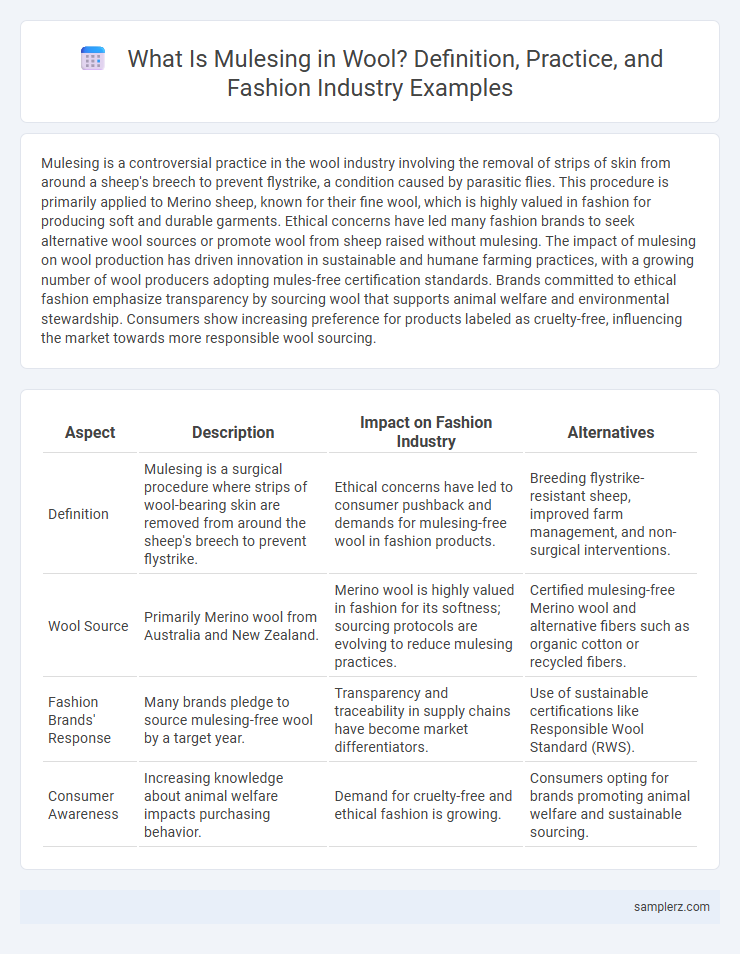
Mulesing is a controversial practice in the wool industry involving the removal of strips of skin from around a sheep's breech to prevent flystrike, a condition caused by parasitic flies. This procedure is primarily applied to Merino sheep, known for their fine wool, which is highly valued in fashion for producing soft and durable garments. Ethical concerns have led many fashion brands to seek alternative wool sources or promote wool from sheep raised without mulesing. The impact of mulesing on wool production has driven innovation in sustainable and humane farming practices, with a growing number of wool producers adopting mules-free certification standards. Brands committed to ethical fashion emphasize transparency by sourcing wool that supports animal welfare and environmental stewardship. Consumers show increasing preference for products labeled as cruelty-free, influencing the market towards more responsible wool sourcing.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Description | Impact on Fashion Industry | Alternatives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mulesing is a surgical procedure where strips of wool-bearing skin are removed from around the sheep's breech to prevent flystrike. | Ethical concerns have led to consumer pushback and demands for mulesing-free wool in fashion products. | Breeding flystrike-resistant sheep, improved farm management, and non-surgical interventions. |
| Wool Source | Primarily Merino wool from Australia and New Zealand. | Merino wool is highly valued in fashion for its softness; sourcing protocols are evolving to reduce mulesing practices. | Certified mulesing-free Merino wool and alternative fibers such as organic cotton or recycled fibers. |
| Fashion Brands' Response | Many brands pledge to source mulesing-free wool by a target year. | Transparency and traceability in supply chains have become market differentiators. | Use of sustainable certifications like Responsible Wool Standard (RWS). |
| Consumer Awareness | Increasing knowledge about animal welfare impacts purchasing behavior. | Demand for cruelty-free and ethical fashion is growing. | Consumers opting for brands promoting animal welfare and sustainable sourcing. |
Understanding Mulesing: Definition and Background
Mulesing is a controversial practice in the wool industry where strips of skin are removed from the buttocks of sheep to prevent flystrike, a condition caused by parasitic flies. Originating in Australia during the 1930s, mulesing was introduced as a measure to protect sheep in tight-wool breeds like Merino, which are particularly vulnerable to flystrike. Increasing consumer awareness has driven fashion brands to seek ethical wool alternatives, promoting animal welfare through certifications such as Responsible Wool Standard (RWS).
