In academic writing, the register is characterized by formal language, precise vocabulary, and structured sentence construction. This style avoids slang, contractions, and casual expressions to maintain clarity and professionalism. It often incorporates domain-specific terminology to convey complex ideas effectively within scholarly communications. Academic registers rely heavily on passive voice to emphasize objectivity and reduce focus on the writer. The tone remains impersonal and neutral, ensuring the argument's strength comes from evidence rather than personal opinion. Consistent use of citations and references supports claims and upholds academic integrity throughout the text.
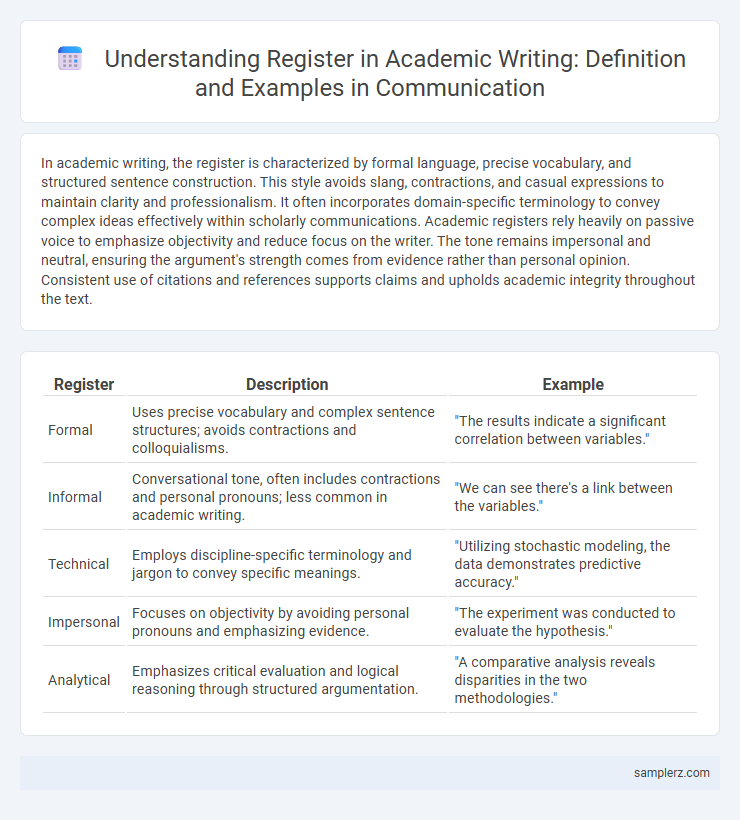
Table of Comparison
| Register | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Formal | Uses precise vocabulary and complex sentence structures; avoids contractions and colloquialisms. | "The results indicate a significant correlation between variables." |
| Informal | Conversational tone, often includes contractions and personal pronouns; less common in academic writing. | "We can see there's a link between the variables." |
| Technical | Employs discipline-specific terminology and jargon to convey specific meanings. | "Utilizing stochastic modeling, the data demonstrates predictive accuracy." |
| Impersonal | Focuses on objectivity by avoiding personal pronouns and emphasizing evidence. | "The experiment was conducted to evaluate the hypothesis." |
| Analytical | Emphasizes critical evaluation and logical reasoning through structured argumentation. | "A comparative analysis reveals disparities in the two methodologies." |
Understanding Register in Academic Writing
Understanding register in academic writing involves recognizing the use of formal language, specialized vocabulary, and objective tone to convey complex ideas clearly and precisely. For instance, scholarly articles employ discipline-specific terminology and avoid colloquialisms to maintain professionalism and credibility. Mastery of this register enhances comprehension and supports effective communication within academic communities.
Key Features of Academic Register
Academic register is characterized by formal tone, precise vocabulary, and complex sentence structures that convey clarity and objectivity. It emphasizes specialized terminology, consistent use of passive voice, and avoidance of contractions or colloquialisms to maintain professionalism. Clear thesis statements, evidence-based arguments, and logical organization are essential components to uphold academic integrity and rigor.
Formal vs. Informal Register: Academic Examples
In academic writing, formal register is characterized by precise vocabulary, complex sentence structures, and objective tone, such as "The study demonstrates a significant correlation between variables." Informal register, often found in personal reflections or emails, uses conversational language and contractions, for example, "I think the results show a strong link." Mastery of formal register enhances clarity and credibility in scholarly communication.
Lexical Choices in Academic Register
Academic writing employs formal lexical choices characterized by precise terminology, discipline-specific vocabulary, and technical words to convey complex ideas clearly. Lexical choices often exclude contractions, colloquialisms, and vague language, favoring instead words with specific denotations and academic precision. Examples include using "utilize" instead of "use," "demonstrate" rather than "show," and terms such as "methodology," "analysis," or "hypothesis" that reflect scholarly discourse.
Grammatical Structures in Academic Writing
In academic writing, the use of formal grammatical structures such as passive voice and complex sentence constructions is prevalent to maintain objectivity and clarity. Precise verb tenses like the present simple for general truths and the past tense for describing specific experiments enhance the coherence of scholarly arguments. Nominalization frequently appears to condense information and emphasize key concepts, contributing to a more professional register.
Tone and Objectivity in Academic Register
Academic writing employs a formal tone characterized by precise vocabulary and complex sentence structures that convey authority and clarity. Objectivity is essential, with writers avoiding personal bias by relying on evidence, logical reasoning, and impartial language. This register emphasizes third-person perspective and passive constructions to maintain neutrality and credibility in scholarly communication.
Use of Passive Voice in Academic Writing
In academic writing, the use of passive voice is prevalent to emphasize processes and results rather than the researcher. Passive constructions such as "The experiment was conducted" allow writers to maintain objectivity and formality by focusing on the action rather than the actor. This register choice enhances clarity and aligns with disciplinary conventions in scientific and scholarly texts.
Discipline-Specific Registers in Academia
Discipline-specific registers in academic writing employ specialized vocabulary and structures tailored to fields such as psychology, engineering, or literature, enhancing clarity and precision for expert audiences. For instance, scientific articles use technical terminology and passive voice to present empirical data objectively, while humanities papers often incorporate critical theory jargon and complex sentence constructions to analyze texts. Mastery of these registers is essential for effective disciplinary communication and scholarly publishing.
Common Mistakes in Academic Register
Academic writing often suffers from informal language use, such as contractions and slang, which undermine its credibility. Overuse of passive voice and vague expressions lead to ambiguity and weaken arguments. Precise vocabulary and formal tone are essential to maintain clarity and professionalism in academic register.
Practical Examples of Academic Register
Academic writing often employs a formal register characterized by precise vocabulary, complex sentence structures, and objective tone to convey research findings. Examples include the use of passive voice ("The experiment was conducted") and discipline-specific terminology ("photosynthesis," "quantitative analysis") to maintain clarity and professionalism. This register excludes contractions and colloquial expressions, ensuring content remains unbiased and credible within scholarly discourse.
example of register in academic writing Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com