Plasticulture in farmland involves the use of plastic materials to enhance agricultural productivity and sustainability. Common applications include plastic mulch films, drip irrigation tubes, and greenhouse covers, which help conserve water, control weeds, and maintain optimal soil temperature. This technology supports efficient resource management and increases crop yields in various agricultural settings. Farmers utilize plasticulture to reduce the environmental impact of traditional farming methods by minimizing soil erosion and chemical runoff. Data shows that plastic mulch can increase crop production by up to 30% while using 30-50% less water compared to conventional practices. The integration of plasticulture practices aligns with sustainable agriculture goals by optimizing resource use and promoting higher efficiency in farmland management.
Table of Comparison
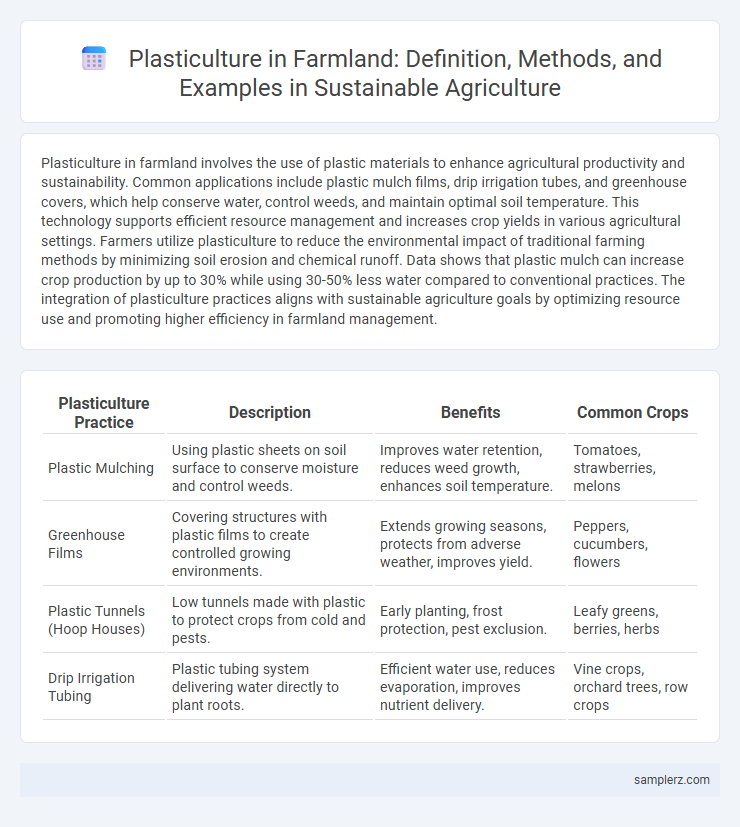
| Plasticulture Practice | Description | Benefits | Common Crops |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Mulching | Using plastic sheets on soil surface to conserve moisture and control weeds. | Improves water retention, reduces weed growth, enhances soil temperature. | Tomatoes, strawberries, melons |
| Greenhouse Films | Covering structures with plastic films to create controlled growing environments. | Extends growing seasons, protects from adverse weather, improves yield. | Peppers, cucumbers, flowers |
| Plastic Tunnels (Hoop Houses) | Low tunnels made with plastic to protect crops from cold and pests. | Early planting, frost protection, pest exclusion. | Leafy greens, berries, herbs |
| Drip Irrigation Tubing | Plastic tubing system delivering water directly to plant roots. | Efficient water use, reduces evaporation, improves nutrient delivery. | Vine crops, orchard trees, row crops |
Introduction to Plasticulture in Farmland
Plasticulture in farmland involves the use of plastic materials such as mulch films, drip irrigation tapes, and greenhouse covers to enhance crop production and conserve resources. These plastics improve soil moisture retention, control weed growth, and regulate soil temperature, leading to increased yields and reduced water usage. Implementing plasticulture techniques supports sustainable farming practices by optimizing inputs and minimizing environmental impacts.
