Backchannel communication involves non-verbal or brief verbal signals that show active listening or engagement without interrupting the speaker. An example is nodding in agreement during a conversation, which signals understanding and encourages the speaker to continue. Another common backchannel is the use of short utterances like "uh-huh" or "I see," which convey attentiveness and feedback without taking the floor. In digital communication, emojis serve as backchannel cues to express emotions or reactions efficiently. For instance, a thumbs-up emoji in a group chat can indicate approval or acknowledgment without a lengthy response. These subtle signals enrich conversations by maintaining interaction flow and reinforcing social bonds between participants.
Table of Comparison
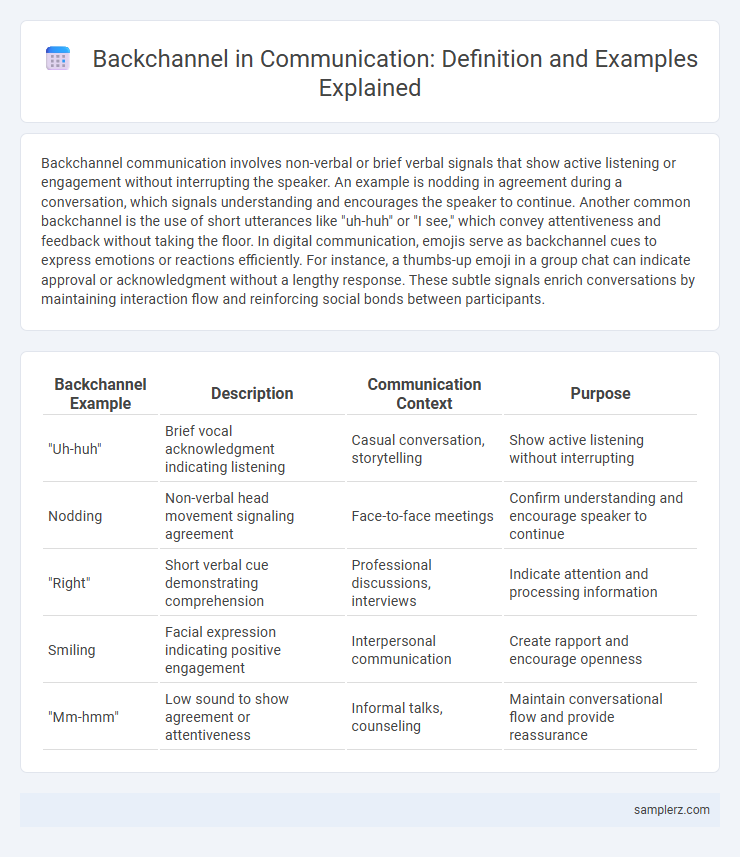
| Backchannel Example | Description | Communication Context | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Uh-huh" | Brief vocal acknowledgment indicating listening | Casual conversation, storytelling | Show active listening without interrupting |
| Nodding | Non-verbal head movement signaling agreement | Face-to-face meetings | Confirm understanding and encourage speaker to continue |
| "Right" | Short verbal cue demonstrating comprehension | Professional discussions, interviews | Indicate attention and processing information |
| Smiling | Facial expression indicating positive engagement | Interpersonal communication | Create rapport and encourage openness |
| "Mm-hmm" | Low sound to show agreement or attentiveness | Informal talks, counseling | Maintain conversational flow and provide reassurance |
Understanding Backchannel in Communication
Backchannel in communication refers to listener responses that signal active engagement without interrupting the speaker, such as nodding, "uh-huh," or brief verbal affirmations like "I see" and "right." These subtle cues enhance mutual understanding and provide feedback that the message is being processed, fostering smoother interactions. Effective use of backchannel signals can improve conversational flow and strengthen interpersonal connections by demonstrating attentiveness and empathy.
Common Verbal Backchannel Examples
Common verbal backchannel examples in communication include brief phrases such as "uh-huh," "I see," and "right." These expressions signal active listening and encourage the speaker without interrupting the flow of conversation. Backchannel cues enhance understanding by providing real-time feedback and maintaining engagement between interlocutors.
Nonverbal Backchannel Cues
Nonverbal backchannel cues, such as nodding, eye contact, and facial expressions, play a crucial role in communication by signaling active listening and understanding without interrupting the speaker. These subtle gestures help maintain the flow of conversation and provide real-time feedback that reinforces engagement and empathy. Effective use of nonverbal backchannels enhances interpersonal connection and ensures smoother, more interactive dialogues.
Backchannel in Face-to-Face Conversations
Backchannel in face-to-face conversations includes verbal cues like "uh-huh," "I see," and nonverbal signals such as nodding or eye contact, which indicate active listening and engagement without interrupting the speaker. These subtle responses help manage conversational flow and reinforce understanding between participants, enhancing rapport and cooperation. Effective backchanneling facilitates smoother communication by signaling attentiveness and feedback in real-time interactions.
Digital Backchanneling: Online Communication Examples
Digital backchanneling in online communication includes real-time chat comments during webinars, social media hashtags facilitating parallel discussions, and instant messaging apps enabling quick feedback in virtual meetings. These channels allow participants to engage, clarify, and respond without interrupting the main speaker, enhancing collaborative interactions. Platforms like Twitter, Slack, and Zoom exemplify effective digital backchannel tools fostering continuous dialogue and participatory communication.
Cross-Cultural Backchannel Differences
In cross-cultural communication, backchannel cues such as nodding, "uh-huh," and brief verbal affirmations vary significantly; for instance, Japanese speakers often use minimal verbal feedback like "hai" to signal attention, while American speakers tend to use more frequent and varied interjections. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective intercultural interactions, as misinterpreting backchannel signals can lead to misunderstandings or perceived disinterest. Research highlights that adapting to diverse backchannel norms enhances mutual comprehension and fosters positive communication dynamics across cultures.
Backchannel in Group Discussions
Backchannel communication in group discussions includes nonverbal cues like nodding, eye contact, and short verbal affirmations such as "uh-huh" or "I see," which signal active listening and encourage speaker participation. These subtle feedback mechanisms help maintain conversational flow and foster collaborative environments by showing attentiveness without interrupting the speaker. Effective backchanneling improves group dynamics, enhances understanding, and supports a more inclusive dialogue.
The Role of Backchannel in Active Listening
Backchannel cues such as nodding, "uh-huh," and brief verbal affirmations play a critical role in active listening by signaling attentiveness and understanding without interrupting the speaker. These subtle responses enhance conversational flow by providing real-time feedback, encouraging the speaker to elaborate and feel heard. Effective backchanneling fosters stronger interpersonal connections and improves overall communication clarity and engagement.
How Backchannel Enhances Communication Flow
Backchannel cues such as nodding, brief verbal affirmations like "uh-huh," and facial expressions signal active listening and understanding during conversations. These subtle feedback mechanisms encourage speakers to continue, reduce misunderstandings, and create a more dynamic and interactive communication flow. Incorporating backchannel responses enhances engagement, promotes clarity, and fosters smoother interpersonal exchanges.
Avoiding Miscommunication with Effective Backchannel
Effective backchannel cues like nodding, brief verbal affirmations, and appropriate eye contact signal active listening and encourage speaker clarity, reducing the risk of miscommunication. These subtle feedbacks ensure the listener's engagement is clear, prompting the speaker to adjust their message for better understanding. Utilizing backchannels strategically enhances conversational flow and minimizes misunderstandings in face-to-face and virtual communication settings.
example of backchannel in communication Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com