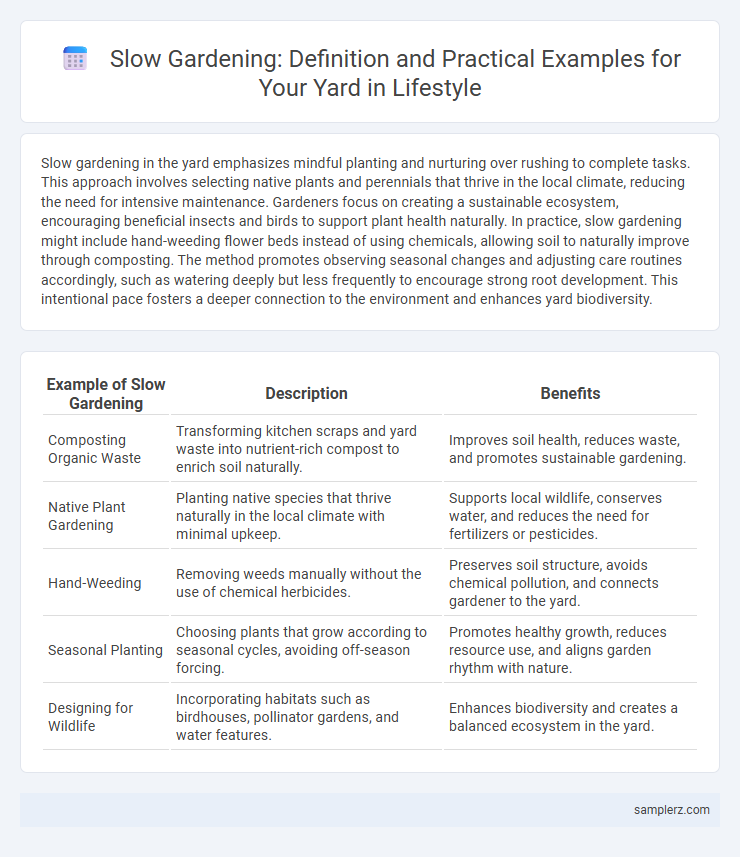
| Example of Slow Gardening | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Composting Organic Waste | Transforming kitchen scraps and yard waste into nutrient-rich compost to enrich soil naturally. | Improves soil health, reduces waste, and promotes sustainable gardening. |
| Native Plant Gardening | Planting native species that thrive naturally in the local climate with minimal upkeep. | Supports local wildlife, conserves water, and reduces the need for fertilizers or pesticides. |
| Hand-Weeding | Removing weeds manually without the use of chemical herbicides. | Preserves soil structure, avoids chemical pollution, and connects gardener to the yard. |
| Seasonal Planting | Choosing plants that grow according to seasonal cycles, avoiding off-season forcing. | Promotes healthy growth, reduces resource use, and aligns garden rhythm with nature. |
| Designing for Wildlife | Incorporating habitats such as birdhouses, pollinator gardens, and water features. | Enhances biodiversity and creates a balanced ecosystem in the yard. |
Embracing Slow Gardening: Principles for Your Yard
Embracing slow gardening in your yard involves nurturing plants mindfully, allowing natural growth rhythms to dictate care rather than rushing with frequent trimming or forced blooms. Prioritizing native species and organic soil health promotes biodiversity and sustainability, enhancing the ecosystem while reducing maintenance. This approach fosters a tranquil space that encourages patience and connection with nature's seasonal cycles.
Planning a Relaxed Garden Layout
Designing a relaxed garden layout begins with selecting native plants that require minimal maintenance and thrive in the local climate, ensuring sustainability and ease of care. Incorporating winding pathways and cozy seating areas encourages leisurely strolls and mindful relaxation, promoting a slower pace in the outdoor space. Prioritizing natural materials and organic shapes helps create a harmonious environment that fosters connection with nature while reducing stress and effort.
Choosing Low-Maintenance Plants for Slow Gardening
Selecting low-maintenance plants such as succulents, native grasses, and drought-tolerant perennials simplifies yard care and supports sustainable slow gardening practices. These plants require minimal watering, pruning, and fertilizing, reducing time spent on yard upkeep while promoting natural growth cycles. Incorporating species like lavender, sedum, and ornamental grasses enhances biodiversity and resilience, creating an eco-friendly outdoor space with reduced environmental impact.
Creating a Pollinator-Friendly Sanctuary
Plant native flowers such as milkweed, coneflowers, and bee balm to attract and support local pollinators like bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. Incorporate a variety of blooming plants throughout the growing season to provide continuous nectar sources, ensuring a thriving pollinator habitat. Avoid pesticides and create habitats with water sources and shelter to promote biodiversity and enhance the slow gardening experience in your yard.
Incorporating Handcrafted Garden Features
Incorporating handcrafted garden features into slow gardening creates a personalized and sustainable outdoor space by using natural materials like reclaimed wood, stone, and terracotta. These artisanal elements enhance the yard's aesthetic appeal while promoting mindfulness and connection with nature. Integrating birdhouses, hand-carved benches, and mosaic stepping stones encourages a slower, more intentional gardening practice that nurtures both the environment and the gardener's well-being.
Practicing Mindful Watering and Composting
Practicing mindful watering in slow gardening promotes efficient water use by observing soil moisture levels and avoiding overwatering, which supports plant health and conserves resources. Composting yard waste and kitchen scraps enriches soil fertility by returning essential nutrients, reducing landfill waste and enhancing sustainable gardening practices. Integrating these methods fosters a balanced ecosystem while encouraging patience and attentiveness in the gardening process.
Inviting Wildlife with Natural Habitats
Creating a slow garden that invites wildlife involves planting native flowers, shrubs, and trees that provide food and shelter for local birds, bees, and butterflies. Incorporating features such as a small pond, birdhouses, and insect hotels enhances natural habitats and encourages biodiversity. Avoiding pesticides and allowing natural growth cycles promotes a healthy ecosystem in your yard.
Seasonal Yard Care with Minimal Stress
Embracing slow gardening in your yard involves focusing on seasonal yard care that prioritizes low-maintenance techniques like mulching, planting native perennials, and allowing natural composting to enrich the soil. This approach reduces stress by aligning gardening tasks with the natural growth cycles of plants, minimizing the need for frequent watering and pruning. Seasonal strategies such as planting cover crops in fall and using organic mulches in spring support soil health and plant resilience with minimal effort.
Enjoying the Garden: Spaces for Reflection
Creating a quiet corner with comfortable seating and fragrant plants encourages mindful reflection and stress relief in the garden. Incorporating native flowers and herbs attracts pollinators, enhancing the sensory experience and fostering a deeper connection to nature. Soft pathways made from natural materials invite slow strolls, promoting relaxation and intentional presence in the outdoor space.
Cultivating Patience and Presence in Your Outdoor Space
Slow gardening in your yard encourages cultivating patience by embracing the natural growth rhythms of plants, allowing you to connect deeply with each stage of development. Engaging mindfully with tasks like weeding, pruning, and watering fosters a presence that transforms your outdoor space into a serene retreat. This approach nurtures both mental well-being and a sustainable environment through intentional, unhurried care.
example of slow gardening in yard Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com