Marouflage is a traditional technique used in tapestry art where a completed textile artwork is adhered to a rigid surface, such as a wall or panel, using a strong adhesive. This method preserves the tapestry's intricate details and vibrant colors while providing stability and longevity. An example of marouflage can be seen in the famous Bayeux Tapestry, where the fabric was mounted onto a firm backing to prevent damage during display. This technique allows large-scale tapestries to be exhibited in museums and galleries without the need for framing or constant rolling and unrolling. The adhesive application ensures that the textile remains flat and securely attached, reducing the risk of creasing or surface wear. Marouflage has been used historically in various cultural settings to maintain the structural integrity of valuable textile art pieces.
Table of Comparison
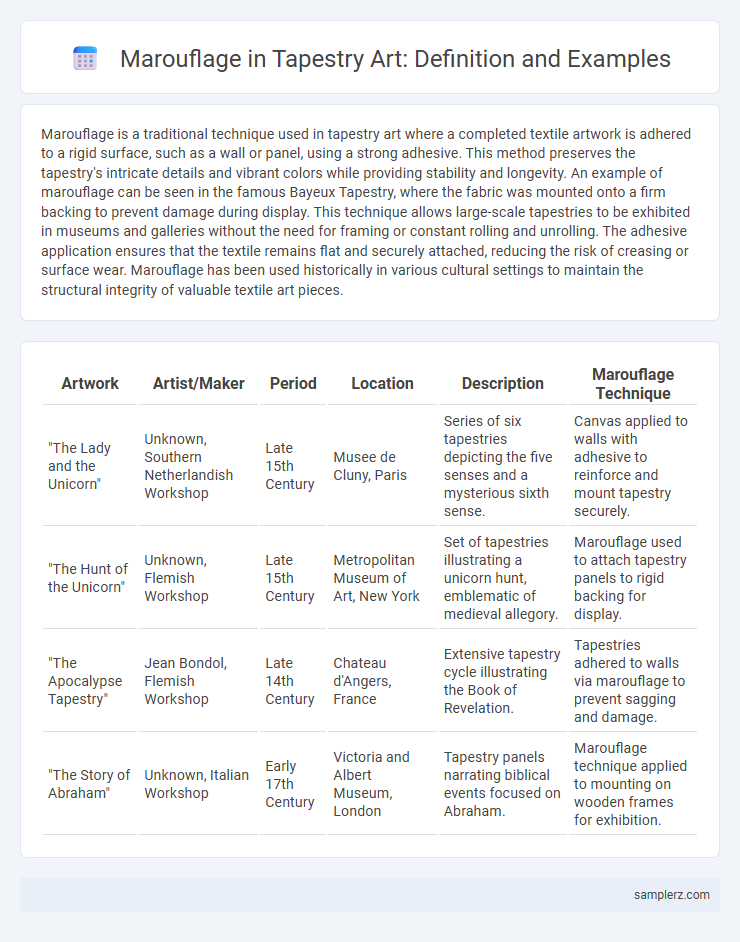
| Artwork | Artist/Maker | Period | Location | Description | Marouflage Technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| "The Lady and the Unicorn" | Unknown, Southern Netherlandish Workshop | Late 15th Century | Musee de Cluny, Paris | Series of six tapestries depicting the five senses and a mysterious sixth sense. | Canvas applied to walls with adhesive to reinforce and mount tapestry securely. |
| "The Hunt of the Unicorn" | Unknown, Flemish Workshop | Late 15th Century | Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York | Set of tapestries illustrating a unicorn hunt, emblematic of medieval allegory. | Marouflage used to attach tapestry panels to rigid backing for display. |
| "The Apocalypse Tapestry" | Jean Bondol, Flemish Workshop | Late 14th Century | Chateau d'Angers, France | Extensive tapestry cycle illustrating the Book of Revelation. | Tapestries adhered to walls via marouflage to prevent sagging and damage. |
| "The Story of Abraham" | Unknown, Italian Workshop | Early 17th Century | Victoria and Albert Museum, London | Tapestry panels narrating biblical events focused on Abraham. | Marouflage technique applied to mounting on wooden frames for exhibition. |
Introduction to Marouflage in Tapestry Art
Marouflage is a traditional technique in tapestry art involving the adhesion of fabric, often a tapestry, onto a rigid surface using a strong adhesive such as glue or paste. This method enhances the durability and display quality of tapestries by preventing sagging and allowing for easier mounting on walls or panels. Notable examples include large-scale Renaissance tapestries preserved with marouflage in museums like the Musee de Cluny in Paris.
