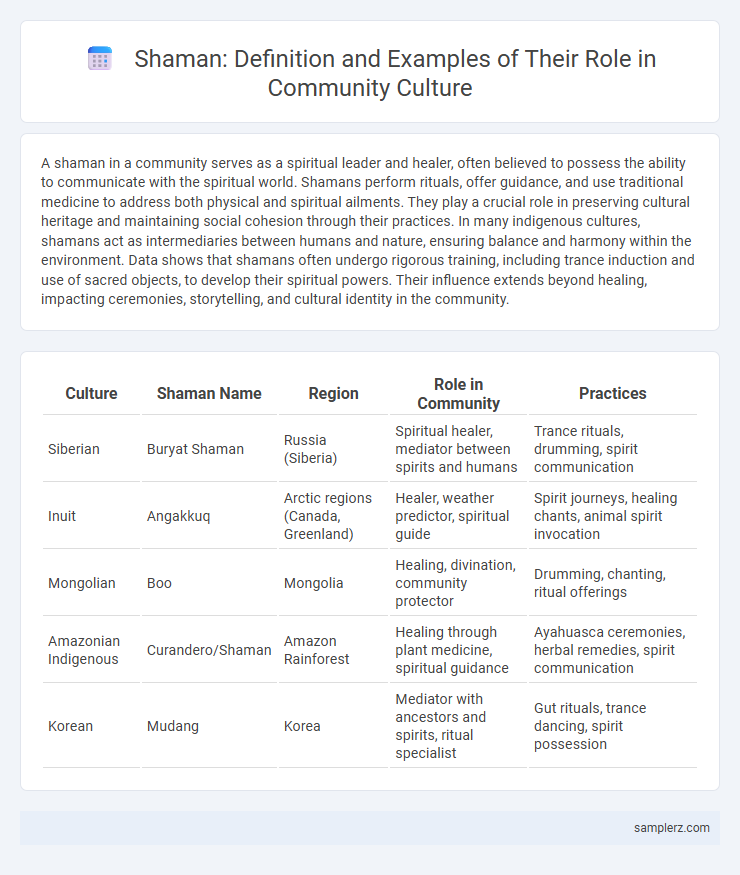
A shaman in a community serves as a spiritual leader and healer, often believed to possess the ability to communicate with the spiritual world. Shamans perform rituals, offer guidance, and use traditional medicine to address both physical and spiritual ailments. They play a crucial role in preserving cultural heritage and maintaining social cohesion through their practices. In many indigenous cultures, shamans act as intermediaries between humans and nature, ensuring balance and harmony within the environment. Data shows that shamans often undergo rigorous training, including trance induction and use of sacred objects, to develop their spiritual powers. Their influence extends beyond healing, impacting ceremonies, storytelling, and cultural identity in the community.
Table of Comparison
| Culture | Shaman Name | Region | Role in Community | Practices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siberian | Buryat Shaman | Russia (Siberia) | Spiritual healer, mediator between spirits and humans | Trance rituals, drumming, spirit communication |
| Inuit | Angakkuq | Arctic regions (Canada, Greenland) | Healer, weather predictor, spiritual guide | Spirit journeys, healing chants, animal spirit invocation |
| Mongolian | Boo | Mongolia | Healing, divination, community protector | Drumming, chanting, ritual offerings |
| Amazonian Indigenous | Curandero/Shaman | Amazon Rainforest | Healing through plant medicine, spiritual guidance | Ayahuasca ceremonies, herbal remedies, spirit communication |
| Korean | Mudang | Korea | Mediator with ancestors and spirits, ritual specialist | Gut rituals, trance dancing, spirit possession |
Historical Roots of Shamanism in Communities
Shamanism traces its historical roots to ancient communities in Siberia and Central Asia, where shamans served as spiritual mediators between humans and the spirit world. These early shamans conducted rituals to heal illnesses, communicate with ancestors, and ensure communal harmony. Archaeological findings and oral traditions from indigenous groups highlight the integral role of shamans in sustaining cultural identity and social cohesion.
