Wangtta is a social phenomenon in Korea where an individual is marginalized or ostracized from a group, often due to differences in behavior, appearance, or social standing. This form of exclusion reflects the collectivist nature of Korean society, emphasizing harmony and conformity within peer groups, particularly in schools and workplaces. Data from various sociological studies indicate that wangtta can lead to significant emotional distress and social isolation for those affected. The term wangtta derives from colloquial Korean, translating roughly to "being left out" or "excluded," illustrating the stigma associated with nonconformity. Wangtta is often observed in educational settings, where students who do not fit the group norm face bullying or exclusion, impacting their mental health and academic performance. Research highlights that addressing wangtta involves community awareness and inclusive social practices to foster acceptance and reduce the negative consequences of social ostracism.
Table of Comparison
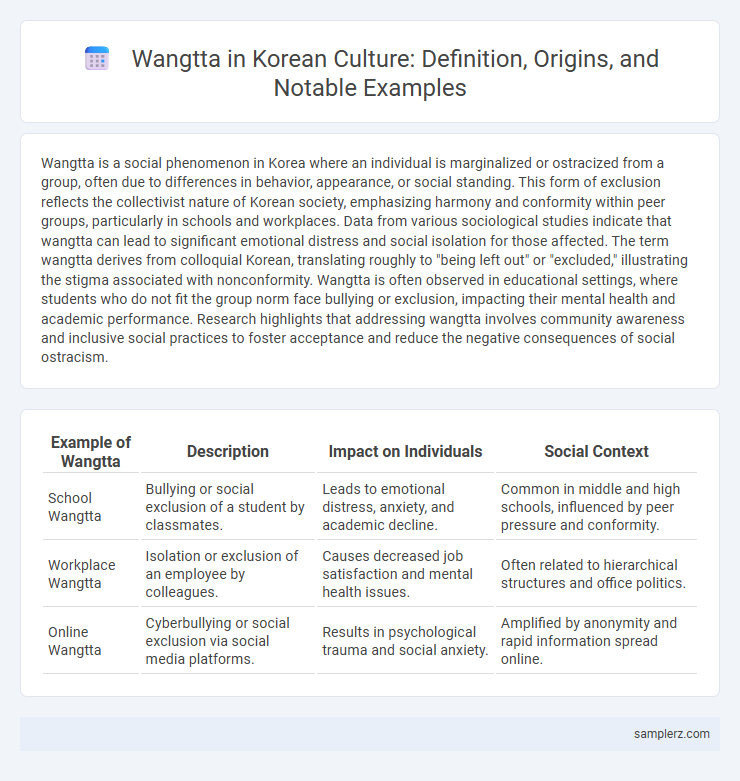
| Example of Wangtta | Description | Impact on Individuals | Social Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| School Wangtta | Bullying or social exclusion of a student by classmates. | Leads to emotional distress, anxiety, and academic decline. | Common in middle and high schools, influenced by peer pressure and conformity. |
| Workplace Wangtta | Isolation or exclusion of an employee by colleagues. | Causes decreased job satisfaction and mental health issues. | Often related to hierarchical structures and office politics. |
| Online Wangtta | Cyberbullying or social exclusion via social media platforms. | Results in psychological trauma and social anxiety. | Amplified by anonymity and rapid information spread online. |
Understanding Wangtta: The Culture of Exclusion in Korea
Wangtta in Korea refers to the social phenomenon where individuals or groups are deliberately excluded or ostracized within their community, often due to differences in appearance, behavior, or opinions. This culture of exclusion significantly impacts mental health, leading to feelings of isolation and social anxiety among those targeted. Understanding Wangtta involves recognizing its deep roots in Korean social dynamics and promoting empathy and inclusivity to counteract its negative effects.
Historical Roots of Wangtta in Korean Society
Wangtta originated in 1990s South Korea as a social phenomenon where individuals, often students or office workers, experienced exclusion from peer groups, reflecting deep-rooted societal pressures for conformity and success. Historically, wangtta highlights the collectivist culture's emphasis on group harmony, where deviating from social norms leads to ostracization. This practice underscores the rigid boundaries of social acceptance and the psychological impact of social rejection in Korean society.
