Roguelike games are a popular subgenre in gaming characterized by procedural generation, turn-based gameplay, tile-based graphics, and permanent death mechanics. One notable example is "The Binding of Isaac," which features randomized dungeons, items, and enemies, providing a unique experience with every playthrough. This game emphasizes strategic decision-making and resource management, hallmarks of the roguelike genre. Another prominent example is "Hades," developed by Supergiant Games, blending roguelike elements with an action-packed narrative. It uses procedural level generation and permadeath mechanics, allowing players to progressively unlock abilities and story content. Hades combines fast-paced combat with depth in character development, exemplifying the evolving design of modern roguelikes.
Table of Comparison
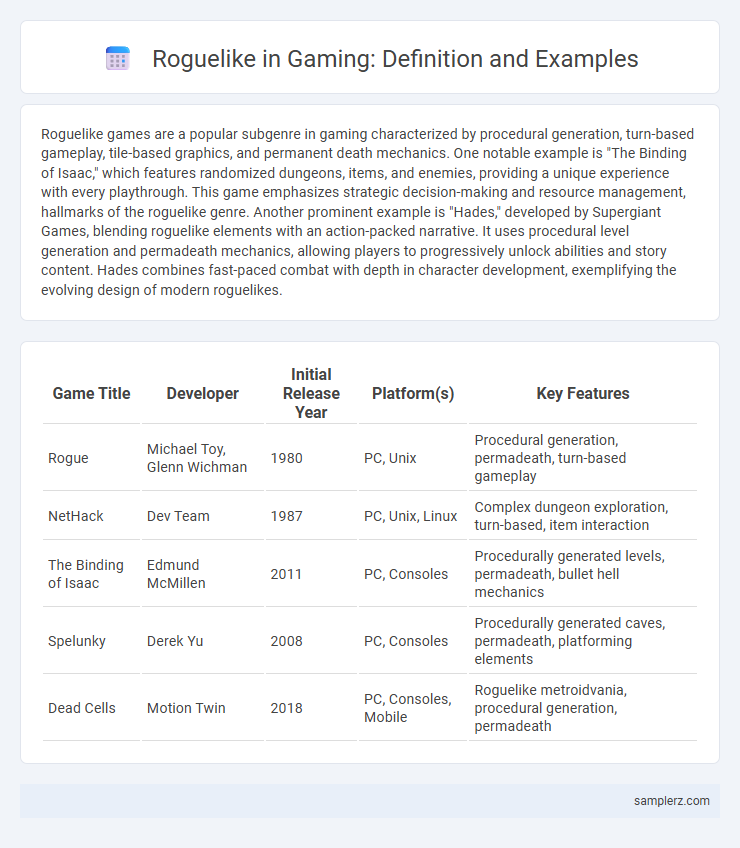
| Game Title | Developer | Initial Release Year | Platform(s) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rogue | Michael Toy, Glenn Wichman | 1980 | PC, Unix | Procedural generation, permadeath, turn-based gameplay |
| NetHack | Dev Team | 1987 | PC, Unix, Linux | Complex dungeon exploration, turn-based, item interaction |
| The Binding of Isaac | Edmund McMillen | 2011 | PC, Consoles | Procedurally generated levels, permadeath, bullet hell mechanics |
| Spelunky | Derek Yu | 2008 | PC, Consoles | Procedurally generated caves, permadeath, platforming elements |
| Dead Cells | Motion Twin | 2018 | PC, Consoles, Mobile | Roguelike metroidvania, procedural generation, permadeath |
Defining Roguelike: Core Characteristics in Gaming
Roguelike games are defined by their procedural generation, turn-based gameplay, and permanent death mechanics. Titles like "The Binding of Isaac" and "Dead Cells" showcase these core elements through randomized levels and unforgiving difficulty. This genre emphasizes strategic decision-making and high replayability, making each playthrough unique and challenging.
