Bioprospecting in rainforests involves the exploration and extraction of biological resources for valuable compounds and genetic materials. A notable example is the discovery of the anti-cancer drug paclitaxel, derived from the Pacific yew tree species found in rainforest ecosystems. Researchers collect plant samples to identify novel enzymes, pharmaceuticals, and bioactive molecules that can benefit medicine and industry. This practice contributes to biodiversity conservation by highlighting the economic value of rainforest species and promoting sustainable use. Indigenous knowledge often plays a crucial role in guiding scientists to specific plants with therapeutic potential. Scientific data from bioprospecting projects drives innovation while supporting environmental protection efforts that maintain ecosystem health.
Table of Comparison
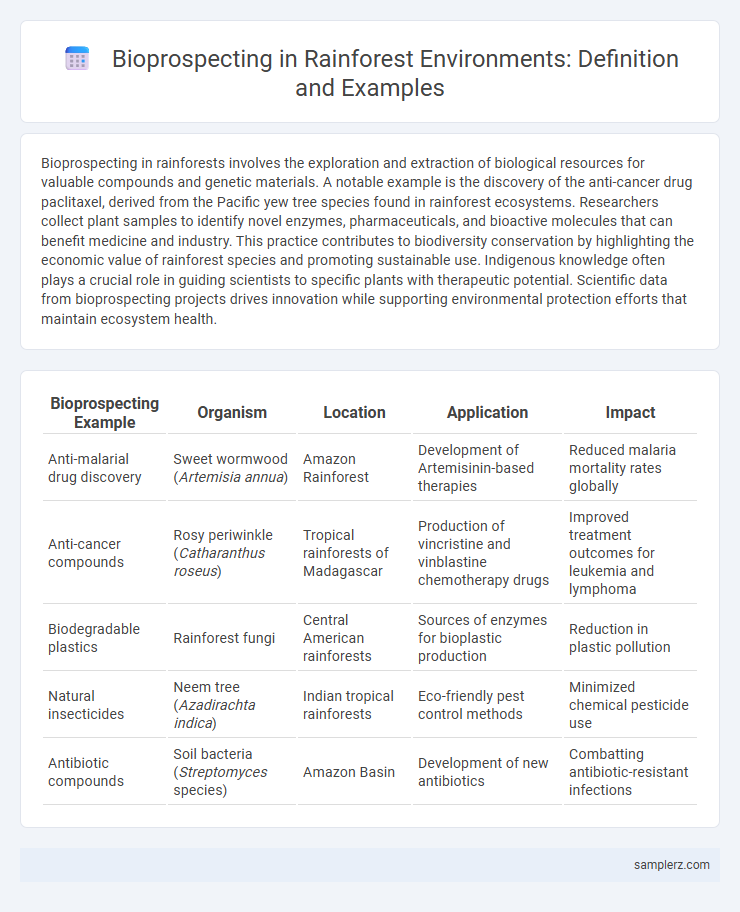
| Bioprospecting Example | Organism | Location | Application | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-malarial drug discovery | Sweet wormwood (Artemisia annua) | Amazon Rainforest | Development of Artemisinin-based therapies | Reduced malaria mortality rates globally |
| Anti-cancer compounds | Rosy periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus) | Tropical rainforests of Madagascar | Production of vincristine and vinblastine chemotherapy drugs | Improved treatment outcomes for leukemia and lymphoma |
| Biodegradable plastics | Rainforest fungi | Central American rainforests | Sources of enzymes for bioplastic production | Reduction in plastic pollution |
| Natural insecticides | Neem tree (Azadirachta indica) | Indian tropical rainforests | Eco-friendly pest control methods | Minimized chemical pesticide use |
| Antibiotic compounds | Soil bacteria (Streptomyces species) | Amazon Basin | Development of new antibiotics | Combatting antibiotic-resistant infections |
Introduction to Bioprospecting in Rainforest Ecosystems
Bioprospecting in rainforest ecosystems involves the systematic search for bioactive compounds from plants, fungi, and microorganisms with potential pharmaceutical, agricultural, and industrial applications. Tropical rainforests, such as the Amazon and Congo basins, are rich reservoirs of biodiversity, providing unique genetic resources that drive innovation in drug discovery and natural product development. This sustainable approach supports conservation efforts by promoting the value of preserving intricate rainforest habitats.
