Response to Intervention (RTI) is an educational strategy used to identify and support students with learning difficulties through targeted remediation. In a typical RTI model, students receiving Tier 1 instruction in the general classroom are monitored for academic progress, and those who struggle are provided with Tier 2 interventions involving small group instruction focused on specific skill deficits. Data collection on student performance guides the intensity and duration of interventions, ensuring tailored support for remedial needs. An example of RTI in remediation involves a third-grade student struggling with reading fluency. The teacher implements a Tier 2 intervention, providing small group sessions emphasizing phonics and decoding skills three times a week. Progress monitoring data after six weeks shows improvement in reading speed and accuracy, supporting continued remediation or escalation to more intensive Tier 3 support if necessary.
Table of Comparison
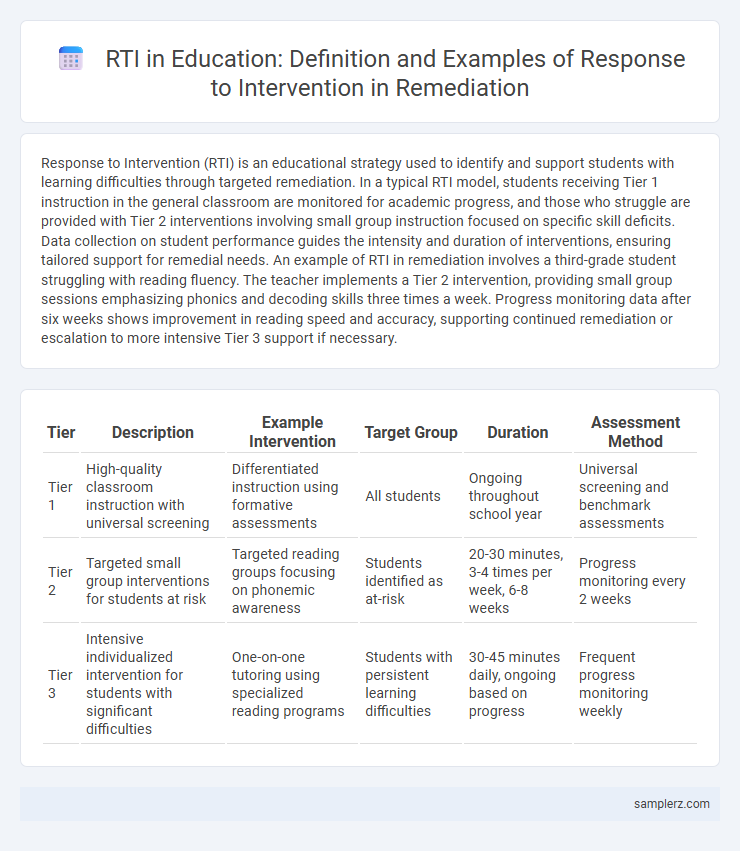
| Tier | Description | Example Intervention | Target Group | Duration | Assessment Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | High-quality classroom instruction with universal screening | Differentiated instruction using formative assessments | All students | Ongoing throughout school year | Universal screening and benchmark assessments |
| Tier 2 | Targeted small group interventions for students at risk | Targeted reading groups focusing on phonemic awareness | Students identified as at-risk | 20-30 minutes, 3-4 times per week, 6-8 weeks | Progress monitoring every 2 weeks |
| Tier 3 | Intensive individualized intervention for students with significant difficulties | One-on-one tutoring using specialized reading programs | Students with persistent learning difficulties | 30-45 minutes daily, ongoing based on progress | Frequent progress monitoring weekly |
Understanding RTI: A Framework for Effective Remediation
RTI (Response to Intervention) is an evidence-based framework designed to identify and support students struggling with academic challenges through tiered levels of intervention. In remediation, RTI involves targeted instruction in small groups, continuous progress monitoring, and data-driven adjustments to teaching strategies. This systematic approach ensures early identification and effective support, improving student outcomes in reading, math, and other key subjects.
