Paraverbal communication in instruction refers to the use of vocal elements such as tone, pitch, volume, and speed to convey meaning beyond the actual words spoken. For example, a teacher might raise their voice to emphasize the importance of a safety rule or slow down their speech when explaining a complex concept. These vocal cues help students understand the urgency or significance of the instruction, enhancing comprehension and retention. Another example of paraverbal communication is the use of pauses and inflection during storytelling or lectures. By strategically pausing, an instructor can create suspense or highlight critical points, making the lesson more engaging. Variation in pitch and tone also helps maintain student attention and can indicate when a question or response is expected, fostering interactive learning environments.
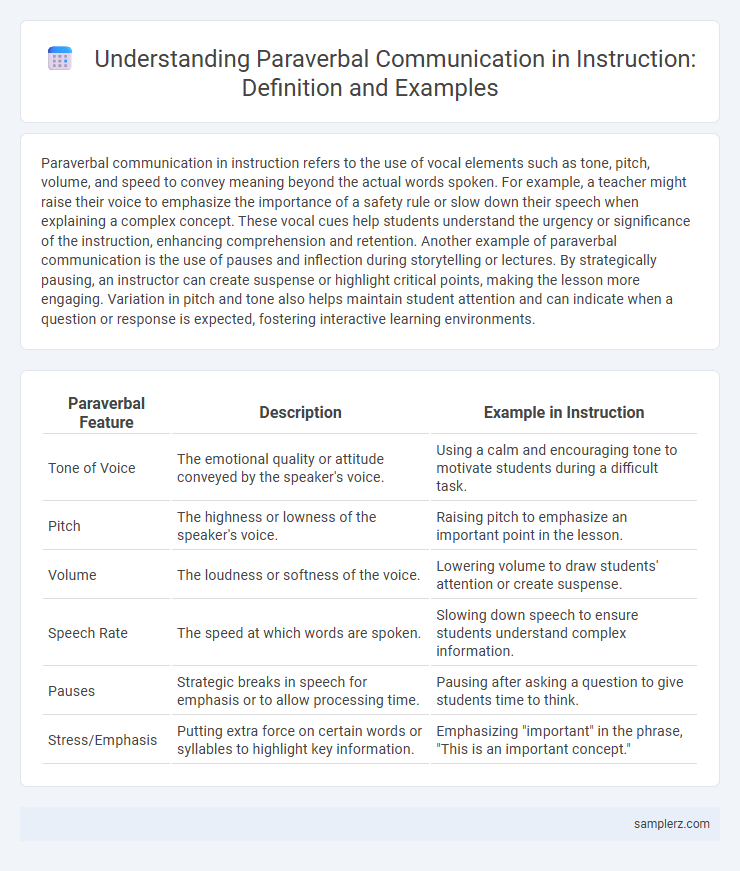
Table of Comparison
| Paraverbal Feature | Description | Example in Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Tone of Voice | The emotional quality or attitude conveyed by the speaker's voice. | Using a calm and encouraging tone to motivate students during a difficult task. |
| Pitch | The highness or lowness of the speaker's voice. | Raising pitch to emphasize an important point in the lesson. |
| Volume | The loudness or softness of the voice. | Lowering volume to draw students' attention or create suspense. |
| Speech Rate | The speed at which words are spoken. | Slowing down speech to ensure students understand complex information. |
| Pauses | Strategic breaks in speech for emphasis or to allow processing time. | Pausing after asking a question to give students time to think. |
| Stress/Emphasis | Putting extra force on certain words or syllables to highlight key information. | Emphasizing "important" in the phrase, "This is an important concept." |
Understanding Paraverbal Communication in Instruction
Paraverbal communication in instruction involves tone, pitch, and pace to convey clarity and emphasis, enhancing student comprehension. For example, a teacher's deliberate pause before important points signals significance, while varied intonation maintains engagement and aids retention. Effective paraverbal cues complement verbal content, supporting differentiated learning styles and reinforcing key messages.
The Role of Tone in Delivering Instructions
Tone plays a crucial role in delivering instructions by conveying clarity, urgency, or calmness through variations in pitch, volume, and speed. A firm but friendly tone can enhance understanding and motivate compliance, while a harsh tone may cause resistance or confusion. Effective paraverbal cues ensure instructions are not only heard but interpreted correctly, improving overall communication efficiency.
Pitch Variations and Their Impact on Learning
Pitch variations in paraverbal communication significantly enhance instructional effectiveness by emphasizing key concepts and maintaining learner engagement. Modulating voice pitch captures attention, aids in distinguishing important information, and supports memory retention during lessons. Educators who skillfully use pitch variation foster a dynamic learning environment that promotes better understanding and active participation.
The Importance of Pace in Teaching
Pace in teaching directly influences student comprehension and engagement, with paraverbal cues such as tone, rhythm, and volume shaping how instructions are received. A well-modulated pace helps emphasize key concepts and allows learners time to process information effectively. Educators who adjust their speaking speed to match the class's understanding foster a more interactive and inclusive learning environment.
Emphasis and Stress for Clearer Understanding
Paraverbal communication in instruction utilizes emphasis and stress to highlight key points, ensuring clearer understanding and retention. By modulating pitch, volume, and rhythm on important words or phrases, instructors guide listeners' attention and convey the significance of concepts. Strategic stress on critical terms reduces ambiguity and enhances the overall effectiveness of verbal messages.
Volume Control in Instructional Communication
Volume control in instructional communication significantly impacts the clarity and effectiveness of message delivery. Modulating volume ensures key points are emphasized and aids in maintaining student engagement. Optimal volume variation prevents monotony and supports auditory processing, enhancing overall comprehension.
Strategic Pausing to Enhance Comprehension
Strategic pausing in instruction involves deliberate breaks in speech to emphasize key points and allow learners to process information effectively. This paraverbal technique enhances comprehension by giving listeners time to reflect on complex material, reinforcing understanding and retention. In educational settings, teachers who utilize well-timed pauses help maintain student engagement and facilitate deeper cognitive connections with the content.
Modulating Intonation for Effective Guidance
Modulating intonation in instructional communication enhances clarity by emphasizing key points and signaling transitions between steps, making guidance more comprehensible. Variations in pitch and tone help maintain listener engagement and convey urgency or importance without changing the verbal content. Effective use of paraverbal cues supports better retention and fosters a more interactive learning environment.
Paraverbal Cues and Student Engagement
Paraverbal cues such as tone, pitch, and speech rate significantly impact student engagement during instruction, signaling enthusiasm or emphasis that captures attention. Modulating voice intensity and pauses helps clarify key points, fostering better comprehension and active participation. Effective use of paraverbal communication creates a dynamic learning environment that enhances motivation and retention.
Optimizing Paraverbal Skills for Classroom Success
Optimizing paraverbal skills in the classroom involves intentional modulation of tone, pitch, and pace to enhance student comprehension and engagement. Clear and varied vocal inflections emphasize key instructional points, making lessons more memorable and dynamic. Consistently applying effective paraverbal cues supports positive teacher-student rapport and fosters an inclusive learning environment.
example of paraverbal in instruction Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com