Famous Cases of Wangtta Among Korean Celebrities
Wangtta, a form of social ostracism commonly experienced in Korea, has notably affected celebrities such as actress Jang Nara and singer IU, whose public struggles highlight the intense pressure of exclusion in the entertainment industry. These cases underscore the impact of wangtta on mental health, often prompting public discussions about bullying and the need for supportive social environments. Prominent incidents involving wangtta have increased awareness and fostered campaigns aimed at reducing social alienation within Korean pop culture.
Wangtta in Korean Schools: Real-life Student Experiences
Wangtta in Korean schools refers to the social phenomenon where students experience exclusion or bullying due to being labeled as outsiders, often based on appearance, behavior, or social status. Real-life student experiences reveal feelings of isolation, psychological distress, and challenges in forming peer relationships, highlighting the impact of wangtta on mental health and academic performance. Efforts in Korean education emphasize anti-bullying programs and peer support to mitigate the negative effects of wangtta on vulnerable students.
Social Media and the Spread of Wangtta in Korea
Wangtta, a form of social exclusion in South Korea targeting individuals who are ostracized for being different or unpopular, rapidly spread through social media platforms like KakaoTalk and Facebook. Viral posts and online communities often amplify instances of wangtta, making it easier for the behavior to propagate among youth and adults alike. The pervasive influence of social media has intensified the impact of wangtta, contributing to widespread societal awareness and concern over its psychological effects.
Wangtta in K-Dramas and Pop Culture: Reflecting Reality
Wangtta, a term describing social outcasts in Korea, is frequently portrayed in K-Dramas as marginalized characters facing bullying and exclusion, providing a critical lens on societal pressures and youth struggles. These depictions highlight themes of loneliness, resilience, and the desire for acceptance, resonating deeply with audiences and sparking conversations about mental health and social alienation in Korean pop culture. The recurring narrative of wangtta serves as a reflection of real-life social hierarchies and the hidden challenges within Korea's highly competitive environment.
Psychological Impact of Wangtta on Victims
Wangtta, a form of social ostracism in Korea, inflicts deep psychological wounds on victims, often leading to decreased self-esteem, anxiety, and depression. The isolation embedded in wangtta disrupts social support networks, amplifying feelings of loneliness and helplessness. Victims frequently experience long-term emotional distress that can impair their overall mental health and social functioning.
Efforts to Combat Wangtta: Korean Campaigns and Laws
Efforts to combat wangtta in Korea include the implementation of strict anti-bullying laws and nationwide campaigns promoting respect and inclusion among youth. The Ministry of Education has introduced programs in schools to raise awareness and provide support for victims, while online platforms are monitored to prevent digital wangtta. Collaboration between government bodies and civil organizations continues to strengthen these initiatives, aiming to reduce social exclusion and cyberbullying effectively.
Wangtta in the Workplace: Stories from Korean Offices
Wangtta, a form of social exclusion often observed in Korean workplaces, manifests as subtle ostracism where targeted employees are ignored or excluded from group activities, affecting team cohesion and individual morale. Stories from Korean offices reveal how wangtta leads to decreased productivity and heightened stress, highlighting the cultural challenges in maintaining harmony amid hierarchical pressures. Addressing wangtta requires awareness of its impact on mental health and promoting inclusive communication within professional environments.
Cross-Cultural Comparison: Wangtta and Bullying Abroad
Wangtta in Korea refers to social exclusion and ostracism within peer groups, often resulting in emotional distress and isolation. This phenomenon contrasts with bullying abroad, where physical aggression and overt harassment are more commonly reported, highlighting cultural differences in how social harm is manifested. Understanding wangtta provides insight into the unique societal pressures in Korean youth culture compared to bullying behaviors observed in Western countries.
example of **wangtta** in **Korea** Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com