In communication, register refers to the variation in language style depending on the context, audience, and purpose. For example, formal register is used in professional settings such as business meetings or academic papers, where precise vocabulary and complex sentence structures are common. Informal register appears in casual conversations among friends, often featuring colloquial expressions and simpler syntax. Register impacts how messages are received and interpreted by the audience, influencing clarity and effectiveness. A technical register is frequently employed in scientific or medical communication, characterized by specialized terminology and jargon relevant to the field. Understanding and selecting the appropriate register enhances the accuracy and appropriateness of communication across different scenarios.
Table of Comparison
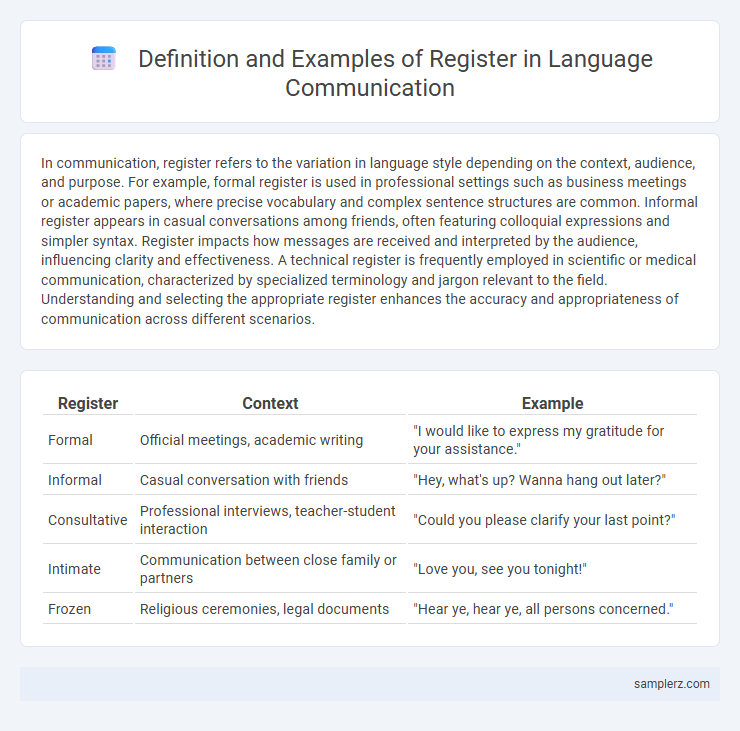
| Register | Context | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Formal | Official meetings, academic writing | "I would like to express my gratitude for your assistance." |
| Informal | Casual conversation with friends | "Hey, what's up? Wanna hang out later?" |
| Consultative | Professional interviews, teacher-student interaction | "Could you please clarify your last point?" |
| Intimate | Communication between close family or partners | "Love you, see you tonight!" |
| Frozen | Religious ceremonies, legal documents | "Hear ye, hear ye, all persons concerned." |
Understanding Language Register: Definition and Importance
Language register reflects variations in tone, vocabulary, and syntax based on context, such as formal, informal, or technical speech. Understanding language register is crucial for effective communication, as it ensures messages are appropriately tailored to audiences like professionals, casual friends, or specialized groups. Mastery of language register enhances clarity, respect, and engagement across diverse communicative settings.
Types of Language Register in Communication
Types of language register in communication include formal, informal, consultative, casual, and intimate registers, each serving different social contexts and levels of politeness. Formal register employs structured grammar and precise vocabulary typical in legal documents, academic writing, and official speeches. Informal and casual registers feature relaxed syntax and slang, suitable for conversations among friends, while consultative register is used in professional or educational settings for polite, cooperative exchanges.
Formal Register: Features and Examples
Formal register in communication utilizes precise vocabulary, complex sentence structures, and a polite tone to convey professionalism and respect. Examples include academic papers, business reports, and official speeches, which avoid slang, contractions, and colloquialisms to maintain clarity and authority. This register is essential in environments where clarity, credibility, and adherence to social norms are paramount.
Informal Register: Usage and Instances
Informal register in communication commonly appears in casual conversations, text messages, and social media interactions, characterized by colloquial language, slang, and contractions. Examples include phrases like "Gonna grab lunch," "What's up?" or "That party was lit," which create a relaxed and friendly tone. This register enhances relatability and immediacy, often used among friends, family, and peers to foster close connections.
Consultative Register: Characteristics in Conversation
Consultative register in conversation features a semi-formal tone used between individuals who are familiar but not intimate, such as teacher-student or doctor-patient interactions. It employs clear and structured language with polite requests, explanations, and clarifications to ensure mutual understanding. Turn-taking is orderly, and the vocabulary is more precise than casual speech, avoiding slang or colloquial expressions.
Casual Register: Everyday Communication Examples
Casual register is commonly used in everyday communication among friends and family, characterized by informal vocabulary, contractions, and colloquial expressions. Examples include greetings like "Hey, what's up?" or phrases such as "Gonna grab some coffee, wanna come?" This register prioritizes simplicity and familiarity to maintain comfort and ease in social interactions.
Intimate Register: Private Language Use
Intimate register in communication involves private language use characterized by unique vocabulary, abbreviations, or gestures understood exclusively by close individuals such as partners, family members, or close friends. This register fosters emotional closeness and shared understanding through personalized expressions that often lack meaning outside the intimate circle. Examples include pet names, inside jokes, and shorthand phrases that strengthen relational bonds and convey affection.
Shifting Registers: When and Why It Happens
Shifting registers in communication occurs when speakers adjust their language style to suit different social contexts or audiences, such as switching from formal to informal speech during a job interview versus a casual conversation with friends. This adaptation helps convey respect, build rapport, or achieve clarity, reflecting the speaker's awareness of social norms and expectations. Register shifts often happen to accommodate power dynamics, cultural settings, or the level of technicality required in the exchange.
The Role of Context in Choosing Registers
The role of context in choosing registers is crucial for effective communication, as it determines the level of formality and vocabulary tailored to the audience and situation. For example, a medical professional uses specialized jargon and a formal tone when discussing patient care within a hospital setting, while adopting simpler, more empathetic language when explaining conditions to patients. Understanding the social context, such as workplace, family, or casual settings, guides speakers in selecting the appropriate register that ensures clarity and engagement.
The Impact of Register on Message Clarity
Formal register enhances message clarity by using precise vocabulary and structured syntax, which minimizes ambiguity in professional communication. Informal register relies on colloquial expressions and relaxed grammar, often suited for casual conversations but can reduce clarity in complex or technical topics. Selecting an appropriate register ensures the intended audience accurately interprets the message, improving overall communication effectiveness.
example of register in language Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com