Roles and Responsibilities of Shamans
Shamans serve as spiritual leaders and healers within their communities, mediating between the physical world and the spirit realm to restore balance and health. Their responsibilities include conducting rituals, providing guidance through divination, and facilitating communication with ancestral spirits or deities. Shamans also act as custodians of cultural knowledge, preserving oral traditions and fostering communal harmony through their spiritual expertise.
Traditional Rituals Led by Shamans
Shamans play a crucial role in traditional rituals by acting as intermediaries between the spiritual and physical worlds, facilitating healing ceremonies and guiding community members through rites of passage. In indigenous cultures across Siberia, the Amazon, and Native American tribes, shamans employ drumming, chanting, and symbolic costumes to invoke spirits and restore balance. These rituals strengthen communal bonds, preserve ancestral knowledge, and maintain cultural identity through generations.
Modern-Day Shamanic Practices
Modern-day shamanic practices often integrate ancient spiritual rituals with contemporary healing methods, emphasizing holistic wellness and community connection. Shamans serve as intermediaries between the physical and spiritual realms, utilizing techniques like drumming, journeying, and energy healing to address mental, emotional, and physical imbalances. These practices have gained popularity in urban communities worldwide, blending indigenous wisdom with modern therapeutic approaches to foster personal transformation and cultural continuity.
Influence of Shamans on Community Health
Shamans play a critical role in community health by bridging the physical and spiritual worlds to diagnose and treat illnesses through ritualistic practices and herbal medicine. Their influence extends beyond physical healing, fostering social cohesion and emotional well-being within the community. Studies show that shamanic healing practices can reduce stress and promote mental health, highlighting their integral role in maintaining holistic community wellness.
Shamans as Cultural Mediators
Shamans act as vital cultural mediators by bridging spiritual traditions and community life, interpreting ancestral wisdom to address contemporary issues. Their role encompasses healing rituals, communication with spirits, and preservation of indigenous knowledge, fostering social cohesion and cultural continuity. These practices reinforce collective identity and facilitate intergenerational transmission of cultural values and beliefs.
Shamanic Symbolism in Local Art and Beliefs
Shamanic symbolism deeply influences local art and beliefs, often depicted through intricate totems, animal motifs, and ritualistic patterns that represent spiritual guides and ancestral connections. These symbols serve as a visual language within the community, embodying the shaman's role in bridging the physical and spiritual worlds. The presence of these motifs in pottery, textiles, and carvings reinforces communal identity and preserves ancient cosmological narratives.
Community Selection and Training of Shamans
In many indigenous cultures, the community plays a crucial role in selecting shamans based on spiritual signs, family lineage, or extraordinary abilities observed from a young age. Training often involves mentorship by experienced shamans, incorporating rituals, herbal medicine knowledge, and trance induction techniques to prepare the candidate for healing and spiritual guidance roles. This community-driven process ensures that shamans maintain cultural traditions and adapt their practices to the specific needs of their people.
Shamans in Festivals and Ceremonies
Shamans play a pivotal role in festivals and ceremonies by acting as spiritual mediators who connect the community with ancestral spirits and natural forces. Their rituals often involve trance states, drumming, and chanting to invoke healing, protection, and guidance, fostering a collective sense of identity and cultural continuity. These ceremonial practices are crucial in preserving indigenous knowledge and reinforcing social cohesion within communities.
Case Studies: Notable Shamans in Different Cultures
Notable shamans such as the Siberian Evenki's Dersu Uzala exemplify the profound connection between spiritual practices and environmental stewardship within their communities. The Mongolian shaman Byambajav employs ritual ceremonies to mediate between natural spirits and villagers, ensuring harmony and health. In Native American cultures, figures like the Navajo Medicine Man integrate healing songs and herbal knowledge, sustaining both physical and spiritual well-being.
example of shaman in community Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com