Historical Evolution of Marouflage Techniques
Marouflage, a technique involving the adhesive mounting of painted canvases onto walls or panels, evolved significantly from ancient Egypt through the Renaissance to modern art conservation. Early examples include Egyptian murals where plaster was applied over canvas, while Renaissance artists refined marouflage for securing large-scale tapestries to ensure durability and seamless display. By the 19th century, advancements in adhesive materials and mounting methods enhanced the preservation and visual impact of tapestry artworks in museums and historic buildings.
Iconic Examples of Marouflage in Famous Tapestries
Iconic examples of marouflage in famous tapestries include the intricate works of the Renaissance period, such as Raphael's tapestries in the Vatican, which were expertly adhered to walls for durability and display. The Bayeux Tapestry, although primarily an embroidery, also utilized techniques akin to marouflage for mounting and preservation. Marouflage played a critical role in maintaining the vibrant colors and intricate details of these historic textile masterpieces, ensuring their longevity in museum collections and historic sites.
Materials Commonly Used in Tapestry Marouflage
Tapestry marouflage typically involves adhering heavy textile works onto rigid surfaces using adhesives such as animal glue, starch paste, or modern synthetic adhesives. Common materials used include linen or cotton canvases, which serve as reliable backings for maintaining the tapestry's durability and tension. The process often incorporates natural pigments and gold leaf in the tapestry fibers, enhancing both texture and visual richness.
Step-by-Step Marouflage Process Illustrated
Marouflage in tapestry involves adhering fabric onto a rigid surface with an adhesive, preserving intricate designs and detail. The step-by-step marouflage process includes preparing the wall or panel, applying a tailored adhesive mixture, and carefully smoothing the tapestry to eliminate air bubbles and wrinkles. This technique ensures long-lasting display while maintaining textile integrity in art installations.
Preservation of Marouflage-Enhanced Tapestries
Marouflage, a technique used to adhere tapestries onto rigid supports, greatly enhances the preservation of delicate textile artworks by preventing sagging and damage caused by handling or environmental factors. Notable examples include the preservation efforts of the 17th-century Gobelins tapestries in the Louvre, where marouflage has maintained structural integrity and vibrancy over centuries. Proper marouflage application ensures tapestries retain their original texture and colors, making it an essential method in textile conservation and museum display practices.
Notable Artists Utilizing Marouflage in Tapestry
Notable artists such as Henri Matisse and Diego Rivera employed marouflage to mount their intricate tapestry works securely to walls, ensuring durability and enhanced visual impact. This technique, involving the application of adhesives to affix fabric art to rigid surfaces, allowed these artists to preserve the texture and detail of their tapestries while facilitating exhibition in various settings. Marouflage remains a critical method in textile conservation, maintaining the integrity of large-scale tapestry masterpieces by prominent creators.
Differences Between Marouflage and Traditional Mounting
Marouflage in tapestry involves adhering the textile to a rigid surface using an adhesive paste, enhancing durability and ease of display compared to traditional stitching methods. This technique prevents sagging and damage by securely bonding the tapestry to wood or canvas, unlike conventional mounting that often relies on simple rods or frames. The preservation benefits and the seamless appearance make marouflage a preferred method in museums and galleries for historical and large-scale tapestries.
Modern Applications of Marouflage in Contemporary Tapestry
Modern applications of marouflage in contemporary tapestry involve adhering fabric artworks to rigid supports using advanced adhesives and specialized techniques to enhance durability and display quality. Artists and conservators leverage marouflage to mount delicate textile pieces on panels or walls, preserving intricate designs while enabling large-scale installations in galleries and public spaces. Innovations in synthetic adhesives and climate-controlled mounting processes optimize the preservation of tapestries, maintaining color vibrancy and texture over time.
Influence of Marouflage on Tapestry Longevity and Display
Marouflage, a technique involving the adhesion of tapestry to a rigid backing, significantly enhances the durability and longevity of textile artworks by providing structural support and preventing fabric distortion. This method allows large tapestries to be securely mounted on walls, improving display stability and reducing exposure to environmental damage like moisture and pollutants. Museums and collectors frequently employ marouflage to preserve the intricate details and vibrant colors of historic tapestries, ensuring their visual integrity for future generations.
example of marouflage in tapestry Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com