Benefits of Plasticulture for Sustainable Agriculture
Plasticulture in farmland enhances water efficiency by reducing evaporation and optimizing irrigation through drip systems, lowering overall water consumption. It increases crop yields and quality by maintaining consistent soil temperatures and protecting plants from pests and diseases, promoting healthier growth. This sustainable practice reduces the need for chemical inputs and minimizes soil degradation, supporting long-term agricultural productivity and environmental conservation.
Common Types of Plastics Used in Farmland
Common types of plastics used in plasticulture on farmland include polyethylene (PE), primarily utilized for mulch films and greenhouse covers due to its durability and flexibility. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is often employed for irrigation pipes and drip tapes because of its chemical resistance and ease of installation. Additionally, polypropylene (PP) is used in crop protection netting and containers, offering strength and UV resistance essential for agricultural applications.
Plastic Mulching: Enhancing Soil and Crop Yield
Plastic mulching in farmland involves covering soil with polyethylene films to conserve moisture, regulate temperature, and reduce weed growth, significantly enhancing crop yield. This technique improves soil structure by minimizing erosion and retaining essential nutrients, promoting healthier root development. Studies show plastic mulching can increase water use efficiency by up to 50% and boost crop production by 30-70% in various agricultural systems.
Drip Irrigation Systems with Plastic Components
Drip irrigation systems with plastic components enhance water efficiency in farmland by delivering precise moisture directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff. These systems typically use polyethylene tubing, emitters, and connectors that resist UV degradation and chemicals, ensuring durability under various environmental conditions. Incorporating plasticulture through such drip irrigation methods supports sustainable agriculture by conserving water resources and improving crop yields.
Plastic Greenhouses: Controlled Environment Farming
Plastic greenhouses enable controlled environment farming by regulating temperature, humidity, and light exposure to optimize crop growth year-round. The use of polyethylene films in these structures enhances water efficiency and reduces pesticide dependency by creating a protective barrier against pests and harsh weather. This sustainable plasticulture method increases crop yields while minimizing environmental impact on farmland ecosystems.
Silage Wraps and Ensiling Techniques in Agriculture
Silage wraps, primarily made from UV-stabilized polyethylene films, are a critical component of plasticulture in modern farmland, enabling efficient preservation of forage crops through airtight sealing. Advanced ensiling techniques utilize these silage wraps to create anaerobic conditions that promote fermentation, minimizing spoilage and nutrient loss in stored feed. The adoption of multilayer silage films enhances durability and oxygen barrier properties, thereby improving silage quality and extending storage life.
Plastic Row Covers for Pest and Weather Protection
Plastic row covers in plasticulture serve as effective barriers against pests and harsh weather conditions, enhancing crop yield and quality. These lightweight polyethylene films create a microclimate by retaining moisture and warmth, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Farmers utilize plastic row covers primarily for vegetables and small fruits to extend growing seasons and improve plant health sustainably.
Environmental Impacts of Plasticulture Practices
Plasticulture practices, such as the use of plastic mulch films and drip irrigation tubes, significantly alter soil temperature and moisture retention, enhancing crop yields while potentially increasing plastic waste accumulation and microplastic pollution in farmland. These plastics can disrupt soil microbial communities and reduce soil fertility over time, posing risks to long-term agricultural sustainability. Effective management and development of biodegradable alternatives are crucial to mitigating negative environmental impacts associated with plasticulture in agricultural ecosystems.
Future Trends and Alternatives to Plasticulture in Farming
Biodegradable mulches and reusable agricultural films represent the leading future trends in plasticulture, aiming to reduce plastic waste and soil contamination. Innovations such as bio-based polymers derived from plant materials offer sustainable alternatives that maintain crop yield and soil health. Advanced sensor-integrated films enhance water efficiency and nutrient management, promoting eco-friendly farming practices.
example of plasticulture in farmland Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com