Waldorf education is a pedagogical philosophy developed by Rudolf Steiner in the early 20th century. It emphasizes holistic learning, integrating intellectual, artistic, and practical skills to foster well-rounded development in students. The curriculum follows a developmental approach, adapting content and teaching methods to the cognitive stages of childhood. This educational model encourages creativity, imagination, and critical thinking through experiential learning and artistic activities. Waldorf schools often incorporate storytelling, music, and movement into lessons, supporting emotional and social growth alongside academic progress. The philosophy aims to cultivate independent and self-motivated learners prepared for lifelong growth.
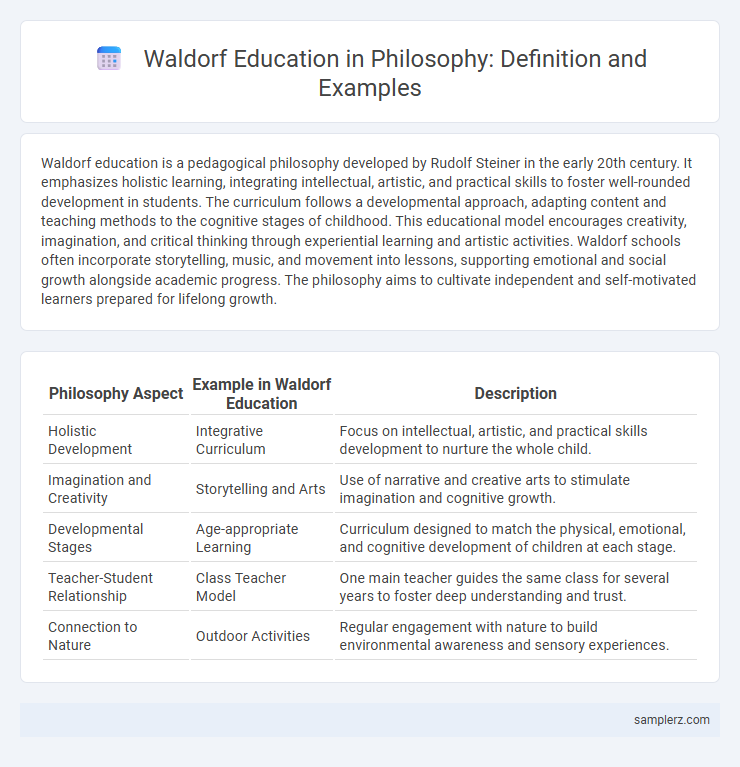
Table of Comparison
| Philosophy Aspect | Example in Waldorf Education | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Holistic Development | Integrative Curriculum | Focus on intellectual, artistic, and practical skills development to nurture the whole child. |
| Imagination and Creativity | Storytelling and Arts | Use of narrative and creative arts to stimulate imagination and cognitive growth. |
| Developmental Stages | Age-appropriate Learning | Curriculum designed to match the physical, emotional, and cognitive development of children at each stage. |
| Teacher-Student Relationship | Class Teacher Model | One main teacher guides the same class for several years to foster deep understanding and trust. |
| Connection to Nature | Outdoor Activities | Regular engagement with nature to build environmental awareness and sensory experiences. |
Foundations of Waldorf Philosophy in Education
Waldorf education is grounded in Rudolf Steiner's anthroposophical philosophy, emphasizing holistic development through balanced intellectual, artistic, and practical activities. The curriculum nurtures creativity, critical thinking, and social responsibility by integrating developmental stages and fostering imagination in learning. This approach cultivates independent, well-rounded individuals equipped for lifelong learning and personal growth.
Rudolf Steiner’s Vision: Core Principles of Waldorf
Rudolf Steiner's vision for Waldorf education emphasizes holistic development, integrating intellectual, artistic, and practical learning to nurture the head, heart, and hands. Core principles include fostering creativity, critical thinking, and social responsibility through age-appropriate curricula tailored to developmental stages. This philosophy values imagination and experiential learning, aiming to cultivate well-rounded individuals prepared for lifelong growth.
