Shadowing in language learning involves a student listening to native speakers and immediately repeating what they hear, which enhances pronunciation and intonation skills. This technique helps learners internalize natural speech patterns and improves their listening comprehension. For example, an English learner might listen to a podcast and repeat each sentence aloud, mimicking the speaker's rhythm and tone. Language shadowing is particularly effective in immersive education environments where real-time interaction is limited. It allows learners to practice speaking fluently without pressure, reinforcing memory through repetition. Tools such as language apps and audio recordings provide extensive data to track progress during shadowing exercises.
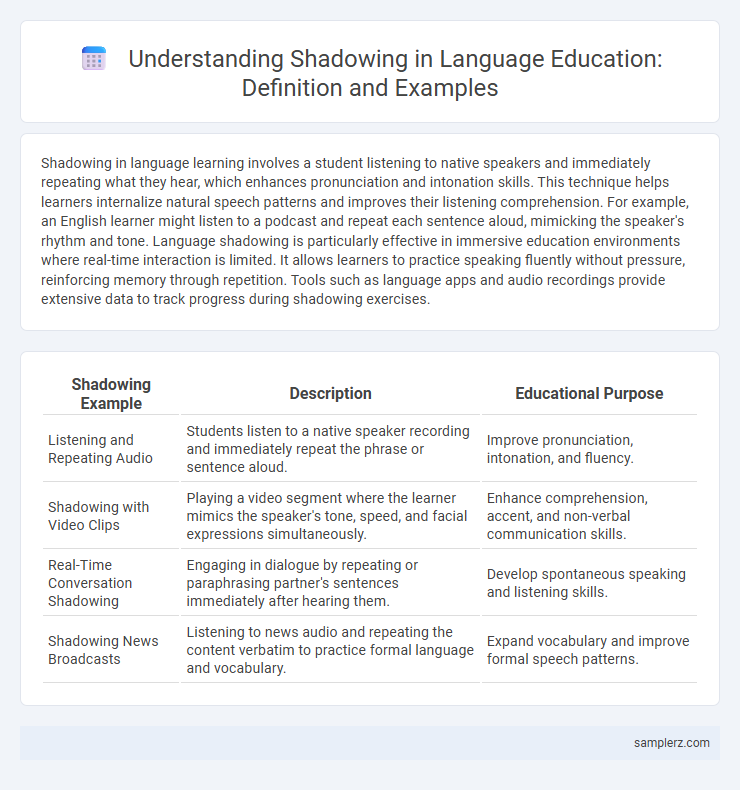
Table of Comparison
| Shadowing Example | Description | Educational Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Listening and Repeating Audio | Students listen to a native speaker recording and immediately repeat the phrase or sentence aloud. | Improve pronunciation, intonation, and fluency. |
| Shadowing with Video Clips | Playing a video segment where the learner mimics the speaker's tone, speed, and facial expressions simultaneously. | Enhance comprehension, accent, and non-verbal communication skills. |
| Real-Time Conversation Shadowing | Engaging in dialogue by repeating or paraphrasing partner's sentences immediately after hearing them. | Develop spontaneous speaking and listening skills. |
| Shadowing News Broadcasts | Listening to news audio and repeating the content verbatim to practice formal language and vocabulary. | Expand vocabulary and improve formal speech patterns. |
Introduction to Shadowing in Language Learning
Shadowing in language learning involves the learner listening to a native speaker's speech and simultaneously repeating it aloud, which enhances pronunciation, intonation, and fluency. This technique boosts auditory processing and helps internalize natural language rhythms by mimicking authentic conversations. Research indicates that shadowing improves overall speaking skills and accelerates vocabulary retention in both beginner and advanced learners.
Why Shadowing is Effective for Language Acquisition
Shadowing enhances language acquisition by promoting active listening and immediate vocal reproduction, which strengthens neural pathways involved in language processing. It forces learners to mimic pronunciation, intonation, and rhythm in real time, leading to improved speaking fluency and listening comprehension. Research shows that shadowing accelerates internalization of vocabulary and grammar structures, making language retention more effective than passive study methods.
Step-by-Step Guide to Shadowing Techniques
Shadowing in language learning involves imitating a native speaker's speech immediately after hearing it, enhancing pronunciation and listening skills. The step-by-step guide starts with selecting clear audio materials, followed by listening attentively, then repeating the phrases aloud while mimicking intonation and rhythm. Consistent practice using this technique accelerates language acquisition and improves fluency effectively.
Real-life Examples of Shadowing in Language Classrooms
Shadowing in language classrooms often involves students repeating phrases immediately after hearing their teacher or a recording, enhancing pronunciation and intonation. For instance, learners might mimic dialogues from authentic audio clips, enabling improved listening comprehension and speaking fluency. Shadowing real-life conversations recorded in various dialects helps students adapt to diverse linguistic environments effectively.
Shadowing Activities for Beginners
Shadowing activities for beginners in language learning involve listening to a native speaker's audio and immediately repeating the words aloud to improve pronunciation and fluency. Common examples include shadowing simple dialogues or short stories designed for beginner levels, which help learners build vocabulary and rhythm. Consistent practice with beginner-friendly materials enhances listening comprehension and speaking confidence effectively.
Shadowing with Audio and Video Resources
Shadowing with audio and video resources enhances language learning by allowing learners to mimic native speakers' pronunciation, intonation, and rhythm in real-time. Using podcasts, language learning apps, and films, students engage in active listening and speaking simultaneously, improving fluency and comprehension. This method accelerates speaking skills by creating immersive, repetitive practice tailored to diverse proficiency levels and learning styles.
Integrating Shadowing into Daily Study Routines
Integrating shadowing into daily study routines enhances language acquisition by mimicking native speakers' pronunciation and intonation in real-time. Students should dedicate 10-15 minutes daily to shadow authentic audio recordings, such as podcasts or dialogues, to reinforce listening comprehension and speaking fluency. Consistent practice with shadowing improves neural pathways for language processing, boosting retention and conversational confidence.
Success Stories: Learners Who Improved with Shadowing
Learners who practiced shadowing reported significant improvements in pronunciation, fluency, and listening skills within weeks, as demonstrated by a study in the Journal of Second Language Writing. One notable success story involved a Japanese student who increased verbal comprehension scores by 30% after consistent daily shadowing exercises. This method's effectiveness is supported by research from the University of California, highlighting shadowing as a powerful tool for accelerating language acquisition.
Common Challenges in Shadowing and How to Overcome Them
Common challenges in language shadowing include difficulty in maintaining consistent pace with native speakers, struggles with pronunciation accuracy, and cognitive overload from simultaneous listening and speaking. Overcoming these challenges involves breaking sessions into manageable intervals, using slower audio initially, and focusing on repetitive practice to enhance muscle memory. Employing shadowing apps with adjustable playback speeds and visual aids can further improve comprehension and fluency.
Measuring Progress and Benefits from Language Shadowing
Language shadowing enhances fluency by requiring learners to immediately repeat words or phrases spoken by a native speaker, which strengthens auditory processing and pronunciation skills. Progress is measured through improvements in speech accuracy, intonation, and speed, often tracked via recording comparisons over time. Benefits include accelerated speaking confidence, better listening comprehension, and reduced language learning plateau, making shadowing a highly effective method in second language acquisition.
example of shadowing in language Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com