The calpulli was a fundamental social unit in the Aztec culture, functioning as a neighborhood or clan group within the larger society. Each calpulli consisted of families who shared land, resources, and responsibilities, with a leader known as the calpullec overseeing administrative and religious duties. This structure enabled efficient organization of labor, land distribution, and communal activities essential to Aztec urban life. Calpullis played a critical role in maintaining social cohesion and economic stability by regulating access to land and ensuring the collective management of agricultural production. Membership in a calpulli determined social identity, political rights, and obligations within the Aztec empire. This entity exemplifies the intricate connection between social structure and resource management in pre-Columbian Mesoamerica.
Table of Comparison
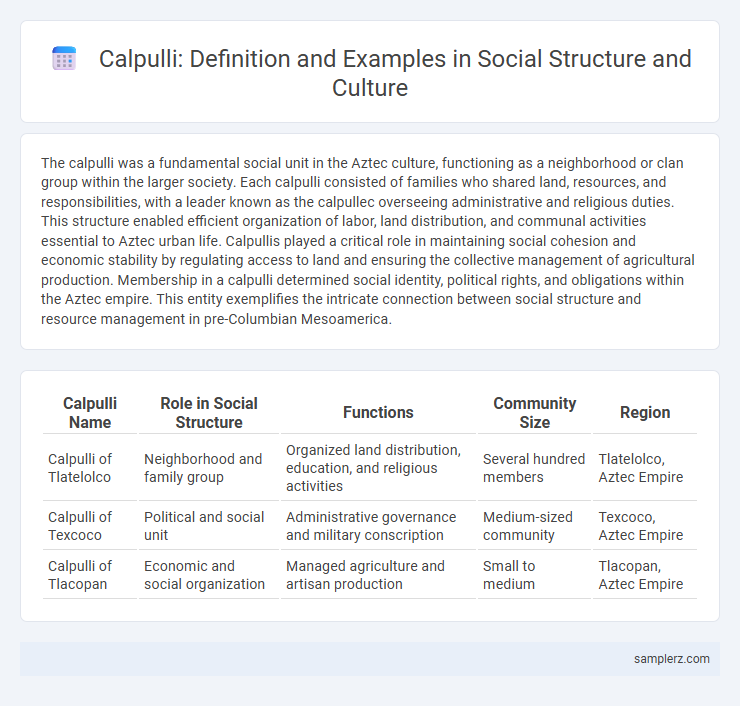
| Calpulli Name | Role in Social Structure | Functions | Community Size | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calpulli of Tlatelolco | Neighborhood and family group | Organized land distribution, education, and religious activities | Several hundred members | Tlatelolco, Aztec Empire |
| Calpulli of Texcoco | Political and social unit | Administrative governance and military conscription | Medium-sized community | Texcoco, Aztec Empire |
| Calpulli of Tlacopan | Economic and social organization | Managed agriculture and artisan production | Small to medium | Tlacopan, Aztec Empire |
Origins of Calpulli in Mesoamerican Societies
Calpulli originated as foundational social units in Mesoamerican societies, particularly among the Aztecs, serving as kin-based clans responsible for land distribution, education, and religious activities. Each calpulli maintained communal lands and organized labor, ensuring the welfare and stability of its members within the larger political system. This structure played a crucial role in maintaining social cohesion and facilitating governance in ancient Mesoamerican cultures.
Calpulli as Foundational Social Units
Calpulli served as foundational social units in Aztec society, organizing families into communal groups responsible for agriculture, religious activities, and local governance. Each calpulli controlled specific land parcels collectively farmed by its members, fostering cooperation and resource sharing that underpinned community stability. This structure facilitated social cohesion and political organization, reinforcing the broader Aztec social hierarchy.
Structure and Organization of Calpulli
Calpulli functioned as fundamental social units in Aztec society, organized as kinship-based clans or neighborhoods that managed communal land and resources collectively. Each calpulli was headed by a chief, or calpullec, who coordinated agricultural activities, tribute collection, and religious responsibilities, ensuring social cohesion and economic stability. This decentralized structure allowed flexibility within the larger Aztec empire, facilitating localized governance and cultural identity.
Roles and Functions within the Calpulli
Calpulli functioned as fundamental social units in Aztec society, organizing members into extended kinship groups responsible for land distribution, religious activities, and mutual aid. Each calpulli managed communal lands and coordinated labor obligations to local temples, ensuring agricultural productivity and social cohesion. Leadership roles within the calpulli included the calpullec, who administered resources and represented the group in political matters, highlighting the calpulli's integral role in maintaining social order.
Calpulli and Social Hierarchy in Aztec Culture
Calpulli functioned as fundamental social units within the Aztec social hierarchy, grouping families linked by kinship or shared land tenure, with each calpulli managing communal lands and local governance. These groups played a critical role in organizing labor, education, and military service, reinforcing the stratified structure of Aztec society by ensuring loyalty and resource distribution among commoners. The calpulli system enabled a cohesive community framework that supported the centralized authority of the tlatoani (ruler) while maintaining local autonomy and social order.
Calpulli’s Influence on Community Identity
Calpulli served as foundational kinship groups in Aztec society, shaping community identity through shared land, communal labor, and religious duties. Each calpulli fostered a strong sense of belonging and social cohesion by organizing local education, resource distribution, and defense mechanisms. Their role in preserving cultural practices and collective responsibilities reinforced distinct neighborhood identities within the broader Aztec empire.
Calpulli in Resource Distribution and Land Ownership
Calpulli served as fundamental units in the Aztec social structure, managing communal land ownership and resource distribution among members. Each calpulli controlled specific agricultural lands, enabling equitable allocation of crops, labor, and housing to families within the group. This system ensured social cohesion and sustainable resource management in Aztec society.
Religious and Educational Roles of Calpulli
Calpulli, fundamental units of Aztec society, served critical religious roles by organizing communal worship and maintaining local temples dedicated to specific deities. They functioned as centers of education, where elders and priests taught youth religious rites, social responsibilities, and cultural traditions essential for community cohesion. This dual role of calpulli ensured the preservation and transmission of spiritual beliefs and knowledge across generations.
Political Representation through Calpulli Leaders
Calpulli functioned as fundamental social units in Aztec society, each governed by a calpullec, who acted as a political representative and leader for their community. These leaders mediated between the calpulli members and higher government authorities, ensuring local interests in tribute, land, and military obligations were addressed. The calpullec's role was crucial for maintaining social cohesion and political organization within the larger Aztec empire.
Legacy of Calpulli in Contemporary Mexican Communities
The calpulli system, an ancient Aztec social structure organizing families into communal units, continues to influence contemporary Mexican communities by fostering strong neighborhood ties and collective land management. Modern indigenous groups often maintain calpulli-inspired practices that emphasize communal responsibility, shared resources, and cultural preservation. This enduring legacy supports social cohesion and indigenous identity throughout Mexico's diverse regions.
example of calpulli in social structure Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com