History and Evolution of Roguelike Games
Roguelike games originated with the 1980 release of *Rogue*, which introduced procedurally generated dungeons, permadeath, and turn-based gameplay as core mechanics defining the genre. Over the decades, roguelikes evolved with titles like *NetHack* and *Dungeon Crawl Stone Soup*, emphasizing complex interactions and ASCII graphics, while modern interpretations such as *The Binding of Isaac* and *Dead Cells* blend roguelike elements with action and platforming. The genre's evolution reflects advances in computing power and player preferences, expanding from minimalist dungeon crawlers to diverse experiences incorporating narrative, real-time combat, and roguelite mechanics.
Iconic Classic Roguelike Titles
Iconic classic roguelike titles such as "NetHack," "Rogue," and "Angband" have defined the genre with procedurally generated dungeons, permadeath mechanics, and turn-based gameplay. These games emphasize strategic decision-making, resource management, and exploration, offering high replayability through randomized levels and unpredictable enemies. Their influence persists in contemporary roguelikes, shaping modern game design and inspiring countless indie developers within the gaming community.
Modern Interpretations of Roguelike Mechanics
Modern interpretations of roguelike mechanics are evident in games such as Hades and Dead Cells, which blend procedural level generation with persistent character progression. These titles emphasize fast-paced combat and narrative elements while maintaining permadeath and randomized environments typical of classic roguelikes. This hybrid approach revitalizes the genre by enhancing replayability and player engagement through evolving storylines and skill unlocks.
Popular Roguelike Games in Recent Years
Hades by Supergiant Games revolutionized roguelike mechanics with its rich narrative and fast-paced combat, becoming a benchmark for modern titles. Dead Cells combines procedural generation with Metroidvania-style exploration, offering challenging yet rewarding gameplay. Slay the Spire merges deck-building strategy with roguelike elements, captivating a wide audience with its unique card-based mechanics.
Indie Success Stories in the Roguelike Genre
Hades by Supergiant Games revolutionized the roguelike genre with its rich narrative and fluid combat, earning critical acclaim and commercial success. Dead Cells, developed by Motion Twin, combines procedurally-generated levels with Metroidvania elements, captivating players with its challenging gameplay and replayability. Enter the Gungeon from Dodge Roll gained a dedicated following through its unique bullet-hell mechanics and charming pixel art style, establishing itself as a staple in indie roguelike titles.
Roguelike vs. Roguelite: Key Differences
Roguelike games, exemplified by classics like "NetHack" and modern titles such as "Dungeon Crawl Stone Soup," emphasize strict procedural generation, permadeath, and turn-based gameplay. In contrast, roguelites like "Dead Cells" and "Hades" blend these elements with persistent progression systems and more forgiving mechanics, allowing players to retain upgrades or resources across runs. The key difference lies in the balance between challenge and accessibility, with roguelikes offering a purist, unforgiving experience, while roguelites provide a more accessible and varied approach to replayability.
Procedural Generation in Roguelikes
Procedural generation in roguelike games creates vast, unpredictable levels by algorithmically assembling environments, enemies, and loot, enhancing replayability. Titles like *The Binding of Isaac* and *Hades* exemplify this mechanic, offering unique experiences each session with varied map layouts and item placements. This dynamic content generation challenges players to adapt strategies, fostering deep engagement and emergent gameplay.
Impact of Permadeath in Roguelike Gameplay
Permadeath in roguelike games, such as "Dead Cells" and "Hades," significantly enhances player engagement by increasing tension and emphasizing strategic decision-making. This mechanic ensures that every choice carries weight, fostering a heightened sense of accomplishment upon progress or success. The permanent loss of characters or progress motivates players to master game mechanics while embracing risk and replayability.
The Future of Roguelike Games in the Industry
Procedurally generated levels and permadeath mechanics define roguelike games, exemplified by titles like "Dead Cells" and "Hades," which combine narrative depth with replayability. The future of roguelike games in the industry lies in integrating advanced AI to create more adaptive enemies and environments, enhancing player immersion. Innovations in procedural storytelling and cross-platform multiplayer features are expected to drive the genre's growth and appeal to a broader audience.
example of roguelike in gaming Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com