Discovery of Novel Medicinal Plants in Tropical Rainforests
Tropical rainforests harbor a vast array of plant species with unique chemical properties, making them prime locations for bioprospecting and the discovery of novel medicinal plants. Researchers have identified compounds from plants like the rosy periwinkle, which contributed to developing effective treatments for cancer and diabetes. The biodiversity-rich ecosystems of rainforests continue to provide invaluable resources for pharmaceutical research and drug development.
Bioprospecting Success Stories: Rainforest-Derived Pharmaceuticals
Rainforest bioprospecting has yielded groundbreaking pharmaceuticals such as the cancer drug paclitaxel, derived from the Pacific yew tree, and the antimalarial compound quinine from Cinchona bark. These natural compounds highlight the invaluable genetic diversity found in tropical ecosystems, providing novel bioactive molecules for drug development. Conservation of rainforests is crucial to preserve these untapped medicinal resources and support future bioprospecting breakthroughs.
Indigenous Knowledge and Its Role in Rainforest Bioprospecting
Indigenous knowledge plays a crucial role in rainforest bioprospecting by guiding researchers to discover medicinal plants and sustainable resources that have been used for generations. Traditional ecological insights from Indigenous communities enable targeted identification of bioactive compounds, accelerating drug development and conservation efforts. Integrating Indigenous expertise ensures ethical bioprospecting practices that protect biodiversity and support cultural heritage preservation.
Ethical Challenges and Benefit-Sharing in Rainforest Bioprospecting
Bioprospecting in rainforests often involves identifying valuable genetic resources or biochemical compounds from plants, fungi, and microbes, but raises ethical challenges such as consent, indigenous rights, and equitable benefit-sharing. Ensuring fair compensation and collaboration with local communities is critical to prevent biopiracy and preserve traditional knowledge. Transparent agreements and legal frameworks are essential to balance commercial interests with environmental conservation and social justice in rainforest bioprospecting projects.
Case Study: Anti-Cancer Compounds from Amazonian Flora
Researchers exploring the Amazon rainforest have identified several plant species containing potent anti-cancer compounds, such as paclitaxel analogs derived from endemic tree bark. These bioactive molecules demonstrate significant efficacy against various cancer cell lines, offering promising leads for pharmaceutical development. Sustainable bioprospecting efforts ensure that local biodiversity is preserved while enabling the discovery of novel therapeutics from Amazonian flora.
The Biodiversity Hotspot: Why Rainforests Are Prime Bioprospecting Sites
Rainforests, as biodiverse ecosystems, are prime bioprospecting sites due to their vast array of unique plant and microbial species with potential medicinal and industrial applications. For instance, the Amazon rainforest harbors compounds used in cancer treatments, like the antineoplastic agent derived from the rosy periwinkle. The concentration of endemic species in these biodiversity hotspots increases the likelihood of discovering novel bioactive substances essential for pharmaceutical innovation.
Sustainable Approaches to Bioprospecting in Rainforest Regions
Sustainable approaches to bioprospecting in rainforest regions emphasize the ethical collection of biological samples without disrupting local ecosystems, ensuring the preservation of biodiversity. Community involvement and benefit-sharing agreements play critical roles in maintaining ecological balance while supporting indigenous livelihoods. Advanced techniques like remote sensing and non-destructive sampling minimize environmental impact and promote long-term conservation goals.
Impact of Bioprospecting on Rainforest Conservation Efforts
Bioprospecting in rainforests involves the exploration of biodiversity for valuable genetic and biochemical resources, often leading to the discovery of new medicines and sustainable products. This practice can incentivize rainforest conservation by providing economic value to intact ecosystems, encouraging local communities and governments to preserve rather than exploit these areas. However, bioprospecting must be managed ethically to ensure benefits are shared equitably and biodiversity is not depleted, supporting long-term conservation goals.
Future Prospects: Emerging Technologies in Rainforest Bioprospecting
Emerging technologies such as AI-driven genomics and advanced bioinformatics are revolutionizing bioprospecting in rainforests, enabling the discovery of novel bioactive compounds with pharmaceutical potential. Remote sensing and drone-based sampling are enhancing the efficiency and precision of exploring vast and inaccessible rainforest areas, accelerating biodiversity assessments. These innovations hold promise for sustainable bioprospecting that balances ecological preservation with economic development.
example of bioprospecting in rainforest Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com