Holistic Child Development: The Waldorf Approach
Waldorf education emphasizes holistic child development by integrating intellectual, emotional, and physical growth through arts, storytelling, and hands-on activities. Rooted in Rudolf Steiner's anthroposophical philosophy, the curriculum fosters creativity, critical thinking, and social responsibility. This approach nurtures each child's unique potential, encouraging a balanced development that prepares students for lifelong learning and personal fulfillment.
Integrating Arts and Academics in Waldorf Classrooms
Waldorf education integrates arts and academics by embedding creative activities such as painting, music, and drama into standard subjects to foster holistic development and enhance cognitive skills. This approach supports multidimensional learning, allowing students to engage multiple intelligences and deepen understanding through experiential and imaginative work. Teachers design curricula that intertwine artistic expression with academic content, promoting emotional, social, and intellectual growth in every lesson.
Spirituality and Anthroposophy in Waldorf Education
Waldorf education integrates Anthroposophy, a spiritual philosophy founded by Rudolf Steiner, emphasizing the holistic development of the child's body, soul, and spirit. Spirituality in Waldorf pedagogy nurtures creativity, moral imagination, and self-awareness through artistic activities, storytelling, and festivals aligned with natural rhythms. This approach supports cognitive and emotional growth by fostering a deep connection to nature, community, and the metaphysical dimensions of human experience.
The Role of Imagination and Creativity in Learning
Waldorf education emphasizes the critical role of imagination and creativity in cognitive development, encouraging students to engage in artistic activities, storytelling, and hands-on projects to deepen understanding. This approach fosters holistic learning by integrating emotional, intellectual, and practical experiences, which enhances problem-solving skills and emotional intelligence. Studies in Waldorf schools demonstrate improved student motivation and creativity, highlighting the effectiveness of nurturing imaginative capacities for lifelong learning.
Stages of Child Growth in Waldorf Philosophy
Waldorf Education emphasizes three distinct stages of child growth: early childhood (birth to age 7), middle childhood (ages 7 to 14), and adolescence (ages 14 to 21), each tailored to developmental characteristics and learning capacities. Early childhood focuses on imitation and sensory experience, fostering creativity through play and artistic activities, while middle childhood prioritizes imagination, intellectual exploration, and social skills. Adolescence centers on critical thinking, self-awareness, and individual responsibility, integrating academic challenges with moral and ethical development in alignment with Rudolf Steiner's anthroposophical principles.
Teacher as Guide: Mentorship in Waldorf Pedagogy
Waldorf pedagogy emphasizes the role of the teacher as a guide who fosters holistic development through personalized mentorship, nurturing students' intellectual, artistic, and practical skills. This approach encourages educators to build deep relationships, understanding each child's unique learning path and fostering intrinsic motivation. By integrating mentorship, Waldorf teachers support critical thinking and creativity, aligning educational content with students' developmental stages and individual interests.
Community Building and Social Responsibility
Waldorf education fosters community building by encouraging collaborative projects, group discussions, and shared responsibilities among students, cultivating a strong sense of belonging and mutual respect. Its philosophy emphasizes social responsibility through experiential learning that connects students with local environmental and social issues, promoting active citizenship. This approach integrates arts, practical activities, and ethical reflection to nurture empathy, cooperation, and a commitment to community well-being.
Modern Applications of Waldorf Philosophical Principles
Waldorf philosophy emphasizes holistic education by integrating creative arts, practical skills, and intellectual development, fostering balanced growth in students. Modern applications include project-based learning and nurturing emotional intelligence, promoting critical thinking alongside empathy. Schools adopting Waldorf principles utilize individualized learning rhythms and interdisciplinary curricula to cultivate adaptive and innovative learners in today's dynamic educational landscape.
example of waldorf in philosophy Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com