Key Components of RTI in Educational Remediation
Response to Intervention (RTI) in educational remediation involves three key components: universal screening to identify students at risk, tiered instruction that intensifies support based on student needs, and continuous progress monitoring to adjust interventions effectively. For example, a third-grade student struggling with reading may receive targeted small-group instruction (Tier 2) after universal screening reveals below-grade-level performance, with bi-weekly assessments tracking improvements. This structured approach ensures timely identification and tailored support, enhancing literacy outcomes and preventing long-term academic difficulties.
Tiered Instruction: RTI in Practice
Tiered Instruction in RTI (Response to Intervention) involves providing targeted support based on students' specific learning needs, with Tier 1 focusing on high-quality classroom instruction, Tier 2 offering small group interventions, and Tier 3 delivering intensive one-on-one remediation. For example, a student struggling with reading fluency might receive Tier 1 whole-class lessons emphasizing phonics, progress to Tier 2 small group sessions for decoding strategies, and advance to Tier 3 personalized tutoring addressing underlying language deficits. Data-driven decision-making and frequent progress monitoring guide the adjustment of interventions across tiers to optimize student outcomes in literacy development.
Early Identification: How RTI Detects Learning Gaps
RTI (Response to Intervention) identifies learning gaps early by systematically screening all students through universal assessments, allowing educators to pinpoint those struggling before significant delays occur. Targeted interventions are then implemented based on data-driven progress monitoring to address specific skill deficits in reading, math, or language. This proactive model ensures timely remediation, minimizing long-term academic challenges through early detection and tailored support.
Data-Driven Decisions in RTI for Remediation
RTI remediation relies on data-driven decisions using frequent progress monitoring tools like curriculum-based measurements or benchmark assessments to identify students' academic gaps. Educators analyze quantitative data to tailor evidence-based interventions, adjusting instruction intensity based on student responsiveness. This systematic approach ensures targeted support, increasing the effectiveness of remediation efforts and promoting student achievement.
Examples of RTI Strategies for Reading Interventions
RTI strategies for reading interventions include targeted small group instruction focusing on phonemic awareness and decoding skills, which helps struggling readers build foundational literacy. Progress monitoring tools such as curriculum-based measurements (CBM) track student improvements and guide instruction adjustments. Incorporating multi-sensory techniques like Orton-Gillingham approaches enhances comprehension and retention for diverse learners.
RTI-Based Math Remediation: Real-World Classroom Examples
RTI-based math remediation in classrooms often begins with universal screenings to identify students struggling with foundational skills like addition and subtraction. Targeted small group interventions use data from progress monitoring to tailor instruction that addresses specific gaps, such as fraction understanding or problem-solving strategies. Real-world examples show improved student outcomes when teachers use RTI frameworks to provide differentiated instruction and frequent assessments to adjust teaching methods.
Role of Progress Monitoring in RTI Remediation
Progress monitoring in RTI remediation involves frequent assessments that track student performance and inform instructional adjustments. By systematically collecting data on academic skills, educators identify specific areas where students struggle and tailor interventions accordingly. This ongoing evaluation ensures timely support, enhances learning outcomes, and prevents long-term academic difficulties.
Collaborative Approaches: Teachers and RTI Remediation Teams
Teachers collaborate closely with RTI remediation teams to design targeted intervention plans addressing students' specific learning gaps. By analyzing assessment data collectively, educators develop differentiated instruction strategies that enhance skill acquisition and monitor progress continuously. This collaborative approach ensures timely support and maximizes student achievement through shared expertise and coordinated efforts.
Measuring Success: Evaluating Outcomes in RTI Remediation
Measuring success in RTI remediation involves frequent progress monitoring through curriculum-based assessments and data analysis to evaluate student improvements in targeted skills. Educators use benchmark comparisons and formative evaluation tools to adjust interventions, ensuring alignment with individual learning needs. Effective RTI models demonstrate statistically significant gains in reading fluency and math problem-solving accuracy, supported by clearly defined growth metrics.
example of RTI in remediation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com