A thermal plume in a river occurs when industrial processes release heated water into a natural water body, causing localized temperature increases. Power plants, especially those using water for cooling, commonly generate these thermal plumes, which can elevate river temperatures by several degrees Celsius. This phenomenon impacts aquatic ecosystems by altering oxygen levels and affecting species sensitive to temperature changes. Monitoring data from rivers near industrial sites often reveals spatial temperature gradients associated with thermal plumes. Remote sensing and in situ measurements help map the extent and intensity of these plumes, providing critical information for environmental management. Regulatory agencies use this data to enforce thermal discharge limits, aiming to protect river biodiversity and maintain ecological balance.
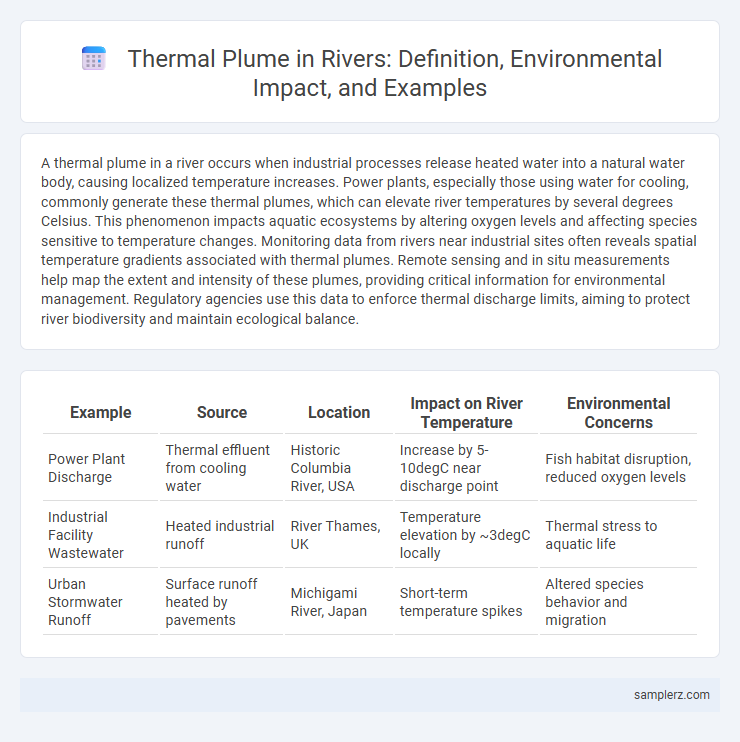
Table of Comparison
| Example | Source | Location | Impact on River Temperature | Environmental Concerns |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Plant Discharge | Thermal effluent from cooling water | Historic Columbia River, USA | Increase by 5-10degC near discharge point | Fish habitat disruption, reduced oxygen levels |
| Industrial Facility Wastewater | Heated industrial runoff | River Thames, UK | Temperature elevation by ~3degC locally | Thermal stress to aquatic life |
| Urban Stormwater Runoff | Surface runoff heated by pavements | Michigami River, Japan | Short-term temperature spikes | Altered species behavior and migration |
Understanding Thermal Plumes in River Environments
Thermal plumes in river environments occur when industrial facilities or power plants discharge heated water into rivers, raising local water temperatures significantly. These temperature changes can disrupt aquatic ecosystems by altering species composition, reducing dissolved oxygen levels, and affecting reproductive cycles of fish and invertebrates. Monitoring thermal plumes using remote sensing and in-situ temperature measurements is critical for managing thermal pollution and protecting riverine biodiversity.
Common Sources of River Thermal Plume Formation
Thermal plumes in rivers commonly originate from industrial discharges, such as power plants and manufacturing facilities, that release heated water during cooling processes. Urban runoff and stormwater can also contribute to elevated river temperatures by carrying warm surface water into the river system. Agricultural activities, including irrigation return flows, further influence thermal plume formation by altering water temperatures and flow patterns.
Industrial Discharges and Their Thermal Effects on Rivers
Industrial discharges often release heated water from manufacturing processes into rivers, creating thermal plumes that elevate local water temperatures. These thermal plumes can disrupt aquatic ecosystems by reducing dissolved oxygen levels and altering species composition. Continuous monitoring of temperature fluctuations near discharge points is essential for assessing the environmental impact on river health.
Case Study: Power Plant-Induced Thermal Plumes in Local Rivers
Thermal plumes caused by power plants release heated water into local rivers, significantly raising water temperatures and disrupting aquatic ecosystems. Case studies reveal that these elevated temperatures reduce dissolved oxygen levels, harming fish populations and altering species composition. Monitoring and managing thermal discharges are crucial for preserving riverine biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance.
Urban Runoff as a Contributor to River Thermal Plumes
Urban runoff significantly contributes to river thermal plumes by introducing heated water from impervious surfaces such as roads and rooftops. This runoff elevates river temperatures, disrupting aquatic ecosystems and reducing oxygen levels critical for fish and other wildlife. Studies show that thermal plumes from urban areas can increase river temperatures by several degrees Celsius, exacerbating stress on sensitive species and altering natural thermal regimes.
Impacts of Thermal Plumes on Aquatic Ecosystems
Thermal plumes in rivers, often caused by industrial discharges or power plant cooling water, significantly alter local water temperatures, disrupting aquatic ecosystems. Elevated temperatures reduce dissolved oxygen levels, stressing fish populations such as trout and salmon while favoring heat-tolerant species, leading to biodiversity loss. Changes in thermal regimes also affect nutrient cycling and promote algal blooms, further degrading water quality and habitat health.
Monitoring and Measuring Thermal Plumes in Riverine Systems
Thermal plumes in riverine systems are monitored using temperature sensors and remote sensing technologies to capture spatial and temporal variations in water temperature. Deploying continuous monitoring stations along affected river sections allows for precise measurement of temperature gradients and plume dispersion patterns. Data collected supports environmental impact assessments and informs management strategies aimed at mitigating thermal pollution effects on aquatic ecosystems.
Regulatory Approaches to Managing River Thermal Pollution
Regulatory approaches to managing river thermal pollution often involve setting temperature limits for discharge effluents to control thermal plumes and protect aquatic ecosystems. Agencies like the EPA implement temperature variance permits under the Clean Water Act to ensure industrial cooling water discharges do not exceed harmful thermal thresholds. Continuous monitoring and thermal modeling are critical tools used to assess compliance and mitigate the ecological impacts of elevated river temperatures.
Mitigation Strategies for Reducing Thermal Plumes in Rivers
Mitigation strategies for reducing thermal plumes in rivers include the installation of cooling towers and cooling ponds to dissipate heat from industrial discharges before entering waterways. Riparian buffer zones with native vegetation help shade rivers, lowering water temperatures and improving aquatic habitat. Implementing temperature control technologies in power plants and wastewater treatment facilities also minimizes thermal pollution, protecting river ecosystems and biodiversity.
Future Trends in Thermal Plume Research and River Health
Emerging technologies like remote sensing and AI-driven modeling are revolutionizing thermal plume monitoring in rivers, enabling precise real-time data on temperature variations and ecological impacts. Researchers are increasingly focusing on the integration of thermal plume analysis with river health indicators to predict and mitigate effects on aquatic biodiversity and water quality. Future trends aim to develop adaptive management strategies that address climate change-induced thermal stress and promote sustainable river ecosystems.
example of thermal plume in river Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com