Code-switching in communication refers to the practice of alternating between two or more languages or dialects within a conversation. For example, a bilingual speaker might say, "I need to buy some groceries, ?quieres venir conmigo?" Here, the speaker switches from English to Spanish, demonstrating a fluid integration of both languages depending on context and audience. This phenomenon frequently occurs in multicultural communities where speakers share proficiency in multiple languages. Code-switching enhances expressiveness and can convey nuanced social meanings or group membership. Researchers analyze these patterns to understand language use, identity, and communication strategies in diverse environments.
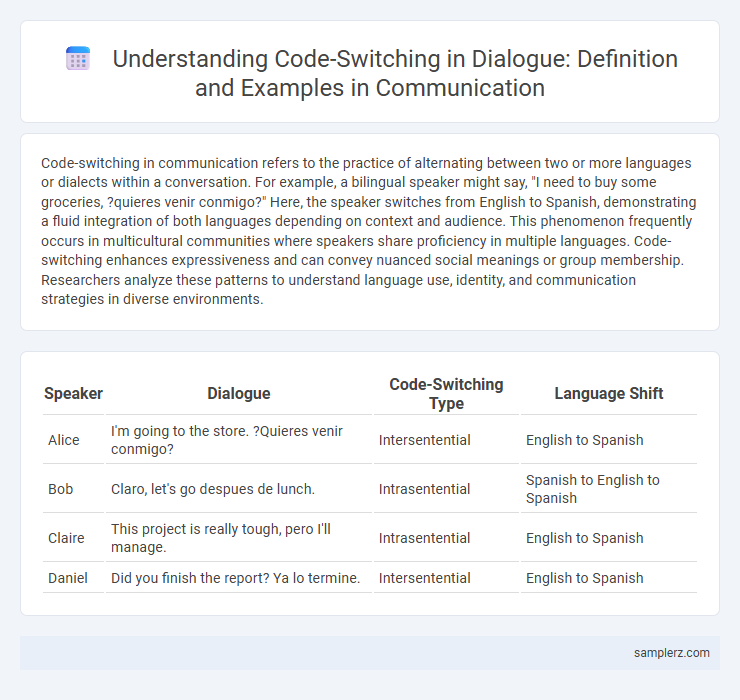
Table of Comparison
| Speaker | Dialogue | Code-Switching Type | Language Shift |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alice | I'm going to the store. ?Quieres venir conmigo? | Intersentential | English to Spanish |
| Bob | Claro, let's go despues de lunch. | Intrasentential | Spanish to English to Spanish |
| Claire | This project is really tough, pero I'll manage. | Intrasentential | English to Spanish |
| Daniel | Did you finish the report? Ya lo termine. | Intersentential | English to Spanish |
Introduction to Code-Switching in Communication
Code-switching in communication occurs when speakers alternate between languages or dialects within a conversation, such as switching from English to Spanish depending on the audience or context. An example dialogue might include a bilingual individual saying, "Let's meet at the cafe, ?a que hora te viene bien?" to seamlessly blend languages for clarity or cultural connection. This practice highlights the dynamic nature of linguistic identity and effective interpersonal communication in multicultural environments.
Understanding Code-Switching: Key Concepts
Code-switching occurs when bilingual speakers alternate between languages within a conversation, such as saying "I'm going to the tienda later, do you need anything?" This linguistic practice reflects social and cultural identity, signaling group membership or conveying nuanced meaning. Understanding code-switching involves recognizing its role in effective communication, where speakers strategically select language to enhance clarity and connection.
Everyday Examples of Code-Switching in Dialogue
Code-switching frequently occurs in everyday conversations, such as when bilingual speakers alternate between English and Spanish within a single sentence: "I'm going to the store, ?quieres algo?" This practice helps convey cultural identity and adapt to conversational context, enhancing mutual understanding among diverse interlocutors. Workplace dialogues often exhibit code-switching as professionals switch languages to clarify technical terms or build rapport, reflecting social dynamics and linguistic flexibility.
Code-Switching Between Different Languages
Code-switching between different languages commonly occurs in bilingual conversations, such as a speaker alternating between English and Spanish to express ideas more fluidly or convey cultural identity. For example, a bilingual individual might say, "I was going to the tienda to buy some groceries," seamlessly integrating the Spanish word "tienda" for store. This linguistic practice enhances communication by bridging language gaps and reflecting the speaker's multicultural background.
Code-Switching in Multicultural Workplaces
Code-switching in multicultural workplaces often occurs when employees alternate between languages or dialects to enhance understanding and foster collaboration. For example, a team member might switch from English to Spanish during a meeting to clarify technical terms for bilingual colleagues. This linguistic flexibility promotes inclusivity and improves communication efficiency in diverse professional environments.
Code-Switching in Educational Settings
Code-switching in educational settings occurs when bilingual students alternate between languages to enhance comprehension and participation. For instance, a student might explain a complex math problem in English but use their native language to clarify key concepts to peers. This strategic language shift supports cognitive processing and fosters inclusive classroom discussions.
Code-Switching in Family Interactions
In family interactions, code-switching often occurs when bilingual members alternate between languages to express emotions or clarify meaning, such as a mother switching from English to Spanish to comfort her child. This linguistic practice enhances understanding and strengthens cultural identity within the family unit. Studies reveal that code-switching in familial settings facilitates emotional bonding and effective communication across generations.
Social Media and Code-Switching in Online Conversations
Code-switching in online conversations often involves alternating between languages, dialects, or jargon to connect with diverse social media audiences, enhancing relatability and engagement. For example, a user might switch from English to Spanish or from formal language to internet slang within a single tweet to appeal to bilingual followers or specific communities. This linguistic flexibility not only reflects cultural identity but also strategically boosts interaction and inclusivity in digital communication platforms.
The Impact of Code-Switching on Communication Effectiveness
Code-switching in dialogue, such as alternating between English and Spanish in a conversation, can enhance communication effectiveness by bridging cultural gaps and increasing mutual understanding among bilingual speakers. This linguistic strategy allows speakers to express nuanced concepts and emotions more precisely, catering to the listener's language proficiency and cultural background. Research indicates that strategic code-switching facilitates smoother interactions and improves message clarity in multicultural communication settings.
Strategies for Navigating Code-Switching in Dialogue
Effective strategies for navigating code-switching in dialogue include maintaining linguistic flexibility and cultural awareness to enhance mutual understanding. Speakers can use context cues and shared language proficiencies to smoothly transition between languages or dialects without disrupting communication flow. Employing active listening and clarifying intent ensures the dialogue remains coherent and respectful of diverse linguistic identities.
example of code-switching in dialogue Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com