Historical Origins of Mulesing in the Wool Industry
Mulesing originated in 1930s Australia as a response to flystrike, a severe parasitic infection affecting Merino sheep's wool-producing areas. The practice involves removing strips of skin around the sheep's breech to create wool-free patches that reduce flystrike risk. Historically adopted to protect wool quality and sheep welfare, mulesing remains controversial due to animal welfare concerns despite its efficacy in the wool industry.
The Process: How Mulesing is Performed on Sheep
Mulesing involves surgically removing strips of wool-bearing skin from around a sheep's breech to prevent flystrike, a parasitic infection common in wool-bearing areas. The procedure is typically done without anesthesia by firmly stretching the skin and excising sections with sharp blades, often when lambs are between four and twelve weeks old. This process aims to create smooth, scarred skin that resists flystrike but has sparked significant animal welfare debates within the fashion industry.
Examples of Mulesing Practices in Major Wool-Producing Countries
Australia, the largest wool producer, practices mulesing extensively on Merino sheep to prevent flystrike, despite increasing ethical concerns and growing demand for cruelty-free wool. New Zealand employs minimal mulesing due to widespread adoption of parasite control alternatives and selective breeding programs. South Africa and Argentina have largely phased out mulesing, focusing instead on innovative sheep management techniques to maintain wool quality while prioritizing animal welfare.
Impact of Mulesing on Animal Welfare
Mulesing, a practice used in wool production, involves removing strips of skin from sheep to prevent flystrike but causes significant pain and distress, raising critical animal welfare concerns. This procedure leads to open wounds and prolonged suffering, prompting increased scrutiny from animal rights organizations and consumers seeking ethically sourced wool. Brands adopting humane alternatives or certified cruelty-free wool help reduce the negative impact on animal welfare while meeting growing demand for ethical fashion.
Fashion Industry’s Use of Mulesed Wool
The fashion industry's use of mulesed wool primarily originates from Australian sheep farming practices, where strips of skin are removed to prevent flystrike, raising significant animal welfare concerns. Prominent fashion brands increasingly face scrutiny for sourcing mulesed wool, prompting a shift towards ethically certified, non-mulesed wool alternatives. Consumer demand for cruelty-free materials accelerates industry-wide adoption of sustainable and humane wool production standards.
Sustainable Alternatives: Mulesing-Free Wool Certification
Mulesing-free wool certification guarantees that wool is sourced from sheep not subjected to mulesing, addressing animal welfare concerns within the fashion industry. Brands adopting sustainable alternatives prioritize ethical sourcing by promoting certified mulesing-free wool standards such as the Responsible Wool Standard (RWS). This certification supports transparency and traceability in wool production, encouraging eco-friendly and cruelty-free fashion practices.
Case Studies: Brands Committed to Mulesing-Free Wool
Brands like Patagonia, Icebreaker, and Amour Vert are leading examples committed to mulesing-free wool, prioritizing animal welfare and sustainable sourcing in their supply chains. These companies collaborate closely with wool producers who practice ethical shearing, ensuring transparency and traceability from farm to fashion. Their dedication not only supports humane treatment of sheep but also aligns with growing consumer demand for responsible and cruelty-free apparel.
Consumer Awareness and Demand for Ethical Wool
Consumer awareness about the ethical implications of mulesing in wool production has significantly increased, driving demand for cruelty-free and sustainably sourced wool. Brands that prioritize non-mulesed wool certification attract ethical consumers who seek transparency and animal welfare in fashion products. This shift influences industry standards, encouraging widespread adoption of humane practices within the wool supply chain.
Future Trends: Phasing Out Mulesing in Fashion
The fashion industry is increasingly adopting sustainable wool sourcing by phasing out mulesing, a controversial practice aimed at preventing flystrike in sheep. Brands committed to ethical fashion are shifting towards certified mulesing-free wool and supporting animal welfare initiatives. Innovations in wool treatment and alternative protective measures are expected to drive the future trend of mulesing-free wool in premium and eco-conscious fashion markets.
example of mulesing in wool Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com