A jongleur in a medieval court was a versatile entertainer skilled in music, storytelling, and acrobatics. These performers often played instruments such as the lute or harp while reciting epic poems and humorous tales. Their role was essential for courtly entertainment, blending artistic talent with engaging performances to amuse nobility. Data from historical records shows jongleurs were itinerant artists who gained patronage from kings and nobles during the Middle Ages. They contributed to the preservation and dissemination of oral literature, including chansons de geste and fables. The presence of jongleurs in royal courts highlights the cultural importance of live entertainment during medieval times.
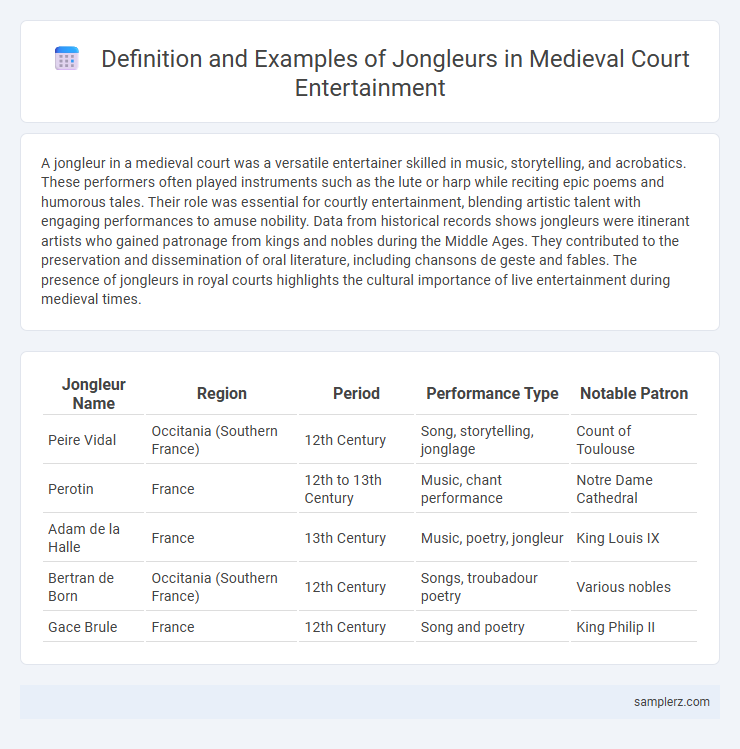
Table of Comparison
| Jongleur Name | Region | Period | Performance Type | Notable Patron |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peire Vidal | Occitania (Southern France) | 12th Century | Song, storytelling, jonglage | Count of Toulouse |
| Perotin | France | 12th to 13th Century | Music, chant performance | Notre Dame Cathedral |
| Adam de la Halle | France | 13th Century | Music, poetry, jongleur | King Louis IX |
| Bertran de Born | Occitania (Southern France) | 12th Century | Songs, troubadour poetry | Various nobles |
| Gace Brule | France | 12th Century | Song and poetry | King Philip II |
Introduction to Jongleurs in Medieval Courts
Jongleurs in medieval courts were versatile entertainers skilled in music, storytelling, and acrobatics, captivating noble audiences with their diverse performances. These itinerant performers played crucial roles in preserving oral traditions and disseminating news through their lyrical and theatrical acts. Their presence in medieval courts highlighted the cultural importance of entertainment in shaping social and political life during the Middle Ages.
Roles and Responsibilities of Jongleurs
Jongleurs in medieval courts performed as versatile entertainers, combining music, storytelling, acrobatics, and comedic acts to engage nobility and their guests. Their responsibilities included reciting epic poetry, playing instruments like the hurdy-gurdy or lute, and delivering witty or satirical commentary to enhance courtly events. Skilled jongleurs played a crucial role in preserving oral traditions and providing both amusement and social critique within the medieval entertainment landscape.
Notable Jongleurs in Medieval History
Notable jongleurs in medieval history include performers like Rutebeuf, a 13th-century French jongleur known for his witty poetry and songs performed in royal courts. Another prominent figure is Beatriz de Dia, a trobairitz whose lyrical compositions entertained nobles in the courts of Provence. These artists combined storytelling, music, and acrobatics to captivate medieval audiences, influencing the development of European performing arts.
Performance Art: Skills Exhibited by Jongleurs
Jongleurs in medieval courts showcased a versatile repertoire including music, storytelling, acrobatics, and juggling, captivating noble audiences with their dynamic performance art. Their skills in playing instruments like the lute and harp, combined with vocal prowess, created immersive entertainment experiences that blended artistic expression with physical dexterity. Mastery of improvisation and engaging stage presence allowed jongleurs to adapt performances, ensuring their relevance and appeal across diverse medieval social settings.
Instruments Commonly Played by Jongleurs
Jongleurs in medieval courts commonly played instruments such as the lute, vielle, and pipe, which allowed them to accompany their singing and storytelling. The tambourine and small drums provided rhythmic support, enhancing the overall performance's liveliness. Their musical versatility contributed significantly to the entertainment and cultural atmosphere of the court.
Jongleurs and Courtly Entertainment Traditions
Jongleurs in medieval courts performed a vital role as versatile entertainers, combining music, storytelling, and acrobatics to engage nobility during feasts and celebrations. These wandering minstrels preserved oral traditions, often adapting heroic epics and romantic tales to suit courtly tastes, thereby enhancing the cultural atmosphere. Their performances contributed to the flourishing of courtly entertainment traditions, blending artistic expression with social interaction in the medieval aristocratic setting.
Relationship Between Jongleurs and Nobility
Jongleurs in medieval courts served as versatile entertainers who strengthened the bond between nobility and their subjects through storytelling, music, and acrobatics. Their performances often included praise for noble patrons, reinforcing the social hierarchy and showcasing the wealth and cultural sophistication of the court. This reciprocal relationship allowed jongleurs to gain protection and patronage while enhancing the prestige of the aristocracy.
Famous Medieval Court Events Featuring Jongleurs
Jongleurs captivated audiences at famous medieval court events such as the Tournament of Chauvency in 1285, where their musical storytelling and acrobatics entertained nobles and knights. The court of King Richard the Lionheart frequently welcomed jongleurs who performed epic ballads and humorous tales during feasts and celebrations. Notable performances also took place at the court of Philip IV of France, where jongleurs played a key role in courtly gatherings by blending music, poetry, and theatrical acts.
Literary and Artistic Depictions of Jongleurs
Medieval literary and artistic depictions of jongleurs vividly portray their role as versatile entertainers skilled in music, storytelling, and acrobatics, often symbolizing the cultural vibrancy of courtly life. Manuscripts and tapestries from the 12th and 13th centuries frequently illustrate jongleurs performing before nobility, emphasizing their contribution to preserving and transmitting epic poems and chansons de geste. These depictions highlight the jongleur's dual identity as both common entertainer and vital cultural agent within medieval society.
Legacy of Jongleurs in Modern Entertainment
Jongleurs in medieval courts were versatile performers skilled in music, storytelling, and acrobatics, laying the foundation for modern entertainment forms such as theater, circus, and street performances. Their legacy is evident in contemporary variety shows, stand-up comedy, and musical acts that emphasize audience interaction and improvisation. The jongleur's role in preserving oral traditions and engaging diverse audiences continues to influence today's multimedia entertainment industries.
example of jongleur in medieval court Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com